
What are the basic electrical principles?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Electrical principles includes the concepts of charge, electric current, voltage,electric power, conductors and insulators.
Complete step by step solution:
Some of the electrical principles are as follows:
Charge: While some electrons are bound in an atom, they are all similarly attached to protons. The atom's electrons that are farthest from the nucleus can be extracted. Because there are fewer electrons in the atom when some electrons are taken out, there are more protons than electrons.
The electrically neutral body becomes positively charged after the elimination of electrons. The body can also get electrons from an outside source, which is the opposite of the first scenario. In this instance, the body's electron count rises and it acquires a negative charge. An electric charge is a difference between an excess or shortage of electrons in a body. In coulombs, the electric charge is expressed.
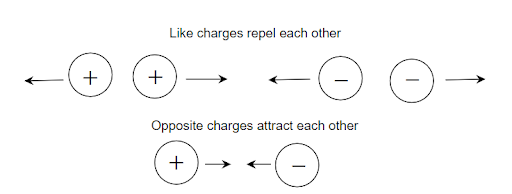
Image: Basic electrical principles
Conductors and insulators: Materials with weakly bonded valence or outside electrons are referred to as conductors. Aluminium, copper, gold, and silver are all effective conductors. Materials with securely bonded valence electrons are known as insulators. Insulators include things like glass, air, and stone.
Electric current: Electric current is defined as the number of charges per unit time passing through a boundary. In metals, because electrons are free to move around, the movement of electrons constitutes the electric current.
Voltage: As a measure of potential energy, the voltage between two locations or points is frequently arbitrary. It is frequently known as a "drop" voltage. When a voltage source is linked to a circuit, the voltage can induce a regular flow of charge carriers through the circuit, known as a current.
Electric power: In physics, electric power measures the rate of electrical energy transfer by an electric circuit per unit of time.
Note: The relationship between current, voltage, and resistance is expressed by Ohm's Law. This states that if the temperature stays stable, the current flowing in a circuit is exactly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the circuit resistance.
Complete step by step solution:
Some of the electrical principles are as follows:
Charge: While some electrons are bound in an atom, they are all similarly attached to protons. The atom's electrons that are farthest from the nucleus can be extracted. Because there are fewer electrons in the atom when some electrons are taken out, there are more protons than electrons.
The electrically neutral body becomes positively charged after the elimination of electrons. The body can also get electrons from an outside source, which is the opposite of the first scenario. In this instance, the body's electron count rises and it acquires a negative charge. An electric charge is a difference between an excess or shortage of electrons in a body. In coulombs, the electric charge is expressed.

Image: Basic electrical principles
Conductors and insulators: Materials with weakly bonded valence or outside electrons are referred to as conductors. Aluminium, copper, gold, and silver are all effective conductors. Materials with securely bonded valence electrons are known as insulators. Insulators include things like glass, air, and stone.
Electric current: Electric current is defined as the number of charges per unit time passing through a boundary. In metals, because electrons are free to move around, the movement of electrons constitutes the electric current.
Voltage: As a measure of potential energy, the voltage between two locations or points is frequently arbitrary. It is frequently known as a "drop" voltage. When a voltage source is linked to a circuit, the voltage can induce a regular flow of charge carriers through the circuit, known as a current.
Electric power: In physics, electric power measures the rate of electrical energy transfer by an electric circuit per unit of time.
Note: The relationship between current, voltage, and resistance is expressed by Ohm's Law. This states that if the temperature stays stable, the current flowing in a circuit is exactly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the circuit resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




