Motion In A Straight Line Class 11 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
NCERT for Chapter 2 Motion In A Straight Line Class 11 Solutions by Vedantu, introduces the basics of kinematics, which deals with the motion of objects. This chapter explains how objects move along a straight path, providing the essential concepts required for further studies in physics. In this chapter, you will study motion and the different kinds of motion. Also read about concepts like path lengths, displacement, velocity, and speed and their various numerical associated. Through these Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions, we aim to simplify complex concepts into easy-to-understand explanations, helping you with each topic effectively. With Vedantu's NCERT Solutions, you will find step-by-step explanations of all the questions in your textbook, ensuring that you understand the concepts thoroughly.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentNote:➤Unlock your dream college possibilities with our NEET College Predictor!
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 – Motion in a Straight Line
1. In which of the following examples of motion, can the body be considered approximately a point object:
(a) a railway carriage moving without jerks between two stations.
Ans: As the size of a carriage is very small as compared to the distance between two stations, the carriage can be treated as a point sized object.
(b) a monkey sitting on top of a man cycling smoothly on a circular track.
Ans: As the size of a monkey is very small as compared to the size of a circular track, the monkey can be considered as a point sized object on the track.
(c) a spinning cricket ball that turns sharply on hitting the ground.
Ans: As the size of a spinning cricket ball is comparable to the distance through which it turns sharply on hitting the ground, the cricket ball cannot be considered as a point object.
(d) a tumbling beaker that has slipped off the edge of a table.
Ans: As the size of a beaker is comparable to the height of the table from which it slipped, the beaker cannot be considered as a point object.
