ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 4 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Updated ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 4 - Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved Selina Solutions are provided by Vedantu in a step by step method. Selina is the most famous publisher of ICSE textbooks. Studying these solutions by Selina Concise Biology Class 10 Solutions which are explained and solved by our subject matter experts will help you in preparing for ICSE exams. Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions can be easily downloaded in the given PDF format. These solutions for Class 10 ICSE will help you to score good marks in ICSE Exams 2024-25.
The updated solutions for Selina textbooks are created in accordance with the latest syllabus. These are provided by Vedantu in a chapter-wise manner to help the students get a thorough knowledge of all the fundamentals.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Biology Chapter No. 4 - Adsorption by Roots- The Process Involved
Progress Check
1. List the three primary functions of root.
Ans:
1. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport it to the various parts of the plant.
2. The roots provide support and anchor to plant.
3. Roots also store food.
2. Mention four purposes for which the plants need water.
Ans: Four purposes for which the plants need water are-
(i) Photosynthesis- the green leaves of plants use water as raw material for the synthesis of carbohydrates.
(ii) Transpiration- Water is evaporated from stomatal pore during the exchange of gases to create suction pressure and provide cooling in hot weather.
(iii) Transportation-Water is required in plants for the transport of minerals and nutrients (transported in dissolved forms).
(iv) Turgidity- Water provides mechanical stiffness to the plant tissues.
3. Where are the minerals and nutrients mostly used in the plants?
Ans: The minerals and nutrients are mostly required for the synthesis of various enzymes and compounds, these are also required as cell constituents and cell organelles as such Nitrate is required for the synthesis of amino acids which further constitute cell building materials called protein. Similarly, Magnesium is essential for the synthesis of Chlorophyll.
4. List three main characteristics of the roots that enable them to draw water from the soil.
Ans: Three main characteristics of the roots that enable them to draw water from the soil.
i. Enormous surface area provided by rootlets and root hairs.
ii. Highly concentrated cell sap in the root hairs than that of surrounding soil water which facilitates osmosis. This refers to the water from the soil moving from high concentration to lower concentration (inside the root ).
iii. The thin walls of the root hairs- the root hairs have two covering cell walls and cell membrane. The cell wall is thin and permeable, allowing water molecule movement freely in and out of the cell whereas the cell membrane is thin and semi-permeable. The cell membrane allows water molecules to pass through but does not allow large or hydrophobic molecules to pass through.
The high concentration of cell sap and permeability of cell membrane ensures the water movement inside the cell.
Progress check
1. Write true or false.
(i) Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of their lower concentration to that of a higher concentration.
Ans: False
Explanation- Diffusion occurs under a concentration gradient which means the movement of molecules takes place from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration until the equilibrium is attained.
(ii) Osmosis includes diffusion, but not vice versa.
Ans: True
Explanation- Osmosis is the process of diffusion of solvent molecules (water) takes place from a region of a higher concentration gradient to a region of lower concentration gradient through a semipermeable membrane. For diffusion to take place, the semipermeable membrane is not required whereas it is a mandatory requirement for osmosis to take place.
(iii) Osmosis is unidirectional.
Ans: True
Explanation- Osmosis is the process of diffusion of solvent molecules (water) takes place from a region of a higher concentration gradient to a region of lower concentration gradient through a semipermeable membrane. It is a unidirectional phenomenon because the movement of water (solvent molecules) always takes place with concentration gradient, not against the concentration gradient.
(iv) Exosmosis may cause bursting of a cell.
Ans: False
Explanation- When a cell is put in hypertonic solution (where the concentration of solutes is higher outside than that of inside the cell); the water molecules move more outside the cell than inside which means the water comes out of the cell due to which the cell shrinks and loses its shape.
(v) Semi permeable membrane prevents the passage of solute molecules.
Ans: True
Explanation. Semipermeable membrane is the one which allows the passage of solvent molecules selectively across the membrane but prevents the passage of solute molecules.
(vi) In an experiment on osmosis, if external pressure is applied on a dilute solution, less water will pass into the concentrated solution.
Ans: False.
Explanation - Osmosis is the process of diffusion of solvent molecules (water) takes place from a region of a higher concentration gradient to a region of lower concentration gradient through a semipermeable membrane. In other words, the movement of water occurs from low solute concentration (dilute solution) to high solute concentration (concentrated solution).
