
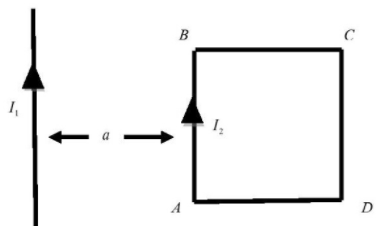
A square loop of a side ‘a’ is placed at ‘a’ distance away from a long wire carrying a current ${I_1}$. If the loop carries as current ${I_2}$ as shown in figure. Then the nature of the force and its amount is:
$\left( A \right)$ \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}\], attractive
$\left( B \right)$ \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{4\pi }}\], attractive
$\left( C \right)$ \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{4\pi }}\], repulsive
$\left( D \right)$ \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{4\pi a}}\], repulsive
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The concept of the Left-hand rule can be used to solve this problem. When a current-carrying conductor/wire is placed in a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the wire.
Hence Fleming gave a simple rule to determine the direction of force acting on a current-carrying conductor/wire placed in a magnetic field. This can be used to calculate the force of nature.
Complete step by step answer:
If the direction of electric currents flowing in two parallel straight conductors is the same then they will attract each other.
If the direction of electric currents flowing two parallel straight conductors are opposite then they repel each other.
In this question, current $({I_1})$ produces a magnetic field around it which at any point on current $({I_2})$carrying wire is,
${B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}}}{{2\pi a}}$ Directed inwards perpendicular to planes or wires
So current $({I_2})$ carrying wire then experiences a force due to its magnetic field which on its length $l$ given by,
$\Rightarrow F = {I_2}l{B_1}\sin {90^ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow F = {I_2}l \times \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}$
Or,\[\] $F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}l$
So force per unit length than the two wires exert on each other is,
$\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{F}{L}$
Hence \[f = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}\]
The answer will be $\left( A \right),$ thus nullifying other options.
Note: The strong force of nature is considered as the most powerful force. The electric, weak, and gravitational forces are followed in decreasing order.
Despite its strength, because of its exceedingly small range, the strong force does not manifest itself in the macroscopic universe.
When a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field of another current-carrying wire, it experiences a magnetic force.
The direction of the force depends on the direction of the magnetic field as well as the current and is perpendicular to it.
Hence Fleming gave a simple rule to determine the direction of force acting on a current-carrying conductor/wire placed in a magnetic field. This can be used to calculate the force of nature.
Complete step by step answer:
If the direction of electric currents flowing in two parallel straight conductors is the same then they will attract each other.
If the direction of electric currents flowing two parallel straight conductors are opposite then they repel each other.
In this question, current $({I_1})$ produces a magnetic field around it which at any point on current $({I_2})$carrying wire is,
${B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}}}{{2\pi a}}$ Directed inwards perpendicular to planes or wires
So current $({I_2})$ carrying wire then experiences a force due to its magnetic field which on its length $l$ given by,
$\Rightarrow F = {I_2}l{B_1}\sin {90^ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow F = {I_2}l \times \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}$
Or,\[\] $F = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}l$
So force per unit length than the two wires exert on each other is,
$\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{F}{L}$
Hence \[f = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_1}{I_2}}}{{2\pi a}}\]
The answer will be $\left( A \right),$ thus nullifying other options.
Note: The strong force of nature is considered as the most powerful force. The electric, weak, and gravitational forces are followed in decreasing order.
Despite its strength, because of its exceedingly small range, the strong force does not manifest itself in the macroscopic universe.
When a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field of another current-carrying wire, it experiences a magnetic force.
The direction of the force depends on the direction of the magnetic field as well as the current and is perpendicular to it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