2. The position-time (x-t) graphs for two children A and B returning from their school O to their homes P and Q respectively are shown in figure. Choose the correct entries in the brackets below:

a. (A/B) lives closer to the school than (B/A)
Ans: From the graph, it is clear that $OP<OQ$. Therefore, A lives closer to the school than B.
b. (A/B) starts from the school earlier than (B/A)
Ans: From the graph it is clear that for \[x\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }t\text{ }=\text{ }0\] for A and t has some finite value for B. Hence, A starts from the school earlier than B.
c. (A/B) walks faster than (B/A)
Ans: As the velocity is equal to slope of x-t graph, in case of uniform motion and slope of x-t graph for B is greater than that for A. Thus B walks faster than A.
d. A and B reach home at the (same/different) time
Ans: From the graph it is clear that both A and B reach their respective homes at the same time.
e. (A/B) overtakes (B/A) on the road (once/twice).
Ans: As B moves later than A and his/her speed is greater than that of A. From the graph, it is clear that B overtakes A only once on the road.
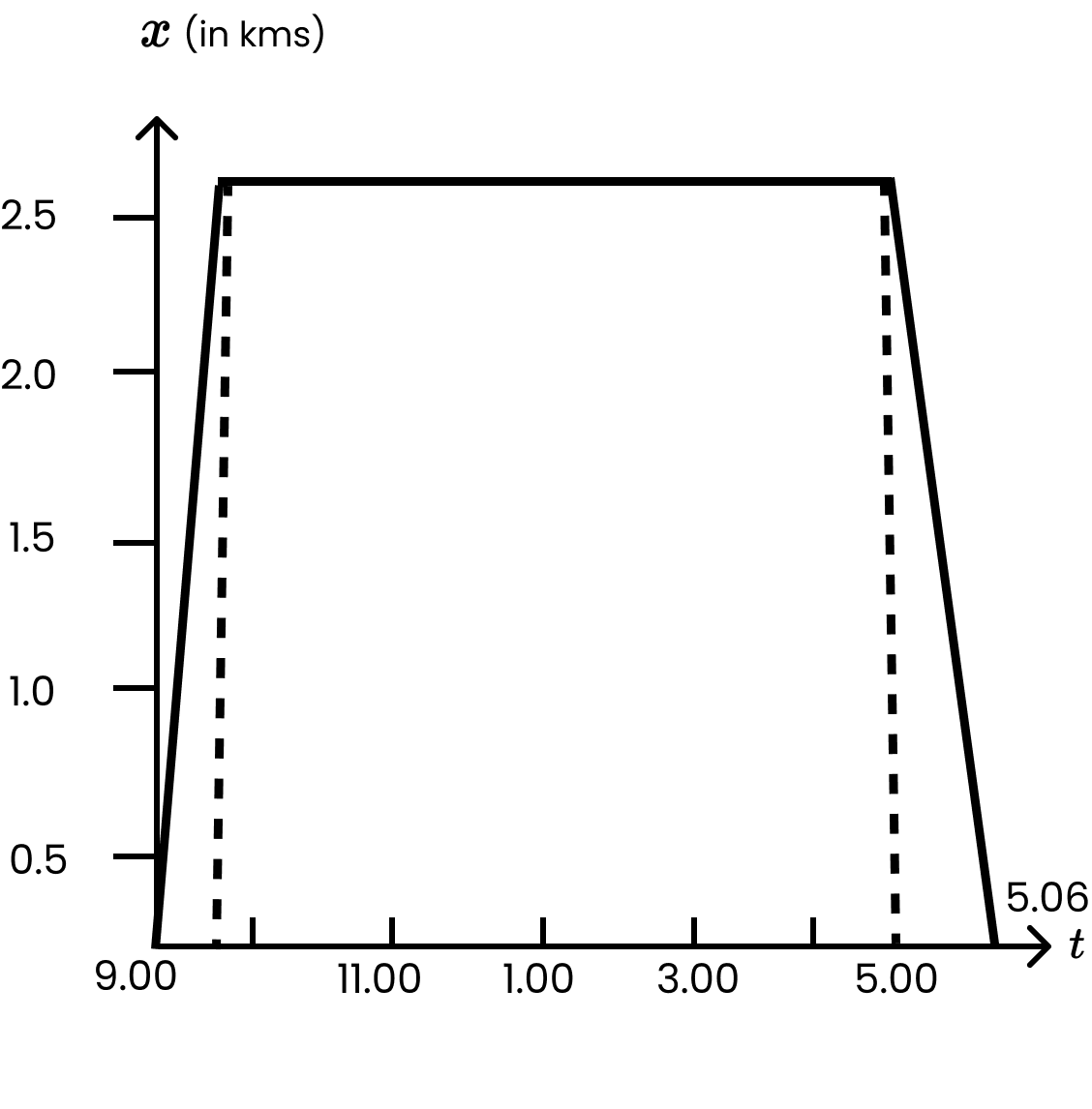
3. A woman starts from her home at 9.00 am, walks with a speed of \[5\text{ }km/hr\] on a straight road up to her office 2.5 km away, stays at the office up to 5.00 pm, and returns home by an auto with a speed of \[25\text{ }km/hr\]. Choose suitable scales and plot the x-t graph of her motion
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Speed of the woman \[=\text{ }5\text{ }km/h\].
Distance between her office and home \[=\text{ }2.5\text{ }km\].
\[Time\text{ }taken\text{ }=\text{ }Distance\text{ }/\text{ }Speed\]
\[=\text{ }2.5\text{ }/\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }0.5\text{ }h\text{ }=\text{ }30\text{ }min\]
It is given that she covers the same distance in the evening by an auto.
Now, \[speed\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }auto\text{ }=\text{ }25\text{ }km/h\].
\[Time\text{ }taken\text{ }=\text{ }Distance\text{ }/\text{ }Speed\]
\[=\text{ }2.5\text{ }/\text{ }25\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }/\text{ }10\text{ }=\text{ }0.1\text{ }h\text{ }=\text{ }6\text{ }min\]
The suitable x-t graph of the motion of the woman is shown in the given figure.
