
If a graph is plotted with the atomic number on x-axis and the square root of the frequency of a spectral line of characteristic X-rays on the y-axis, then it will be
A) A straight line passing through the origin
B) A parabola
C) A straight line not passing through the origin
D) A rectangular hyperbola
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The atomic number or proton number is the number of protons found in the nucleus. A spectral line is a characteristic line in the entire continuous spectrum of an element, resulting from light emission and absorption in a narrow range of frequency when compared with the nearby frequencies.
Complete step by step solution:
The atomic number of an element can be related to the square root of the frequency of a spectral line of characteristic X-rays using Moseley’s law. Moseley’s law is an empirical law concerning the characteristic X-rays emitted by atoms. It states that the square root of the frequency of emitted X-rays is approximately proportional to the atomic number.
Mathematically, the law can be represented using the equation \[\sqrt{\upsilon }\propto Z\] where \[\upsilon \] is the frequency of the emitted X-ray.
The final equation of Moseley’s law can be written as \[\upsilon =A{(Z-b)}^2\] where and are constants depending upon the X-ray emission. Moseley measured and plotted the X-ray frequencies of about 40 elements of the periodic table following his law and observed the graph to be a straight line. The plot of the graph with atomic numbers on the x-axis and the square root of frequencies on the y-axis furnished a straight line not passing through the origin.
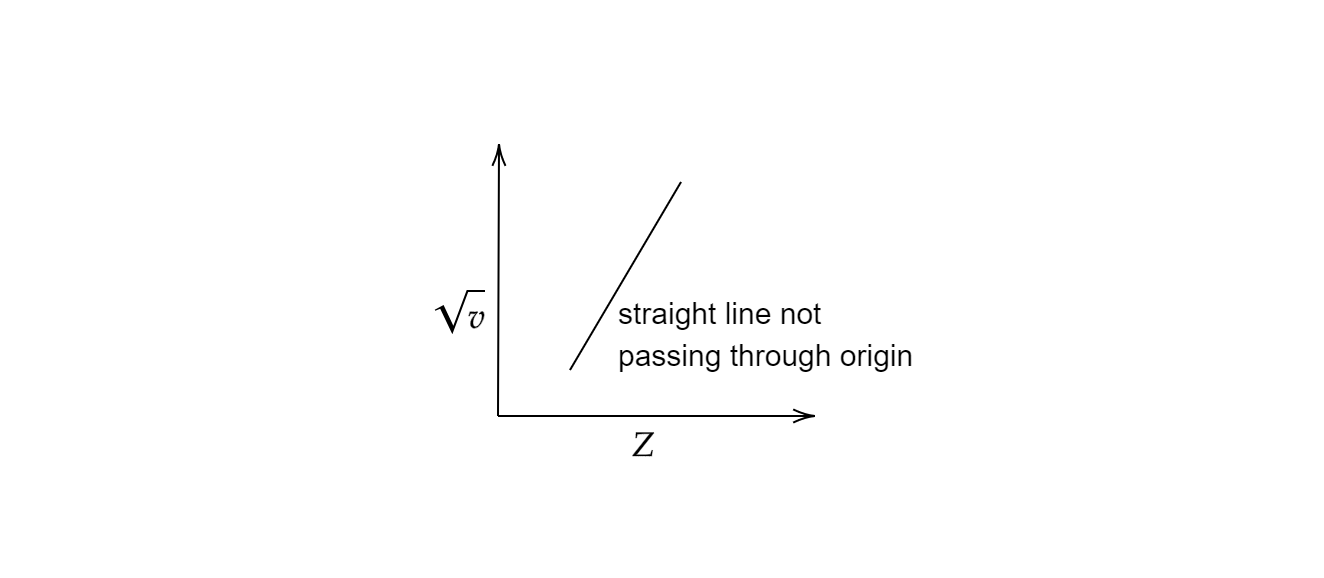
Hence, option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Moseley’s law was the first law to associate the atomic number of elements with any known physical quantity. It established the atomic number as a measurable experimental quantity and also gave it a viable physical meaning. Henry Moseley, the physicist behind this law, has also made major contributions to the periodic table.
Complete step by step solution:
The atomic number of an element can be related to the square root of the frequency of a spectral line of characteristic X-rays using Moseley’s law. Moseley’s law is an empirical law concerning the characteristic X-rays emitted by atoms. It states that the square root of the frequency of emitted X-rays is approximately proportional to the atomic number.
Mathematically, the law can be represented using the equation \[\sqrt{\upsilon }\propto Z\] where \[\upsilon \] is the frequency of the emitted X-ray.
The final equation of Moseley’s law can be written as \[\upsilon =A{(Z-b)}^2\] where and are constants depending upon the X-ray emission. Moseley measured and plotted the X-ray frequencies of about 40 elements of the periodic table following his law and observed the graph to be a straight line. The plot of the graph with atomic numbers on the x-axis and the square root of frequencies on the y-axis furnished a straight line not passing through the origin.

Hence, option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Moseley’s law was the first law to associate the atomic number of elements with any known physical quantity. It established the atomic number as a measurable experimental quantity and also gave it a viable physical meaning. Henry Moseley, the physicist behind this law, has also made major contributions to the periodic table.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