2. In what way is active transport opposite to diffusion?
Ans: Active transport takes place against the concentration gradient and requires energy to take place whereas diffusion takes place along the concentration gradient and does not need energy.
3. A cell kept in a certain solution brusts after some time. Comment on the kind of solution.
Ans: Hypotonic solution, in this solution the concentration solvent is more as compared to the inside of the cell. Thus solvent moves inside the cell till it bursts.
4. Which process diffusion, osmosis or active transport, needs the involvement of energy?
Ans: Active transport needs the involvement of energy as it occurs against the concentration gradient i.e, movement of molecules from a lower concentration to higher concentration gradient.
5. Can we call diffusion, a passive transport. If so, how?
Ans: Yes, We can call diffusion a type of passive transport as it takes place along the concentration gradient i.e, from high concentration to lower concentration and it does not require energy to take place.
Progress check
1. Name the following.
(i) The state of a cell when it can not accommodate any more water.
Ans: Turgidity
(ii) Pressure of the cell contents on the cell wall.
Ans: Turgor pressure
(iii) The condition that is opposite of turgidity.
Ans: Flaccid.
(iv) The state of a plasmolysed cell after the re-entry of water.
Ans: Turgid
(v) The pressure under which water passes from the living cells of a root into xylem.
Ans: Root pressure
Progress Check
1. Look at the Fig. 4.15. Why was oil added over water in the test tube?
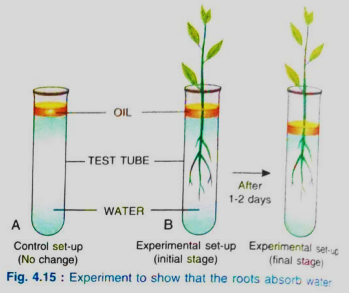
Ans: Oil is added over water in the test tube to ensure that no direct water loss takes place from the evaporation during experiment to observe that root absorbs water.
2. Look at the experiment shown in Fig. 4.16. Why is it necessary to take coloured eosin solution in the water in xylem?
Ans: Xylem is a vascular tissue which conducts water in various parts of the plants.
The eosin dye in water is necessary to observe the conduction of water taking place upward in the plant body through xylem. This colour is observable in the transverse section when observed under a microscope.
3. Which part of the stem, the xylem or the phloem, is located deeper initially?
Ans: Lenticels are the small opening present on the stem of plants through which transpiration occurs. Thus, to avoid excessive water loss through transpiration from lenticel that's why the xylem is located deep internally.
4. Look at Fig.4.18. Why has the stem below the ring stopped growing and even slightly decayed?
Ans: Girdling is a process in which a ring is cut around the stem, deep enough to penetrate the phloem but leaving the xylem unharmed.
The cell sap flows in the peripheral region of the stem with the help of phloem which is removed during girdling. Thus, no food is transported below the girdle of the stem, resulting in less nourishment to lower regions of the plant. Hence, the region below gridle stopped growing and started decaying.
A. Multiple Choice Type
(Select the most appropriate option in each case)
1. Absorption of water by the plant cell by surface attraction is called
(a) Diffusion
(b) Osmosis
(c) Imbibition
(d) Endosmosis
Ans: Imbibition
Imbibition is defined as the process by which a solid surface absorbs water or any liquid without forming any solution.
2. A plant cell placed in a certain solution got plasmolyzed. What was the kind of solution?
(a) Isotonic sugar solution
(b) Hypotonic salt solution
(c) Hypertonic salt solution
(d) Isotonic salt solution
Ans: (c) Hypertonic salt solution
Hypertonic solution contains more solute concentration as compared to cell inside which creates a concentration gradient due to which water moves from higher concentration gradient to a lower concentration (outside the cell). This results in cell shrinkage which is called plasmolysis i.e., shrinkage of protoplasm.
3. The state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption of water is called
(a) Flaccidity
(b) Turgidity
(c) Capillarity
(d) Tonicity
Ans: (b) Turgidity
Turgidity is the state of the cell in which its cell wall becomes rigid and stretched by increase in volume due to absorption of water.
4. Which one of the following is a characteristic NOT related with suitability of the roots for absorbing water?
(i) Tremendous surface area
(ii) Contain cell sap at a higher concentration than the surrounding soil water
(iii) Root hairs have thin cell walls
(iv) Grow downward into the soil
Ans: (iv) Grow downward into the soil
These three are the characteristics of roots -
Enormous surface area provided by rootlets and root hairs.