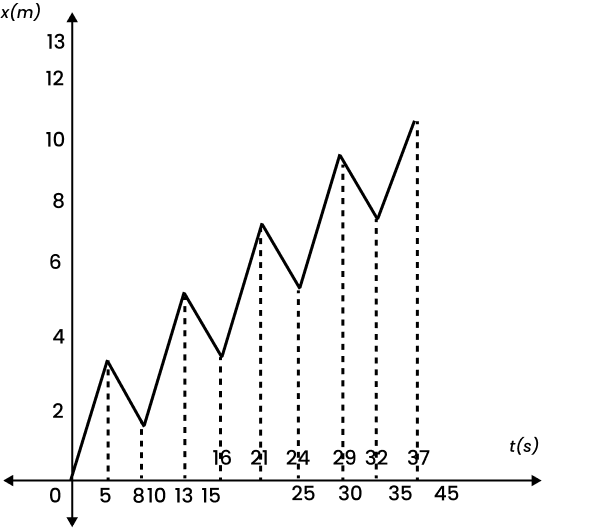
4. A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and requires 1 s. Plot the x-t graph of his motion. Determine graphically and otherwise how long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start.
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Distance covered with 1 step \[=\text{ }1\text{ }m\]
Time taken \[=\text{ }1\text{ }s\]
Time taken to move first \[5\text{ }m\] forward \[=\text{ }5\text{ }s\]
Time taken to move \[3\text{ }m\]backward \[=\text{ }3\text{ }s\]
\[Net\text{ }distance\text{ }covered\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }m\]
Net time taken to cover \[2\text{ }m\text{ }=\text{ }8\text{ }s\].
Hence,
Drunkard covers \[2\text{ }m\]in \[8\text{ }s\].
Drunkard covered \[4\text{ }m\]in \[16\text{ }s\].
Drunkard covered \[6\text{ }m\]in $2\text{4 s}$.
Drunkard covered \[8\text{ }m\]in \[32\text{ }s\].
In the next \[5\text{ }s\], the drunkard will cover a distance of \[5\text{ }m\] and a total distance of \[13\text{ }m\] and then fall into the pit.
Net time taken by the drunkard to cover $km$\[13\text{ }m\text{ }=\text{ }32\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }37\text{ }s\]
The x-t graph of the drunkard’s motion can be shown below:
5. A car moving along a straight highway with speed of \[126\text{ }km/hr\] is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. What is the retardation of the car (assumed uniform), and how long does it take for the car to stop?
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Initial velocity of the car is \[u=126\text{ }km/hr=35m/s\].
Final velocity of the car is $v=0km/hr$.
Distance covered by the car before coming to rest is \[200\text{ }m\].
Consider retardation produced in the car $=a$
From third equation of motion, ${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
Therefore, $-{{35}^{2}}=2a\left( 200 \right)$
$a=-3.0625m/{{s}^{2}}$
From first equation of motion, time (t) taken by the car to stop can be obtained as:
$v=u+at$
$0=35-\left( 3.065 \right)t$
$t=11.44s$
Hence, the retardation of the car (assumed uniform) is $3.0625m/{{s}^{2}}$, and it takes $11.44s$ for the car to stop.
6. A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of \[29.4\text{ }m/s\].
a. What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball?
Ans: Acceleration of the ball (which is actually acceleration due to gravity) always acts in the downward direction towards the centre of the Earth, irrespective of the direction of the motion of the ball.
b. What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion?
Ans: Acceleration due to gravity at a given place is constant and acts on the ball at all points (including the highest point) with a constant value i.e.,n\[g\text{ }=\text{ }9.8\text{ }m/{{s}^{2}}\]. At maximum height, velocity of the ball becomes zero.
c. Choose the x = 0 m and t = 0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically downward direction to be the positive direction of x-axis, and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward, and downward motion.
Ans: The sign of position is positive, sign of velocity is negative, and sign of acceleration is positive during upward motion. During downward motion, the signs of position, velocity, and acceleration are all positive.
d. To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hands? (Take \[g\text{ }=\text{ }9.8\text{ }m/{{s}^{2}}\] and neglect air resistance).
Ans: Initial velocity of the ball, \[u\text{ }=\text{ }29.4\text{ }m/s\].
