
Why distillation is a chemical reaction?
(A) Formation of products occur
(B) Change in state of reactants
(C) Both A and B
(D) Distillation is not a chemical reaction.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Distillation is a physical separation process. It is used to separate a mixture of substances by heating a liquid that undergoes a phase change; from liquid to gas. There is no involvement of reactants or products in the whole process.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Distillation refers to the selective boiling of a liquid mixture and subsequent condensation of a component in that mixture. It is a separation technique that can be used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture. The process of distillation explains the difference in the boiling points of the components in the liquid mixture by transforming one of them into a gaseous state.
Distillation is not a chemical reaction but it can be considered as a physical separation process. Physical changes include the changes of state: solid to liquid, fusion; liquid to gas, vaporization; gas to solid, deposition. No chemical bonds are damaged in this process, other than the weak dispersion forces between molecules.
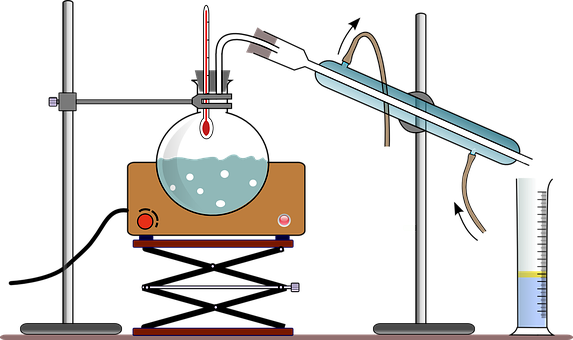
While a chemical reaction is a process in which reactants are converted into products by either bond-breaking or bond-making. As no such step occurs in the process of distillation, it is not a chemical reaction. Thus, no product is formed and no change in the state of reaction occurs.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: Distillation is a powerful technique used for separating the component from a miscible fluid mixture by means of selective evaporation and condensation. It is a purification method that involves boiling a liquid and purifying it by different types of distillation processes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Distillation refers to the selective boiling of a liquid mixture and subsequent condensation of a component in that mixture. It is a separation technique that can be used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture. The process of distillation explains the difference in the boiling points of the components in the liquid mixture by transforming one of them into a gaseous state.
Distillation is not a chemical reaction but it can be considered as a physical separation process. Physical changes include the changes of state: solid to liquid, fusion; liquid to gas, vaporization; gas to solid, deposition. No chemical bonds are damaged in this process, other than the weak dispersion forces between molecules.

While a chemical reaction is a process in which reactants are converted into products by either bond-breaking or bond-making. As no such step occurs in the process of distillation, it is not a chemical reaction. Thus, no product is formed and no change in the state of reaction occurs.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: Distillation is a powerful technique used for separating the component from a miscible fluid mixture by means of selective evaporation and condensation. It is a purification method that involves boiling a liquid and purifying it by different types of distillation processes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