Highly concentrated cell sap in the root hairs than that of surrounding soil water which facilitates osmosis. This refers to the water from the soil moving from high concentration to lower concentration (inside the root).
The thin walls of the root hairs- the root hairs have two covering cell walls and cell membrane. The cell wall is thin and permeable, allowing water molecule movement freely in and out of the cell whereas the cell membrane is thin and semi-permeable.
5. Movements of molecules of a substance form the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration without the involvement of a separating membrane, is called
(i) Osmosis
(ii) Diffusion
(iii) Active transport
(iv) Capillarity
Ans: (ii) Diffusion
Diffusion occurs under a concentration gradient which means the movement of molecules takes place from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration until the equilibrium is attained. It does not require any separating membrane.
6. Osmosis and diffusion are the same excepts that osmosis there is
(i) a freely permeable are the excepts that in osmosis there is
(ii) a cell wall in between
(iii) A selectively permeable membrane in between
(iv) an endless inflow of the water into a cell
Ans: (iii) a selectively permeable membrane in between
Osmosis is the process of diffusion of solvent molecules (water) that takes place from a region of a higher concentration gradient to a region of lower concentration gradient through a semipermeable membrane.
7. The highest water potential (capacity to move out to higher concentrated solution) is that of
(i) Pure water
(ii) 10% salt solution
(iii) Honey
(iv) Honey 50% sugar solution
Ans: (i) Pure water
Water potential measures the concentration of free water available. The pure water has the highest water potential which is 0. The water potential decreases as the solute concentration increases in the solution.
8. The space between the cell wall and plasma membrane in a plasmolysed cell is filled with
(i) Isotonic solution
(ii) hypotonic solution
(iii) hypertonic solution
(iv) water
Ans: (iii) hypertonic solution
When a cell is put in hypertonic solution (where the concentration of solutes is higher outside than that of inside the cell); the water molecules move more outside t\he cell than inside, this results in cell shrinkage which is called plasmolysis i.e., shrinkage of protoplasm.
9. What is responsible for guttation?
(i) Osmotic pressure
(ii) Root pressure
(iii) Suction pressure
(iv) Capillarity
Ans: (ii) Root pressure
In the vascular plants, the root pressure is very high. Thus, water rushing up to leaves is higher than water transpiring. Thus water is lost in the form of droplets. This process is called Guttation.
10. The most appropriate characteristic of a semi-permeable membrane is that?
(a) It has minute pores.
(b) It has no pores .
(c) It allows the solute to pass through but.
(d) It allows a solvent to pass through freely but prevents the passage of the solute.
Ans: (d) It allows solvents to pass through freely but prevents the passage of the solute.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Name the following.
(a) The condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution.
Ans: Turgid
(b) The process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets form leaf margins.
Ans: Guttation
(c) The process by which water enters in root hairs.
Ans: Osmosis
(d) The tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
Ans: Root Pressure
(e) The term for the inward movements of solvents molecules through the plasma membrane of a cell.
Ans: Endosmosis
(f) The process by which molecules distribute themselves evenly within the space they occupy.
Ans: Diffusion
(g) The pressure which is responsible for the movements of water molecules across the cortical cells of the root.
Ans: Root Pressure
2. Give the equivalent for the following.
(a) Pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
Ans: Turgor pressure
(b) The condition in which the cell contents are shrunk in.
Ans: Flaccidity
(c) Loss water through a cut stem.
Ans: Bleeding
3. Complete the following statements.
(a) Hypotonic solution is one in which the solution kept outside the cell has lower solute concentration than …………… the cell.
Ans: Inside
When the concentration of solutes is lower in a solution than that of inside the cell, this solution is called a hypotonic solution.
(b) Active transport is one in which the ions outside the roots move in with expenditure of energy ………
Ans: At lower concentration
Active transport is a process in which the ions, salts and other substances move from its lower concentration to its higher concentration using the energy from the cell.
(c) The bending movements of certain flower toward the sun and the sleep movements of certain plants at night are example of ………………………
Ans: Turgor movements.