Final velocity of the ball, \[v\text{ }=\text{ }0\] (At maximum height, the velocity of the ball becomes zero)
Acceleration, \[a=g\text{ }=9.8\text{ }m/{{s}^{2}}\]
From first equation of motion,
$v=u+at$
$0=-29.4+\left( 9.8 \right)t$
$t=\frac{29.4}{9.8}=3s$
\[Time\text{ }of\text{ }ascent\text{ }=\text{ }Time\text{ }of\text{ }descent\]
Hence, the total time taken by the ball to return to the player’s hands\[=\text{ }3\text{ }+\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }6\text{ }s\].
7. Read each statement below carefully and state with reasons and examples, if it is true or false; A particle in one-dimensional motion
a. with zero speed at an instant may have non-zero acceleration at that instant
Ans: The above statement is true. When an object is thrown vertically up in the air, its speed becomes zero at maximum height. It has acceleration equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g) Which acts in the downward direction at that point.
b. with zero speed may have non-zero velocity,
Ans: The above statement is false as speed is the magnitude of velocity. If speed is zero, the magnitude of velocity along with the velocity is zero.
c. with constant speed must have zero acceleration,
Ans: The above statement is true. If a car is moving on a straight highway with constant speed, it will have constant velocity. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. Hence, the acceleration of the car is also zero.
d. with a positive value of acceleration must be speeding up.
Ans: The above statement is false. If acceleration is positive and velocity is negative at the instant time is taken as origin. Thus, for all the time before velocity becomes zero, there is slowing down of the particle. This case occurs when a particle is projected upwards. This statement will be true when both velocity and acceleration are positive, at that instant time taken as origin. This case happens when a particle is moving with positive acceleration or falling vertically downwards from a height.
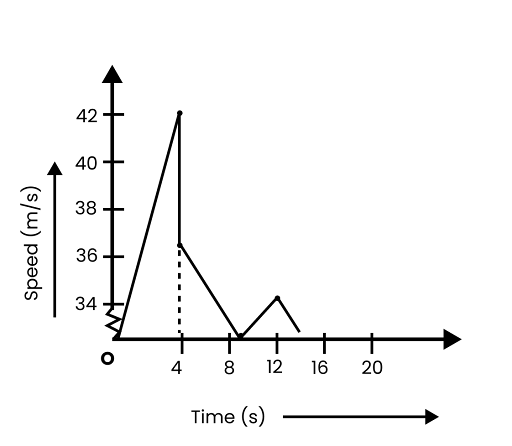
8. A ball is dropped from a height of 90 m on a floor. At each collision with the floor, the ball loses one tenth of its speed. Plot the speed-time graph of its motion between \[\mathbf{t}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{0}\text{ }\mathbf{to}\text{ }\mathbf{12}\text{ }\mathbf{s}\].
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Ball is dropped from a height is \[s\text{ }=\text{ }90\text{ }m\].
Initial velocity of the ball is \[u\text{ }=\text{ }0\].
Acceleration is $a=g=9.8m/{{s}^{2}}$.
Consider,
Final velocity of the ball to be v.
Using second equation of motion, time (t) taken by the ball to hit the ground can be obtained
as:
$s=ut+\left( 1/2 \right)a{{t}^{2}}$
$90=0+\left( 1/2 \right)9.8{{t}^{2}}$
$t=\sqrt{18.38}=4.29s$
Using, first equation of motion, final velocity is given as:
$v=u+at$
$v=0+9.8\left( 4.29 \right)=42.04m/s$
Rebound velocity of the ball is calculated as:
${{u}_{r}}=9v/10=9\left( \frac{42.04}{10} \right)=37.84m/s$
Time (t) taken by the ball to reach maximum height is obtained with the help of first equation of motion as:
$v={{u}_{r}}+at'$
$0=37.84+\left( -9.8 \right)t'$
$t'=37.84/9.8=3.86s$
Total time taken by the ball will be $t+t'=4.29+3.86=8.15s$.
As the time of ascent is equal to the time of descent, the ball takes \[3.86\text{ }s\] to strike back on the floor for the second time.
