
A ferrimagnetic material is one that has populations of atoms with opposing magnetic moments, the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains.
If this is true enter 1 if false enter 0.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you ought to recall the concept of ferrimagnetic materials. These are almost like anti-ferromagnetic materials, but the magnitude of 1 set of spins isn't adequate to the magnitude of another set of spins.
Complete Step by step solution:
Ferrimagnetic materials have high resistivity and have anisotropic properties which are induced by an externally applied field. When this applied field aligns with the magnetic dipoles, it causes a net dipole moment. Ferrimagnetic materials are wont to produce optical isolators and circulators. Ferrimagnetic minerals in various rock types are wont to study ancient magnetic properties of Earth and other planets referred to as palaeomagnetism.
The most important ferrimagnetic materials are the twin oxides composed of iron and another metal, generally referred to as ferrites. These ferrites exist in a cubic or hexagonal shape. Ferrites are ionic and therefore the ions are liable for their magnetic properties. The spins occurring in the ionic lattice result in spontaneous magnetic moments.
In a ferrimagnetic material, populations of atoms are present with opposing magnetic moments but the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains. This happens when the populations consist of different materials or ions. The arrangement is shown in the figure:
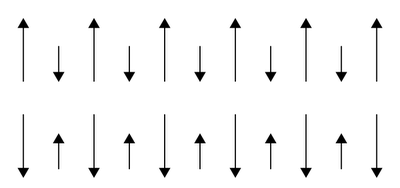
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is 1.
Note: Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon, in which certain materials like iron strongly attract each other. Ferromagnets occur in rare earth materials and gadolinium. It is one of the common phenomena that is encountered in life that is responsible for magnetism in magnets. One of the vital requirements of ferromagnetic material is that ions and atoms should possess permanent magnetic moments. Some ions and atoms contain the permanent moment of a magnet which can be considered as a dipole that comprises the North Pole separated from the South Pole. Some degree of dipole alignment is often witnessed has there existed an outsized atomic moment of a magnet. This type of magnetic arrangement is often found in some elements like iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. Ferrimagnetic materials are like ferromagnets therein they hold a spontaneous magnetization below the Curie temperature and show no magnetic order (are paramagnetic) above this temperature. However, there's sometimes a temperature below the Curie temperature, at which the two opposing moments are equal, resulting in a net moment of a magnet of zero; this is often called the magnetization compensation point.
Complete Step by step solution:
Ferrimagnetic materials have high resistivity and have anisotropic properties which are induced by an externally applied field. When this applied field aligns with the magnetic dipoles, it causes a net dipole moment. Ferrimagnetic materials are wont to produce optical isolators and circulators. Ferrimagnetic minerals in various rock types are wont to study ancient magnetic properties of Earth and other planets referred to as palaeomagnetism.
The most important ferrimagnetic materials are the twin oxides composed of iron and another metal, generally referred to as ferrites. These ferrites exist in a cubic or hexagonal shape. Ferrites are ionic and therefore the ions are liable for their magnetic properties. The spins occurring in the ionic lattice result in spontaneous magnetic moments.
In a ferrimagnetic material, populations of atoms are present with opposing magnetic moments but the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains. This happens when the populations consist of different materials or ions. The arrangement is shown in the figure:

Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is 1.
Note: Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon, in which certain materials like iron strongly attract each other. Ferromagnets occur in rare earth materials and gadolinium. It is one of the common phenomena that is encountered in life that is responsible for magnetism in magnets. One of the vital requirements of ferromagnetic material is that ions and atoms should possess permanent magnetic moments. Some ions and atoms contain the permanent moment of a magnet which can be considered as a dipole that comprises the North Pole separated from the South Pole. Some degree of dipole alignment is often witnessed has there existed an outsized atomic moment of a magnet. This type of magnetic arrangement is often found in some elements like iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. Ferrimagnetic materials are like ferromagnets therein they hold a spontaneous magnetization below the Curie temperature and show no magnetic order (are paramagnetic) above this temperature. However, there's sometimes a temperature below the Curie temperature, at which the two opposing moments are equal, resulting in a net moment of a magnet of zero; this is often called the magnetization compensation point.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