During the day, leaves perform transpiration (Loss of water), it creates a suction pull of water from soil. The pressure applied by water on the cell wall is called turgor pressure and keeps the cell turgid. During the night, the transpiration does not occur, and the leaves wilts due to loss of turgidity. Thus certain flowers show sleep movement at night and bend towards the sun.
4. Fill in the blanks by choosing the correct alternative from those given in brackets.
(a) When placed in a more concentrated solution the cell concentrated solution the cell contents will ……… (shrink/swell up)
Ans: Shrink
In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes is higher in solution than that of a cell. This creates a concentration due to which water moves from higher concentration to lower concentration region (the water moves out of the cell), causing the cell to shrink.
(b) The pressure by which the ………. molecules tend to cross the semipermeable membrane called osmotic pressure. (salt/water).
Ans: Water
Osmotic pressure is defined as the minimum pressure required to prevent movement of pure solvent into the solution. Water is a pure solvent, passing through the semipermeable membrane into the cell sap (highly concentrated).
(c) Active transport is in a direction ……….. to that of diffusion. ( opposite/same)
Ans: Opposite
Active transport is a process in which the ions, salts and other substances move from its lower concentration to its higher concentration using the energy from the cell whereas in diffusion, the movement of molecules takes place from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
5. Match the item in column I with column II
Column II | Column II |
(1) Xylem | (a) semi-permeable |
(2) Phloem | (b) Permeable |
(3) Cell Membrane | (c) downward flow of water |
(4) Root Pressure | (d) upward flow of sap |
(5) Cell wall | (e) guttation |
Ans:
Column II | Column II |
(1) Xylem | (d) upward flow of water |
(2) Phloem | (c) downward flow of sap |
(3) Cell Membrane | (b) Semi- permeable |
(4) Root Pressure | (e) guttation |
(5) Cell wall | (a) Permeable |
Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues responsible for the upward movement of water and minerals and downward movement of sap respectively.
Cell wall and cell membrane are two outer covering of the cell which provides support and protection. Cell wall is permeable to most substances whereas the cell membrane is semi permeable.
In the vascular plants, the root pressure is very high. Thus, water rushing up to leaves is higher than water transpiring. Thus water is lost in the form of droplets. This process is called Guttation.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Differentiate between the following.
(a) Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis
Ans:
Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis |
1. It takes place when a plasmolysed cell is kept in a hypotonic solution 2. The protoplasm of the cell swells up and touches the cell wall, resulting in the turgid condition of the plant. | 1. It take place when a plant cell is kept in hypertonic solution 2. The protoplasm of the cell shrinks away from the cell wall, results in the flaccid condition of the plant. |
(b) Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Ans:
Turgor Pressure | Wall Pressure |
1. The pressure of the cell contents on the cell wall is called Turgor pressure. 2. Turgor pressure occurs due to turgidity of the cell. | 1. The pressure exerted by the cell wall on the cell content is called wall pressure. 2. Wall pressure occurs against the turgor pressure. |
(c) Guttation and bleeding
Guttation | Bleeding |
1. Drop of water along leaf margin to excessive root pressure 2. It occurs due to excess build-up of water in xylem. 3. It takes place due to root pressure in xylem. | 1. The water loss from cell sap through a injured stem is called “bleeding 2. It occurs due to injury. 3. It happens due to pressure in sieve tube |
(d) Turgidity and Flaccidity
Ans:
Turgidity | Flaccidity |
1. The availability of sufficient water causes the cells to become charged with water with its walls in a state of tension making the cells rigid and stretched stretched. 2. This condition makes plants stiff and erect. | 1. The unavailability of sufficient water causes the cells to become weak and soft due to decreased Turgor pressure. 2. This condition causes wilting in plants |
2. Mention whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). Correct the false statements by altering the last word only.
(a) Addition of salt to pickles prevents growth of bacteria because they turn turgid.
Ans: False
Altered Statement- Addition of salt to pickles prevents growth of bacteria because they turn flaccid.
Reason- Addition of salt to pickles increases the concentration of solutes. Thus, when bacterial cells come in contact with pickles, water from the bacterial cells is lost and they become flaccid. Hence, these bacteria can not grow in pickles.
(b) Cells that have lost their water contents are said to be deplasmolysed
Ans: False
Altered Statement- Cells that have their water contents are said to be plasmolysed.
