
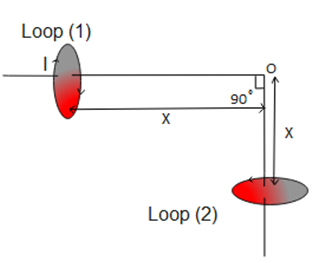
Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents $I$ are placed vertically ( with respect to the plane of the paper) with their geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at point O.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Magnetic field due to current carrying circular loop is given by
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\] where ${\mu _0}$ is called permeability of free space and the value of ${\mu _0}$ is \[4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}\dfrac{{Tm}}{A}\] and $R$ is the radius of the loop and $I$ is the current through the circular loop.
The direction of the magnetic field can be calculated by using the Right hand thumb rule.
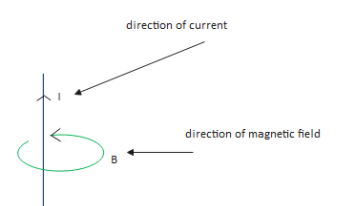
Here is an explanation of Right hand thumb rule in simple words: If a current carrying conductor is imagined to be held in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of current then curled fingers of the right hand tell us the direction of the magnetic field.
First of all, find out the magnetic field at point O due to loop 1, then at point O due to loop 2, then find out their resultant so we will get the magnitude of the net magnetic field & then with the help of right hand thumb rule we will get the direction of the net magnetic field.
Complete solution:
Magnetic field at point O due to circular loop 1 is given by \[{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\] and the direction of ${B_1}$ would be towards left.
Magnetic field at point O due to circular loop 2 is given by ${B_2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$ and the direction of ${B_2}$ is acting vertically upwards.
Therefore, the resultant magnetic field at point O will become, $B = \sqrt {B_1^2 + B_2^2} $… … …(i)
Here, we know that the value of \[{B_1}\] and ${B_2}$is same so we can write, ${B_1} = {B_2}$
Now, put ${B_1} = {B_2}$ in equation (i) so we will get $B = \sqrt {2} {B_1} $ … … …(ii)
By substituting the value of ${B_1}$ in equation (ii) we will get \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{\sqrt 2 {{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\]
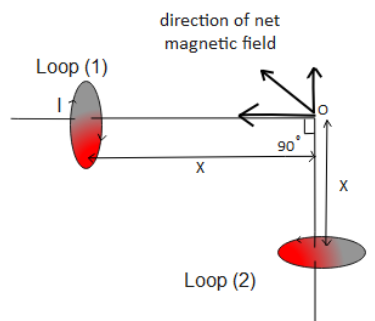
The direction of the net magnetic field would be at an angle $45^\circ $ with the axis of circular loop 1 as shown in the above figure.
Note: When we want to find out the direction of the magnetic field due to a current carrying wire this rule “Right hand thumb rule” can be used. This rule also can be used to find out the direction of current if you know the magnetic field around the current carrying wire. The most important point to learn from this rule: If the current flows in the upward direction, the direction of the magnetic field.
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\] where ${\mu _0}$ is called permeability of free space and the value of ${\mu _0}$ is \[4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}\dfrac{{Tm}}{A}\] and $R$ is the radius of the loop and $I$ is the current through the circular loop.
The direction of the magnetic field can be calculated by using the Right hand thumb rule.

Here is an explanation of Right hand thumb rule in simple words: If a current carrying conductor is imagined to be held in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of current then curled fingers of the right hand tell us the direction of the magnetic field.
First of all, find out the magnetic field at point O due to loop 1, then at point O due to loop 2, then find out their resultant so we will get the magnitude of the net magnetic field & then with the help of right hand thumb rule we will get the direction of the net magnetic field.
Complete solution:
Magnetic field at point O due to circular loop 1 is given by \[{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\] and the direction of ${B_1}$ would be towards left.
Magnetic field at point O due to circular loop 2 is given by ${B_2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{2{{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$ and the direction of ${B_2}$ is acting vertically upwards.
Therefore, the resultant magnetic field at point O will become, $B = \sqrt {B_1^2 + B_2^2} $… … …(i)
Here, we know that the value of \[{B_1}\] and ${B_2}$is same so we can write, ${B_1} = {B_2}$
Now, put ${B_1} = {B_2}$ in equation (i) so we will get $B = \sqrt {2} {B_1} $ … … …(ii)
By substituting the value of ${B_1}$ in equation (ii) we will get \[\dfrac{{{\mu _0}i{R^2}}}{{\sqrt 2 {{({x^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}\]

The direction of the net magnetic field would be at an angle $45^\circ $ with the axis of circular loop 1 as shown in the above figure.
Note: When we want to find out the direction of the magnetic field due to a current carrying wire this rule “Right hand thumb rule” can be used. This rule also can be used to find out the direction of current if you know the magnetic field around the current carrying wire. The most important point to learn from this rule: If the current flows in the upward direction, the direction of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




