Step-by-Step Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 In Hindi - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology in Hindi Chapter 9 Biomolecules (2025-26)
1. What are the key steps followed in solving NCERT questions from Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 as per the CBSE 2025–26 pattern?
To solve questions effectively in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9, follow these steps:
- Identify the type of biomolecule or process described in the question.
- Refer to the correct terminology and definitions as per NCERT guidelines.
- Structure the answer by addressing each part of the question sequentially.
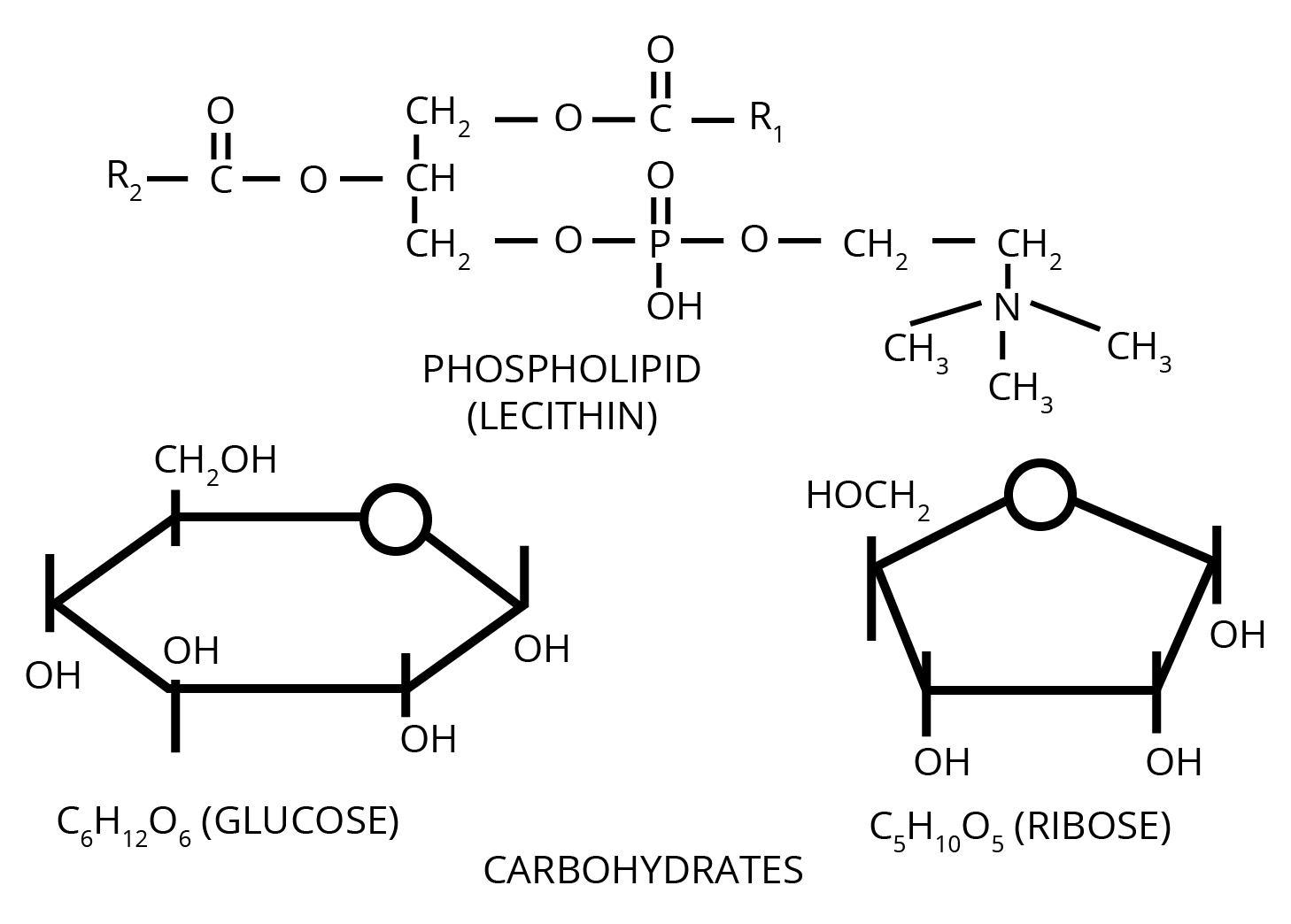
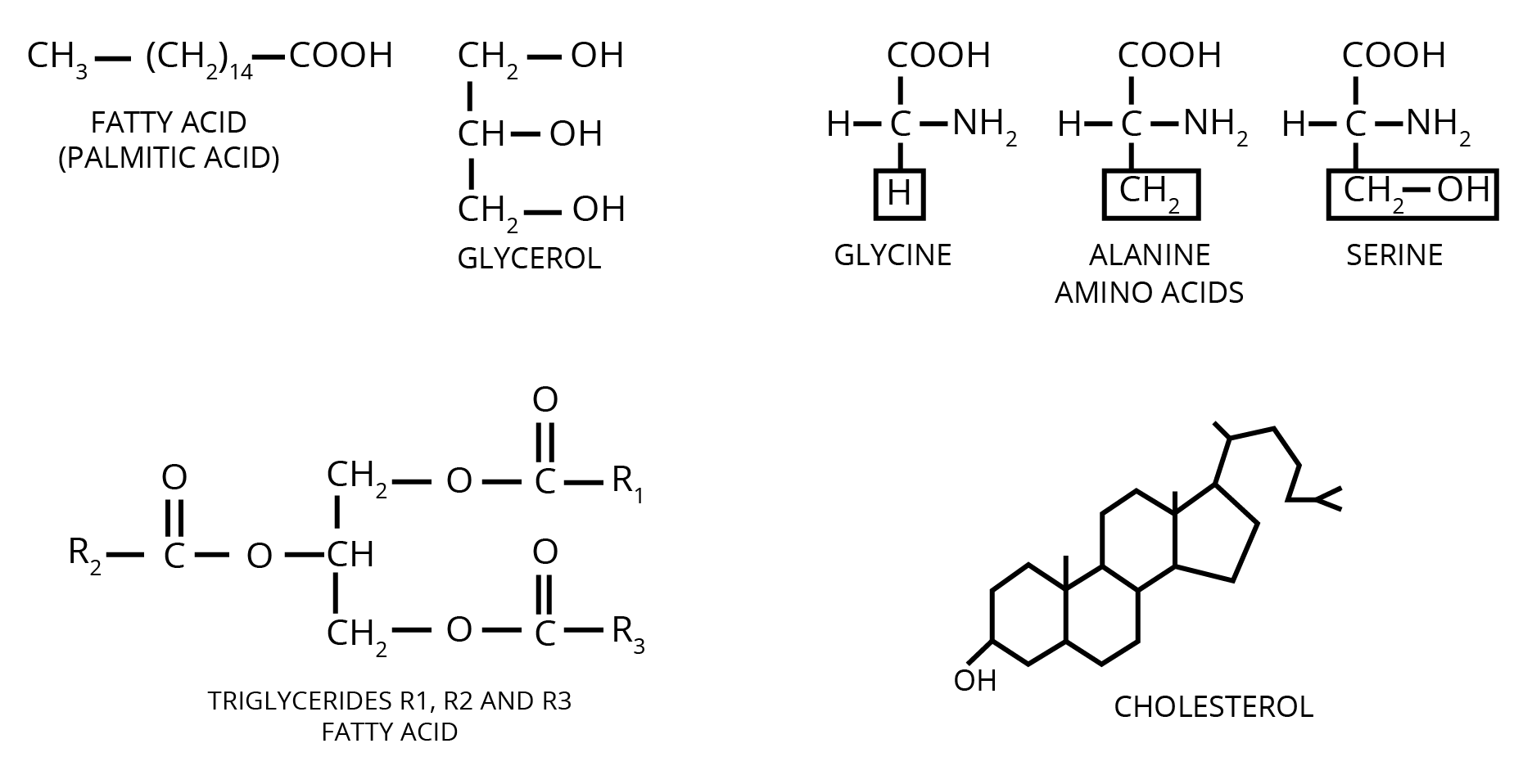
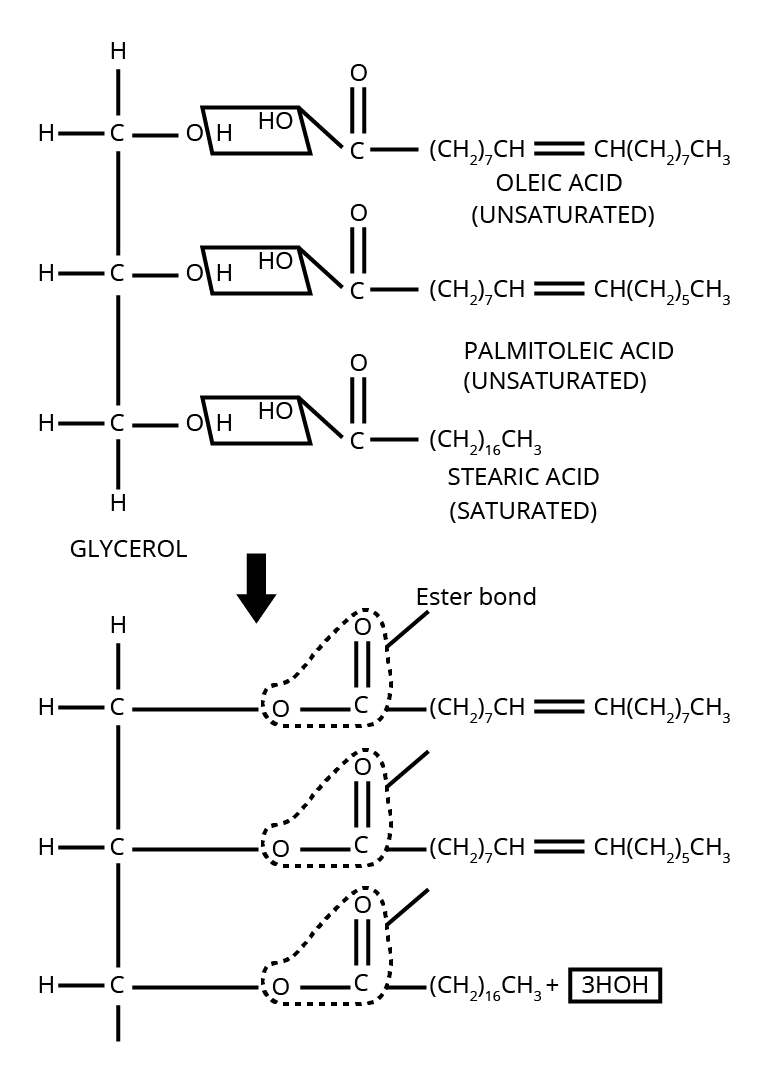
- Use diagrams or flowcharts where processes are involved, like in enzyme reactions or protein structure.
- Conclude with a summary or an application if asked.
2. How does using step-by-step NCERT solutions help improve accuracy in Biology answers?
Using step-by-step NCERT solutions helps ensure that no point is missed and that answers are presented logically. Each step clarifies reasoning, reduces errors, and enables better retention of biologically accurate terminology, which matches CBSE marking schemes.
3. Why is understanding the structure of biomolecules essential for solving NCERT questions in this chapter?
Understanding the structure of biomolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids is crucial for answering NCERT questions because:
- Many questions directly ask about the types of bonds, molecular shapes, or arrangements.
- Knowledge of structure helps explain the function and interactions of biomolecules.
- Detailed answers with structures fetch better marks in CBSE exams.
4. What are common mistakes students make while answering CBSE NCERT Biology Chapter 9 questions, and how can they avoid them?
Common mistakes include:
- Confusing structural details such as peptide vs. glycosidic bonds.
- Omitting diagram labels or stepwise explanations.
- Mixing up primary and secondary metabolites.
5. How are enzyme properties and their CBSE-specified functions typically addressed in NCERT Solutions for this chapter?
NCERT Solutions explain enzyme properties by listing key points such as specificity, optimum conditions, and the catalytic role of enzymes. Answers address functions using points like substrate specificity, reaction acceleration, optimal pH and temperature, supporting these with relevant textbook examples as per CBSE requirements.
6. What approach should be used to write answers for questions involving metabolic pathways or enzyme actions?
The ideal approach includes:
- Starting with a concise definition of the process or biomolecule.
- Sequentially describing each step or stage in the pathway.
- Supporting explanations with diagrams or reaction equations where needed.
- Summarizing the significance to the organism.
7. How does analyzing CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 help clarify differences between types of biomolecules?
Examining NCERT Solutions enables students to directly compare biomolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, highlighting differences in their building blocks, biological roles, and structural features, making answers more precise and exam-ready.
8. In what ways can detailed NCERT solutions benefit students during Biology exam preparation for Chapter 9?
Detailed NCERT solutions provide:
- Clear, stepwise explanations matching CBSE marking schemes.
- Accurate diagrams and labeled structures to support answers.
- Sample application of concepts to likely exam scenarios.
- Practice in formal answer presentation, boosting confidence and accuracy.
9. How can students relate lab testing of biomolecules, as covered in NCERT Solutions, to real-life biological or industrial applications?
By following NCERT solution procedures for testing biomolecules, students learn how foundational laboratory skills apply to real-world tasks, such as identifying food nutrients, drug formulation in pharmaceuticals, or quality control in food industries.
10. What misconceptions about metabolism or macromolecules typically arise and how are they addressed in CBSE NCERT Solutions?
Common misconceptions include thinking all biomolecules are similar or that metabolic reactions only occur during digestion. NCERT Solutions clarify the unique features, structural diversity, and widespread biological relevance of differing macromolecules—helping students avoid these errors in exam answers.