Reason- In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes is higher than that of inside the cell. Thus, when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water flows outside the cell. The cell protoplasm shrinks and becomes plasmolysed
(c) Xylem is the water conducting tissue in plants.
Ans: True
(d) The shrinkage of protoplasm, when a cell is kept in hypotonic solution.
Ans: False
Altered statement- The protoplasm shrinks, when a cell is kept in hypertonic solution.
Reason- When the concentration of solutes is higher than that of inside the cell in a solution, it is called a hypertonic solution. Thus, when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water flows outside the cell causing protoplasm to shrink.
(e) The cell wall of a root cell is a differentially permeable membrane.
Ans: True
3. Mention whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
a. Guttation is another name for bleeding in plants.
Ans: False
Explanation- Guttation is the process in which water is lost from the leaf margins due to excessive root pressure whereas bleeding is the loss of cell sap through a cut stem.
b. Soaked seeds burst their seed coats.
Ans: True
Explanation- The seed has three different layers called seed coats. When seeds are soaked in water, they swell up due to endosmosis. During this process, the seed coat is unable to bear the turgor pressure and hence, the seed coat bursts.
c. If the phloem of a twig is removed keeping the xylem intact, the leaves of a twig wilts.
Ans: False
Explanation- The cell sap flows in the peripheral region of the stem with the help of phloem which can be removed during girdling. Thus, no food is transported below the girdle of the stem, resulting in less nourishment to lower regions of the plant. Hence ,the region below gridle stopped growing and started decaying but not twig
d. Guttation in plants occurs maximum at mid-day.
Ans: False
Explanation- Guttation is the process in which water is lost from the leaf margins due to excessive root pressure which is maximum during night or at early morning.
e. Raisins when submerged in water swell up due to endosmosis.
Ans: True
Explanation- When the concentration of solutes is lower in a solution than that of inside the cell, this solution is called a hypotonic solution. For example - When raisins are soaked in water, the water flows inside. This is called endosmosis.
D. Descriptive Answer-
1. Give two examples of turgor movement in plants.
Ans: Examples of turgor movements in plants-
(i) The ‘touch me not’ is a sensitive plant. The stimulus of touch leads to loss of turgor at the base of the leaflets and at the base of the petioles called pulvinus. This causes the folding and drooping of leaves of the plant.
(ii) The leaves of insectivorous plants close up to entrap living prey. When the insect comes in close proximity with leaf, it loses turgor pressure hence closing the leaves of the plant.
2. Define the following terms.
(a) Imbibition
Ans: Imbibition is a phenomenon by which the living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction.
(b) Diffusion
Ans: Diffusion is the free movement of molecules of a substance from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration when the two are in direct contact.
(c) Osmosis
Ans: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration to their region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
(d) Osmotic Pressure
Ans: Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure that must be exerted to prevent the passage of the pure solvent into the solution when the two are separated by a semipermeable membrane.
(e) Active Transport
Ans: Active transport is the passage of a substance from its lower to higher concentration through a living cell membrane using energy from the cell.
(f) Tonicity
Ans: Tonicity is defined as the relative concentration of the solutions surrounding the cell that can determine the direction and extent of diffusion is called tonicity.
(g) Root Pressure
Ans: The upward flow of water due to heavy pressure from the roots is called root pressure.
3. Give reasons for the following.
a) If you sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at that spot.
Ans: Due to plasmolysis, the water inside the roots of grass is drawn out. Because of this, If you sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at that spot.
b) If you uproot a plant from the soil, its leaves soon wilt.
Ans: If uprooted, the absorption of water does not take place by roots and the water present in the plant body gets lost in transpiration. The scarcity of water causes wilting of leaves.
c) It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning.
Ans: The transplant of seedling in the flower bed is better in the evening because stomata are closed at that time. Due to closed stomata, there will be no loss of water and the plant will get enough time to fix roots in soil. While, this will not be possible during the morning and the plant may die.
d) A plant cell when kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about 30 minutes turns flaccid.
Ans: When a plant cell is kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about 30 minutes, the water will come out from the cell due to exosmosis causing plasmolysis of the cell.
e) Potato cubes when placed in water become firm and increase in size.
Ans: Potato cubes have hypertonic solution in their cells. The outer water moves in due to endosmosis and causes turgidity in the cells of the potato.