The velocity with which the ball rebounds from the floor will be ${{u}_{r}}=9v/10=9\left( \frac{37.84}{10} \right)=34.05m/s$
Total time taken by the ball for second rebound will be $t+t'=8.15+3.86=12.01s$
The speed-time graph of the ball is represented in the given figure as:
9. Explain clearly, with examples, the distinction between:
a. magnitude of displacement (sometimes called distance) over an interval of time, and the total length of path covered by a particle over the same interval;
Ans: The shortest distance (which is a straight line) between the initial and final positions of the particle gives the magnitude of displacement over an interval of time. The total path length of a particle is the actual path length covered by the particle in a given interval of time. For example, suppose a particle moves from point A to point B and then comes back to a point, C taking a total time t, as shown below. Then, the magnitude of displacement of the particle is AC.
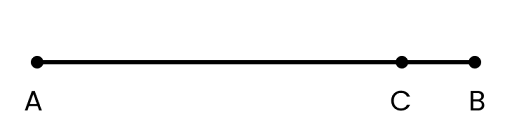
Whereas, total path length \[=\text{ }AB\text{ }+\text{ }BC\]
We know that the magnitude of displacement can never be greater than the total path length. But, in some cases, both quantities are equal to each other.
b. magnitude of average velocity over an interval of time, and the average speed over the same interval. Average speed of a particle over an interval of time is defined as the total path length divided by the time interval. Show in both (a) and (b) that the second quantity is either greater than or equal to the first. When is the equality sign true? (For simplicity, consider one-dimensional motion only).
Ans: We know that:
\[Magnitude\text{ }of\text{ }average\text{ }velocity\text{ }=\text{ }Magnitude\text{ }of\text{ }displacement\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }interval\]
Hence, for the given particle,
Average velocity $=AC/t$
\[Average\text{ }speed\text{ }=\text{ }Total\text{ }path\text{ }length\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }interval\]
\[=\left( AB+BC \right)/t\]
Since, \[AB+BC>AC\], average speed is greater than the magnitude of average velocity. The two quantities will be equal if the particle continues to move along a straight line.
10. A man walks on a straight road from his home to a market 2.5 km away with a speed of \[5\text{ }km/hr\]. Finding the market closed, he instantly turns and walks back home with a speed of \[7.5\text{ }km/hr\].What is the
(a) magnitude of average velocity, and
(b) average speed of the man over the interval of time (i) 0 to 30 min, (ii) 0 to 50 min, (iii) 0 to 40 min ? (Note: You will appreciate from this exercise why it is better to define average speed as total path length divided by time, and not as magnitude of average velocity. You would not like to tell the tired man on his return home that his average speed was zero)
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Time taken by the man to reach the market from home is ${{t}_{1}}=2.5/5=1/2hr=30\min $.
Time taken by the man to reach home from the market is ${{t}_{2}}=2.5/7.5=1/3hr=20\min $.
Total time taken in the whole journey \[=\text{ }30\text{ }+\text{ }20\text{ }=\text{ }50\text{ }min\].
0 to 30 min
\[Average\text{ }velocity\text{ }=\text{ }Displacement/Time\]
\[Average\text{ }speed\text{ }=\text{ }Distance/Time\]
0 to 50 min
\[Time\text{ }=\text{ }50\text{ }min\text{ }=\text{ }50/60\text{ }=\text{ }5/6\text{ }h\]
\[Net\text{ }displacement\text{ }=\text{ }0\]
\[Total\text{ }distance\text{ }=\text{ }2.5\text{ }+\text{ }2.5\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }km\]
\[Average\text{ }velocity\text{ }=\text{ }Displacement\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }=\text{ }0\]
\[Average\text{ }speed\text{ }=\text{ }Distance\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }=\text{ }5/\left( 5/6 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\text{ }km/h\]
0 to 40 min
\[Speed\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }man\text{ }=\text{ }7.5\text{ }km/h\]
\[Distance\text{ }travelled\text{ }in\text{ }first\text{ }30\text{ }min\text{ }=\text{ }2.5\text{ }km\]
Distance travelled by the man (from market to home) in the next 10 min
\[=\text{ }7.5\text{ }\times \text{ }10/60\text{ }=\text{ }1.25\text{ }km\]
\[Net\text{ }displacement\text{ }=\text{ }2.5\text{ }\text{ }1.25\text{ }=\text{ }1.25\text{ }km\]
\[Total\text{ }distance\text{ }travelled\text{ }=\text{ }2.5\text{ }+\text{ }1.25\text{ }=\text{ }3.75\text{ }km\]
\[Average\text{ }velocity\text{ }=\text{ }Displacement\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }=\text{ }1.25\text{ }/\text{ }\left( 40/60 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }1.875\text{ }km/h\]
\[Average\text{ }speed\text{ }=\text{ }Distance\text{ }/\text{ }Time\text{ }=\text{ }3.75\text{ }/\text{ }\left( 40/60 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }5.625\text{ }km/h\].
