
At time $t = {t_1}$ an object’s velocity is given by the vector $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ shown below.
$ \to $
A short time later, at $t = {t_2}$, the object’s velocity is the vector $\overrightarrow {{v_2}} $
$ \nearrow $
If $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ and $\overrightarrow {{v_2}} $ have the same magnitude, which one of the following vectors best illustrates the object’s average acceleration between $t = {t_1}$ and $t = {t_2}$?
(A)
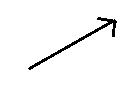
(B)

(C)

(D)
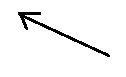
(E)
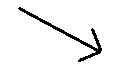
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Since the magnitudes of the vectors are the same so we need to only consider their direction. In order to calculate the acceleration, the direction of the first vector must be reversed to represent the difference.
Complete step by step answer
The basic difference between scalars and vectors is that scalar quantities just represent the magnitude whereas the vector represents both the direction and magnitude of the quantity.
For example, mass of a body does not have any particular direction but it does have a magnitude to represent the quantity. These types of quantities are called scalar quantities. On the other hand, the force acting on a body can be represented by both direction and magnitude. When we push someone or something, we are exerting some amount of force in a particular direction. These quantities are called vectors.
Vectors are usually denoted by drawing an arrow just above the sign representing the quantity.
In this question we need to find the resultant of two vectors.
We are given the velocity vectors at time ${t_1}$ and ${t_2}$
Now, acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity
So, $\overrightarrow a = \dfrac{{\overrightarrow {{v_2}} - \overrightarrow {{v_1}} }}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}$
Now, the resultant of vectors $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ and $\overrightarrow {{v_2}} $results in option A. Since we need to find their difference, we can assume that the direction of vector $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ is reversed.
If this direction is reversed then their resultant vector would be correctly represented by option C.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note: Unlike scalar quantities, vectors have two types of product. Dot and cross. Dot product tells us how much of two vectors are in the same direction whereas the cross product tells us how little the two vectors are in the same direction. Dot product of two vectors gives us a scalar quantity, while the cross product of two vectors gives us a vector quantity.
Complete step by step answer
The basic difference between scalars and vectors is that scalar quantities just represent the magnitude whereas the vector represents both the direction and magnitude of the quantity.
For example, mass of a body does not have any particular direction but it does have a magnitude to represent the quantity. These types of quantities are called scalar quantities. On the other hand, the force acting on a body can be represented by both direction and magnitude. When we push someone or something, we are exerting some amount of force in a particular direction. These quantities are called vectors.
Vectors are usually denoted by drawing an arrow just above the sign representing the quantity.
In this question we need to find the resultant of two vectors.
We are given the velocity vectors at time ${t_1}$ and ${t_2}$
Now, acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity
So, $\overrightarrow a = \dfrac{{\overrightarrow {{v_2}} - \overrightarrow {{v_1}} }}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}$
Now, the resultant of vectors $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ and $\overrightarrow {{v_2}} $results in option A. Since we need to find their difference, we can assume that the direction of vector $\overrightarrow {{v_1}} $ is reversed.
If this direction is reversed then their resultant vector would be correctly represented by option C.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note: Unlike scalar quantities, vectors have two types of product. Dot and cross. Dot product tells us how much of two vectors are in the same direction whereas the cross product tells us how little the two vectors are in the same direction. Dot product of two vectors gives us a scalar quantity, while the cross product of two vectors gives us a vector quantity.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