4. Explain the mechanism of closing and opening of the stomata.
Ans:
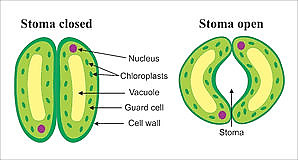
Stomata is a tiny pore opening, present at the epidemic of the leaves, stem and other organs.
These pores are surrounded by a pair of guard cells.
Stomata has two types of cells- guard cells and subsidiary cells
The function of guard cells is to regulate the size of the stomatal opening. The subsidiary cells provide support to the guard cells.
Opening and closing of stomata:
The opening and closing of stomata depends on the light, temperature, CO2 and change in environmental factors.
Stomata function as turgor operated valves, when the osmotic pressure of guard cells increases, water enters the cell and makes stomata open. When the osmotic pressure decreases, water moves out and makes the stomata close due to which the stomata becomes more flaccid.
When sunlight falls on stomata, transpiration occurs where water is reduced into hydrogen ion and oxygen causing exchange of gases by stomatal pore i.e, CO2 is taken by plants and O2 is released in the environment.
5. What is transpiration pull? How is it caused?
Ans: This is created due to transpiration, which pulls the water from a lower level to higher level is called transpiration pull. It is created as the water is lost from the leaf surface by transpiration and more water molecules are pulled up due to the tendency of water molecules to remain joined. Thus, a continuous column of water is produced through the stem of the plant.
E. Structured/Application/ Skill Type
1. A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After some time it assumed a shape as shown below:
(a) Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
Ans: (Plasmolysis) Flaccid
(b) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
Ans: Plasma membrane
(c) Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
Ans: Hypertonic solution
(d) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
Ans: Cell wall is present in plant cells but absent in animal cells.
(e) Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
Ans: The cell will become turgid if placed in ordinary water for some time.
2. The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the process.
Ans: Osmosis
(b) Define the above named process.
Ans: Osmosis is the process in which the movement of water (solvent particles) takes place from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
(c) What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
Ans: After a few hours, we will observe that the amount of sugar inside the funnel has risen up and the water level in the beaker has slightly dropped due to osmosis.
(d) What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
Ans: For the control experiment, the thirst funnel with parchment paper will contain water instead of sugar and the beaker will also contain water. By this, we can observe the development of concentration gradient in experimental set-up as compared to control experiment setup.
(e) Keeping in mind the root-hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to
(1) concentrated sugar solution
Ans: Cell sap in the root hair (Develops concentration gradient)
(2) parchment paper and
Ans: Cell membrane of root hair
(3) water in the beaker.
Ans: Water in soil
(f) Name any other substance that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.
Ans: Egg membrane, animal bladder and cellophane paper, any one of these can be used instead of parchment paper.
(g) Mention any two advantages of the process to the plants.
Ans: Advantages-
1. Osmosis allows plant roots to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
2. Osmosis is also responsible for the opening and closing of stomata which lead to transpiration and photosynthesis, major process responsible for food synthesis.
3. The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
a. Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
Ans: A- Cell wall
B- Cell membrane
C- Cytoplasm
D- Nucleus
b. The root hair cell is in a turgid state. Name and explain the process that caused this state.
Ans: Endosmosis
The root hair cells absorb water and minerals from the soil due to difference concentration gradients between soil and root hair constituents. The root hair contains cell sap in which the concentration of water is less compared to the soil. Thus, the water moves from a region of higher concentration (soil) to a region of lower concentration (root hairs) through a semipermeable membrane. This process is called endosmosis. And cells become turgid.
c. Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
Ans:
Cell wall | Cell membrane |
The cell wall is the outermost layer in plant cells but absent in animal cells and it is fully permeable. | The cell membrane is the outermost layer in animal cells whereas it is present beneath the cell wall in plant cells. It is semi-permeable membrane |
d. Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
Ans:
4. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
Ans: The process of Osmosis by which roots absorb water from the soil is studied here.
(b) Explain the process mentioned in (a) above
Ans: Osmosis is the process in which the movement of water (solvent particles) takes place from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
(c) Why is oil placed over water?
Ans: The oil is placed over water to prevent any loss of water by evaporation.
(d) What do we observe with regard to the level of water when this setup is placed in (1) bright sunlight (2) humid conditions (3) windy day?