11. In Exercises 13 and 14, we have carefully distinguished between average speed and magnitude of average velocity. No such distinction is necessary when we consider instantaneous speed and magnitude of velocity. The instantaneous speed is always equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity. Why?
Ans: We know that instantaneous velocity is the first derivative of distance with respect to time.
Here, the time interval is so small that it is assumed that the particle does not change its direction of motion. Therefore, both the total path length and magnitude of displacement become equal in this interval of time. Thus, instantaneous speed is always equal to instantaneous velocity.
12. Look at the graphs (a) to (d) (figure) carefully and state, with reasons, which of these cannot possibly represent one-dimensional motion of a particle.
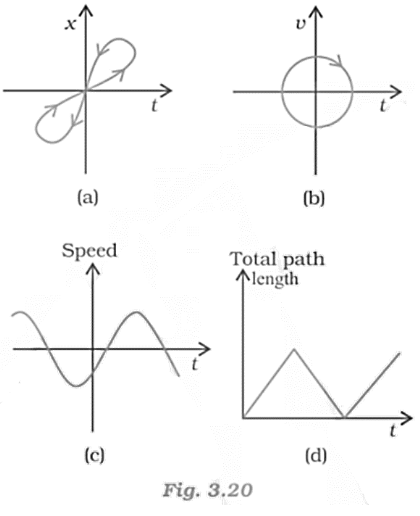
Ans:
a. Consider the x-t graph, given in fig (a). It does not represent the one-dimensional motion of the particle. This is because a particle cannot have two positions at the same instant of time.
b. Consider the x-t graph, given in fig (b). It does not represent the one-dimensional motion of the particle. This is because a particle can never have two values of velocity at the same instant of time.
c. Consider the x-t graph, given in fig (c). It does not represent the one-dimensional motion of the particle. This is because speed being a scalar quantity cannot be negative.
d. Consider the x-t graph, given in fig (d). It does not represent the one-dimensional motion of the particle. This is because the total path length travelled by the particle cannot decrease with time.
13. Figure shows the x-t plot of the one-dimensional motion of a particle. Is it correct to say from the graph that the particle moves in a straight line for $t<0$ and on a parabolic path for $t>0$? If not, suggest a suitable physical context for this graph.
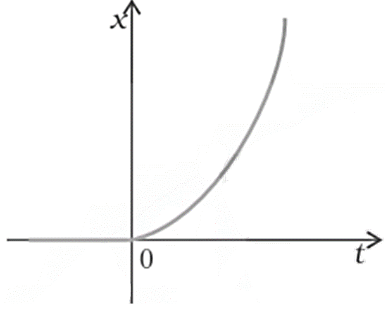
Ans: No, this is because the x-t graph does not represent the trajectory of the path followed by a particle. Also from the graph, it is clear that at \[t=0,\text{ }x=0\].
14. A police van moving on a highway with a speed of \[30\text{ }km/hr\] fires a bullet at a thief’s car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of \[192\text{ }km/hr\]. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is \[150\text{ }m/s\], with what speed does the bullet hit the thief’s car? (Note: Obtain that speed which is relevant for damaging the thief’s car).
