
Initial and final pressures and volumes of a gas in a thermodynamic process are ${P_i}$, ${V_i}$ and ${P_f}$, ${V_f}$, respectively. If $P{V^n}$=constant, then the amount of work done is:
$\left( A \right)$ minimum for $n = \gamma $
$\left( B \right)$ minimum for $n = 1$
$\left( C \right)$ minimum for $n = 0$
$\left( D \right)$ minimum for $n = \dfrac{1}{\gamma }$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Here the initial and final pressure and volume are given. Using the equation of the gas, plot the graph of pressure versus volume for different values of \[n\] . The area under the graph pressure versus volume gives the work done by the gas. Then using the graph determine the minimum work done by the gas. Here the given thermodynamic process is an adiabatic process.
Complete step by step answer:
A system undergoing physical changes in such a way that neither the heat is allowed to enter the system from the surrounding nor allowed to leave the system to the surrounding is called the adiabatic process. In adiabatic compression, the temperature increases as work is done on the gas. In adiabatic expansion, the temperature decreases as the work is done by the gas.
We know that
$P{V^n}$= constant
$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^n}}}$
Where $C$ is a constant,$P$ is the pressure,$V$ is the volume.
 Now for $n = 0$, we get
Now for $n = 0$, we get
$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^0}}} = C$
The pressure is constant since $P = C$.
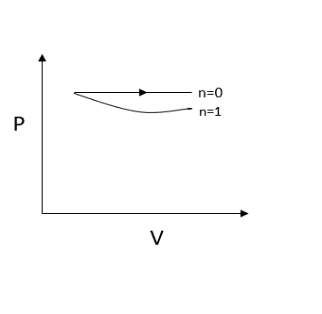
Now let us substitute $n = 1$, we get $P = \dfrac{C}{V}$
Here we obtain a rectangular hyperbola since the pressure is inversely proportional to volume.
Now $n = \gamma $, we get
$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}}$
We know that the adiabatic constant $\gamma $ is greater than one, we can write
${V^\gamma } > V$
And we can also write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}} < \dfrac{C}{V} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
From the above equation, I can also write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma }}}}} > \dfrac{C}{V} - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
From comparing the two-equation we can write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}} < \dfrac{C}{{{V^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma }}}}}$
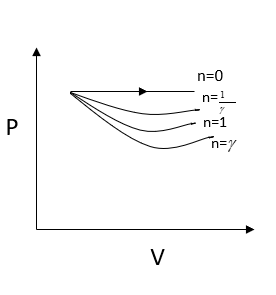
Here work done is given by the area under the curve. It is clear that work is done is minimum for $n = \gamma $
Hence option$\left( A \right)$is the correct option.
Note: Pressure, Volume, Temperature changes suddenly from ${P_1}$ , ${V_1}$,${T_1}$ to ${P_2}$,${V_2}$${T_2}$ if a gas is compressed suddenly in the thermally insulated flask. This is an adiabatic process. In adiabatic compression, the temperature increases as work is done on the gas. In adiabatic expansion, the temperature decreases as the work is done by the gas. A system undergoing physical changes in such a way that neither the heat is allowed to enter the system from the surrounding nor allowed to leave the system to the surrounding is called the adiabatic process.
Complete step by step answer:
A system undergoing physical changes in such a way that neither the heat is allowed to enter the system from the surrounding nor allowed to leave the system to the surrounding is called the adiabatic process. In adiabatic compression, the temperature increases as work is done on the gas. In adiabatic expansion, the temperature decreases as the work is done by the gas.
We know that
$P{V^n}$= constant
$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^n}}}$
Where $C$ is a constant,$P$ is the pressure,$V$ is the volume.
 Now for $n = 0$, we get
Now for $n = 0$, we get$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^0}}} = C$
The pressure is constant since $P = C$.
Now let us substitute $n = 1$, we get $P = \dfrac{C}{V}$
Here we obtain a rectangular hyperbola since the pressure is inversely proportional to volume.

Now $n = \gamma $, we get
$P = \dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}}$
We know that the adiabatic constant $\gamma $ is greater than one, we can write
${V^\gamma } > V$
And we can also write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}} < \dfrac{C}{V} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
From the above equation, I can also write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma }}}}} > \dfrac{C}{V} - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
From comparing the two-equation we can write
$\dfrac{C}{{{V^\gamma }}} < \dfrac{C}{{{V^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma }}}}}$

Here work done is given by the area under the curve. It is clear that work is done is minimum for $n = \gamma $
Hence option$\left( A \right)$is the correct option.
Note: Pressure, Volume, Temperature changes suddenly from ${P_1}$ , ${V_1}$,${T_1}$ to ${P_2}$,${V_2}$${T_2}$ if a gas is compressed suddenly in the thermally insulated flask. This is an adiabatic process. In adiabatic compression, the temperature increases as work is done on the gas. In adiabatic expansion, the temperature decreases as the work is done by the gas. A system undergoing physical changes in such a way that neither the heat is allowed to enter the system from the surrounding nor allowed to leave the system to the surrounding is called the adiabatic process.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