Ans:
1. The water level falls steadily under bright sunshine.
2. The level of water should not decline for a long time in humid environments.
3. Water levels drop very rapidly on windy days.
(e) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to foster the process mentioned in (a) above
Ans: Three adaptations found in plants to foster the process of absorption of water:
1. The rootlets and root hairs provide large surface area for water absorption.
2. Root hairs contain cell sap at a high concentration as compared to surrounding water which develops concentration gradients.
3. Root hair has thin membranes.
5. Three cylinders of potato were carefully dried on a blotting paper and weighed. Each piece weighed 3 grams. Each one was placed in the beaker as shown below:
Answer the following questions:
(a) After 48 hours, which potato cylinder would be the heaviest?
Ans: Cylinder B- In distilled water will be heaviest.
(b) The movement of which substance is mainly responsible for the weight change in the potato cylinders?
Ans: Water
(c) Name and define the process which is responsible for the movement of substance mentioned in answer (b).
Ans: Osmosis,
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration to their region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
(d) Write specific names of the processes which occur in beakers B and C (kinds of processes defined in answer (c)).
Ans: Endosmosis occurs in Beaker B and C, which is the diffusion of water through the membrane of potato cells.
The plasmolysis takes place in beaker C as the potato shrinks due to higher concentration of solutes in solution placed in beaker (hypotonic solution of 20% sucrose solution.)
(e) Would there be any difference in the weight of the potato cylinder in beaker A after 48 hours? Give reason.
Ans: The weight of the potato will be less as compared to the initial phase after 48 hours because it will lose water due to plasmolysis in the atmosphere.
6. The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the parts indicated by guidelines 1 to 5.
Ans: 1: Root hair cell,
2: Soil particles,
3: Xylem vessel,
4: Cortex cells,
5: Vacuole
(b) Is the root hair cell unicellular or multicellular?
Ans: Unicellular
(c) Explain what would happen to the root hair cell if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it.
Ans: When fertilizers are added to the moist soil close to the root hair cell, the soil around root hair becomes hypotonic which means the concentration of solutes will be more in soil around root hair. This will result in the outside movement of water molecules from root hairs, causing protoplasm to shrink. Hence, the root hair cells will become flaccid.
(d) Name the process responsible for the entry of water molecules from the soil into A1 and then into A2.
Ans: Osmosis
(e) What pressure is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by arrows?
Ans: Osmotic pressure
(f) How is this pressure set up?
Ans: Osmotic pressure occurs due to the difference in osmotic gradient between solute and solvent in solution
7. Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the questions that follow.
(a) What phenomenon is being studied by this setup?
Ans: Osmosis.
(b) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (a) above.
Ans: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution) through a semipermeable membrane.
(c) What is meant by 'semipermeable membrane'?
Ans: The membrane is called semi permeable since it allows only the solvent particle to pass through them and not the solutes.
(d) What will you observe in the setup after about half an hour? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: Water molecules will continue to pass from 5% sucrose solution to 10% sucrose solution through the semipermeable membrane due to osmosis. This will continue till the concentration of water molecules becomes the same in both ends of the setup (attain equilibrium).
8. A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker, there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment.
(a) Give the technical terms of the solutions used in the beakers 1, 2 and 3.
Ans: In breaker -1, the external solution was hypertonic i.e, the concentration of water molecules is higher outside the potato than inside. So the water moved from higher to lower concentration (inside the potato). As a result the size of the potato increased.
In breaker -2, the external solution was hypotonic i.e, the concentration of water molecules is lower outside the potato than inside. So the water moved from higher to lower concentration (outside the potato). As a result the size of the potato decreased.
In breaker -3, the external solution was isotonic i.e, equal concentration of water molecules in and outside the potato. So no exchange of water molecules takes place in this condition. As a result the size of the potato remains unchanged.
(b) In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same. Explain the reason in brief.
Ans: The root hair contains cell sap which has a higher concentration of water molecules in and outside the potato. So no exchange of water molecules takes place in this condition. As a result the size of the potato remains unchanged.
(c) Write the specific features of the cell sap of root hair which helps in absorption of water.
Ans: The root hair contains cell sap which has a higher concentration of salts than surrounding water. The facilitator osmosis, as a result of which outside water is drawn inside the root hair.
(d) What is osmosis?
Ans: Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
(e) How does a cell wall and a cell membrane differ in their permeability?
