
The most reactive of the following is
A. Acetone
B. Benzophenone
C. Benzaldehyde
D. Acetaldehyde
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Firstly, for comparison we should know under what category these compounds belong so that the comparison work becomes easier. Acetone and benzophenone come under ketones and benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde are compounds of the aldehyde group. Aldehydes contain a functional group with the structure$\text{-CHO}$, consisting of a carbon which is double-bonded to oxygen with the carbon atom bonded to hydrogen and other R groups which can be alkyl or side chain. Ketone is a functional group in organic chemistry containing a carbonyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us move back to the question to discuss reactivity. Reactivity in case of aldehydes and ketones is decided by two factors: (1) Steric hindrance (2) Electrophilicity of carbon with oxygen
(1) Steric hindrance: It is the congestion created by presence of surrounding atoms or ligands which may slow down or even prevent reaction to occur. In Ketones, there is large hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups attached to$\text{C=O}$; due to which incoming nucleophiles do not have the required space to form bonds with carbon. This lowers the reactivity of ketones in large amounts than aldehydes.
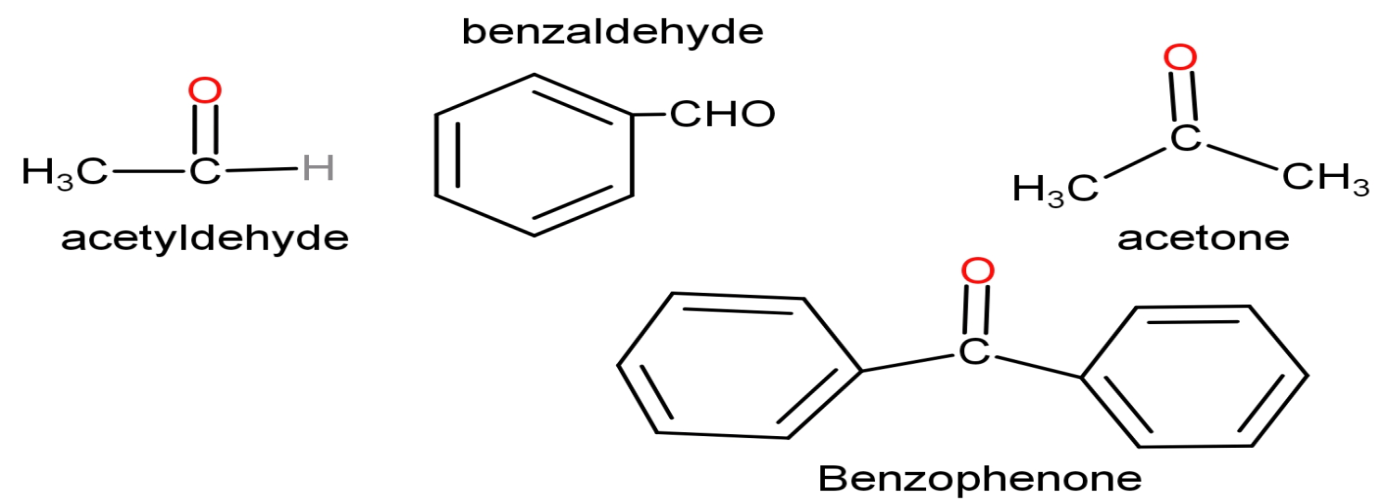
Due to the large and bulky size of the phenyl group, steric hindrance caused by benzaldehyde is more than acetaldehyde. Similarly, benzophenone has two phenyl groups present in its structure; the hindrance created by it is more than that created by methyl groups of acetone. That is why, acetaldehyde is more reactive than benzaldehyde and acetone is more reactive than benzophenone.
(2) Electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon: Due to electronegativity of oxygen the double-bonded carbon attached to it acquires partial positive charge, which makes the attack of nucleophiles easier. But the presence of electron donating groups nullifies the positive charge created. Thus, the presence of electron donating groups decreases the nucleophilic addition reaction.
Hence, the order of reactivity of all compounds is$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHO}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CHOC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CO}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}$. Thus, acetaldehyde is the most reactive compound which is option ‘d’.
Note: Do not mark benzaldehyde as the most reactive compound. As, benzaldehyde is stabilized by resonance effect,
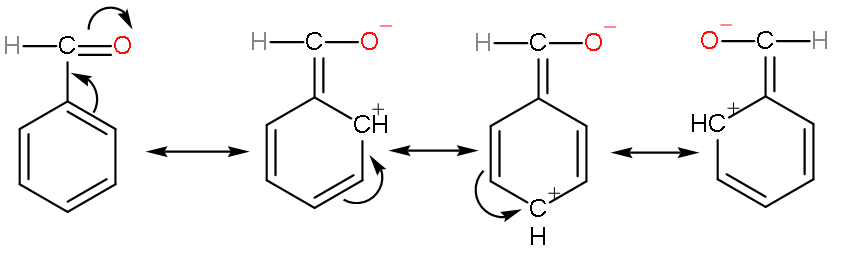
So, reactivity of benzaldehyde will not increase; apparently it will decrease because stability means potential energy to decrease and a compound reacts to lower its potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us move back to the question to discuss reactivity. Reactivity in case of aldehydes and ketones is decided by two factors: (1) Steric hindrance (2) Electrophilicity of carbon with oxygen
(1) Steric hindrance: It is the congestion created by presence of surrounding atoms or ligands which may slow down or even prevent reaction to occur. In Ketones, there is large hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups attached to$\text{C=O}$; due to which incoming nucleophiles do not have the required space to form bonds with carbon. This lowers the reactivity of ketones in large amounts than aldehydes.

Due to the large and bulky size of the phenyl group, steric hindrance caused by benzaldehyde is more than acetaldehyde. Similarly, benzophenone has two phenyl groups present in its structure; the hindrance created by it is more than that created by methyl groups of acetone. That is why, acetaldehyde is more reactive than benzaldehyde and acetone is more reactive than benzophenone.
(2) Electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon: Due to electronegativity of oxygen the double-bonded carbon attached to it acquires partial positive charge, which makes the attack of nucleophiles easier. But the presence of electron donating groups nullifies the positive charge created. Thus, the presence of electron donating groups decreases the nucleophilic addition reaction.
Hence, the order of reactivity of all compounds is$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHO}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CHOC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{CO}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}$. Thus, acetaldehyde is the most reactive compound which is option ‘d’.
Note: Do not mark benzaldehyde as the most reactive compound. As, benzaldehyde is stabilized by resonance effect,

So, reactivity of benzaldehyde will not increase; apparently it will decrease because stability means potential energy to decrease and a compound reacts to lower its potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




