
The difference in the density of low density polymers (LDP) and high density polymers (HDP) is due to the fact that:
A. LDP are highly branched structures while HDP consists of closely packed linear molecules.
B. LDP are linear chains while HDP are branched chains of polythene.
C. Both LDP and HDP are unbranched linear chains with different lengths.
D. At high temperature, the density of polymer is reduced.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Polymers are chemical compounds with high molecular weight and made up of repeated units called monomers. These units can be the same or different. On the basis of the nature of monomers a polymer can be homo or copolymer.
Complete step by step answer:
LDPE and HDPE are thermoplastic polymers. Polymers are high molecular mass compounds whose structures are composed of a large number of simple repeating units. The repeating structural units are usually obtained from low molecular mass of simple compounds called monomers.
(i) Low density polythene (LDPE): It is prepared by heating pure ethylene at $190^\circ - 210^\circ C$ under a pressure of about $1500$atmosphere in the presence of traces of oxygen. The polymer produced consists of highly branched chain molecules. The branching does not allow the polymer molecules to undergo close packing and thus, the density of polymer is low and it has low melting point.
$\mathop {nC{H_2} = C{H_2}}\limits_{ethene} \xrightarrow[{\left( {oxygen} \right)}]{{200^\circ C,{\text{ 1500 atm}}}}\mathop {{{\left[ { - {H_2}C - C{H_2} - } \right]}_n}}\limits_{\left( {polyethene} \right)} $
Low density polythene can be represented as,
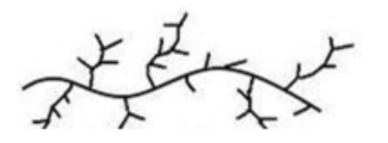
It is chemically inert, tough but flexible. It is a poor electrical conductor. It is used for packaging, cable insulation and in the manufacture of pipes, squeeze bottles and toys.
High density polythene (HDPE): It is manufactured by coordination polymerisation of ethylene in a hydrocarbon solvent at $60^\circ - 70^\circ C$under a pressure of$6 - 7$atmosphere in the presence of a catalyst such as triethyl aluminium and titanium tetra chloride.
\[nC{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{TiC{l_4} + Al{{\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)}_3}}]{{60^\circ - 70^\circ C,{\text{ 6atom}}}}\mathop {{{\left[ { - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - } \right]}_n}}\limits_{\left( {polyethene} \right)} \]
The structure of HDPE can be represented as,

The polymer thus produced, consists of practically linear molecules which are closely packed and have high density.
It is chemically inert but tough and harder. Its tensile strength is more than that of low density polymers. It is used in making housewares such as buckets, dustbin, bottle, pipes, toys, etc.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
In general high density grade polythene have densities up to $0.97g/c{m^3}$and low density grade polythene have density as low as $0.91g/c{m^3}$. High density material is more linear and crystalline. Low density polythene has less stiffness than the high density polythene.
Complete step by step answer:
LDPE and HDPE are thermoplastic polymers. Polymers are high molecular mass compounds whose structures are composed of a large number of simple repeating units. The repeating structural units are usually obtained from low molecular mass of simple compounds called monomers.
(i) Low density polythene (LDPE): It is prepared by heating pure ethylene at $190^\circ - 210^\circ C$ under a pressure of about $1500$atmosphere in the presence of traces of oxygen. The polymer produced consists of highly branched chain molecules. The branching does not allow the polymer molecules to undergo close packing and thus, the density of polymer is low and it has low melting point.
$\mathop {nC{H_2} = C{H_2}}\limits_{ethene} \xrightarrow[{\left( {oxygen} \right)}]{{200^\circ C,{\text{ 1500 atm}}}}\mathop {{{\left[ { - {H_2}C - C{H_2} - } \right]}_n}}\limits_{\left( {polyethene} \right)} $
Low density polythene can be represented as,

It is chemically inert, tough but flexible. It is a poor electrical conductor. It is used for packaging, cable insulation and in the manufacture of pipes, squeeze bottles and toys.
High density polythene (HDPE): It is manufactured by coordination polymerisation of ethylene in a hydrocarbon solvent at $60^\circ - 70^\circ C$under a pressure of$6 - 7$atmosphere in the presence of a catalyst such as triethyl aluminium and titanium tetra chloride.
\[nC{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{TiC{l_4} + Al{{\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)}_3}}]{{60^\circ - 70^\circ C,{\text{ 6atom}}}}\mathop {{{\left[ { - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - } \right]}_n}}\limits_{\left( {polyethene} \right)} \]
The structure of HDPE can be represented as,

The polymer thus produced, consists of practically linear molecules which are closely packed and have high density.
It is chemically inert but tough and harder. Its tensile strength is more than that of low density polymers. It is used in making housewares such as buckets, dustbin, bottle, pipes, toys, etc.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
In general high density grade polythene have densities up to $0.97g/c{m^3}$and low density grade polythene have density as low as $0.91g/c{m^3}$. High density material is more linear and crystalline. Low density polythene has less stiffness than the high density polythene.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