Ans: Cell wall is usually freely permeable which can pass the water molecules and glucose molecules. While the cell membrane is partially permeable or selectively permeable. Only selective materials and water can pass through it.
Introduction to the Chapter
Chapter - 4 - Absorption by Roots - The Processes Involved teaches the fundamentals of plant anatomy. With enough weightage in the ICSE exam, this chapter is one of the important ones from the textbook. The concepts covered in Concise Selina Biology Class 10 ICSE Chapter 4 are Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water, Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology, Concept of Osmosis, Water and Mineral Absorption by Root, Turgidity and Flaccidity, Need of Water and Minerals for Plant, Concept of Diffusion, Concept of Imbibition, Osmotic Pressure, Absorption and Conduction of Water and Minerals in Plants, Root Pressure, Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap), Active Transport, and Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane).
Importance of Selina Concise Solutions Chapter 4 Pdf
The Selina Concise Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology chapter 4 pdf presents you with all the answers required for the preparation of the exams. Here are a few reasons why you should download this pdf right now:
The Selina Concise solutions Chapter 4 pdf includes step-by-step, detailed answers to the exercise questions, making it an easier way to prepare for your ICSE exams.
Unlike many other resources, the Selina concise solution for Biology Chapter 4 is free of cost. With this free pdf, you will get lifetime access to solutions to all the Biology questions.
The pdf contains solutions with clear explanations and neat diagrams that will add more to your knowledge. These diagrams or tables will also come in handy in structural or skill-type questions in your exam.
To the point and accurate answers will save your time during revisions.
The pdf is great for exam preparations as the answers are in accordance with the information, illustrations, and examples provided in the textbook.
The use of coherent language in the Selina solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 4 makes the pdf an easy way to outstanding results.
The pdf is of utmost importance for those who revise in the last moments before the exam.
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 4 - Absorption by Roots : The Processes Involved
1. Why should I choose Selina Concise Solutions for ICSE preparation?
Choosing Selina Concise Solutions for ICSE preparation will be an excellent decision because of its relevant information. The textbook consists of illustrations, tables, examples, and diagrams to make Biology a piece of cake for you. With consistent and easy-to-read language, you can understand the fundamentals of biology without any problems. Moreover, Selina Concise Solutions feature accurate answers with the necessary explanation needed to comprehend a specific topic. So, if you are looking for reference books to score well in your ICSE Biology exam, Selina Concise Solutions is the way to go.
2. What are the characteristics of roots for absorbing water?
There are three factors that help the roots in the absorption of water. The enormous surface area of the rootlets and root hair absorbs water from the soil. Root hair contains highly concentrated cell sap that allows the water to move through osmosis. The thin walls of these root hairs allow the movement of water in and out of the cell. However, the cell membrane does not allow the large water molecules inside the cell as it is thin and semipermeable.
3. Are Class 10 Biology sample papers available on the internet?
Yes, class 10 Biology sample papers are available on the internet. You can find these question papers on Vedantu.com. With no registration fee, Vedantu offers you plenty of study material. You don’t even have to pay for downloading the pdf version of these sample papers as they are available for free on the website. Apart from sample papers, you can also find important questions, popular textbook solutions, revision notes, and pdfs of textbooks for any class.
4. What are the important concepts of Class 10 Biology Chapter 4?
Chapter 4 of Class 10 Biology mainly comprises the processes involved in absorption by roots. Some of the important concepts of this chapter are Plant Anatomy, Plant Physiology, Osmosis, Water and Mineral Absorption by Root, Need of Water and Minerals for Plant, Concept of Diffusion, Concept of Imbibition, Osmotic Pressure, Absorption and Conduction of Water and Minerals in Plants, Root Pressure, Turgidity, and Flaccidity, etc. Make sure to get a firm hold of these topics as they carry a higher weightage in the exams than others.
5. Is it easy to score well in ICSE class 10 Biology exam?
The ICSE Class 10 Biology exam is not as difficult as it seems. If you cover the whole syllabus and have a great understanding of all the concepts, you can easily be the highest scorer in your class. The Selina concise Solutions will aid you in your preparations. With some other reference books, you can practice different questions and conduct a self-assessment test as well. If you know how to revise the curriculum for your ICSE Class 10 Biology exam, it will be much simpler to get a perfect score.







