Ans: In the above question it is given that:
Speed of the police van is \[{{v}_{p}}=30\text{ }km/hr=8.33m/s\].
Muzzle speed of the bullet is \[{{v}_{b}}=150\text{ }m/s\].
Speed of the thief’s car is \[{{v}_{t}}=192\text{ }km/hr=53.33m/s\].
As the bullet is fired from a moving van, its resultant speed will be: $150+8.33=158.33m/s$.
Since both the vehicles are moving in the same direction, the velocity with which the bullet hits the thief’s car can be obtained as:
${{v}_{bt}}={{v}_{b}}-{{v}_{t}}=158.33-53.33=105m/s$
15. Suggest a suitable physical situation for each of the following graphs (figure):
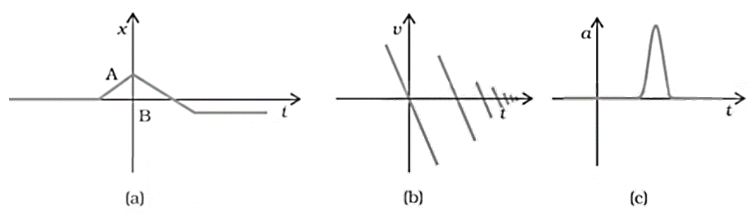
Ans: Consider fig 3.22 given in the question:
a. From the x-t graph given it is clear that initially a body was at rest. Further, its velocity increases with time and attains an instantaneous constant value. The velocity then reduces to zero with an increase in time. Further, its velocity increases with time in the opposite direction and acquires a constant value. A similar physical situation arises when a football (initially kept at rest) is kicked and gets rebound from a rigid wall so that its speed gets reduced. Then, it passes from the player who has kicked it and ultimately stops after sometime.
b. From the given v-t graph it is clear that the sign of velocity changes and its magnitude decreases with a passage of time. This type of situation arises when a ball is dropped on the hard floor from a height. It strikes the floor with some velocity and upon rebound, its velocity decreases by a factor. This continues till the velocity of the ball eventually becomes zero.
c. From the given a-t graph it is clear that initially the body is moving with a certain uniform velocity. Its acceleration increases for a short interval of time, which again drops to zero. This shows that the body again starts moving with the same constant velocity. This type of physical situation arises when a hammer moving with a uniform velocity strikes a nail.
16. Figure gives the x-t plot of a particle executing one-dimensional simple harmonic motion.
(You will learn about this motion in more detail in Chapter14). Give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration variables of the particle at $t=0.3s,1.2s,-1.2s$.
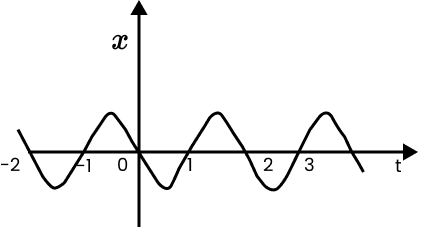
Ans: Negative, Negative, Positive
Positive, Positive, Negative
Negative, Positive, Positive
When a particle executes simple harmonic motion (SHM), acceleration (a) is given by the relation: $a=-{{\omega }^{2}}x$
Where,
$\omega $ is the angular frequency ...
i. \[~t\text{ }=\text{ }0.3\text{ }s\]
For this time interval, x is negative. Hence, the slope of the x-t plot will be negative. Thus, both position and velocity are negative. However, using equation (i), acceleration of the particle will be positive.
ii. \[~t\text{ }=1.2s\]
For this time interval, x is positive. Hence, the slope of the x-t plot will be positive. Thus, both position and velocity are positive. However, using equation (i), acceleration of the particle comes to be negative.
iii. \[\text{t }=-1.2s\]
For this time interval, x is negative. Hence, the slope of the x-t plot will be negative. Thus, both x and t are negative, the velocity comes to be positive. From equation (i), it can be interpreted that the acceleration of the particle will be positive.
17. Figure gives the x-t plot of a particle in one-dimensional motion. Three different equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average speed greatest, and in which is it the least? Give the sign of average velocity for each interval.
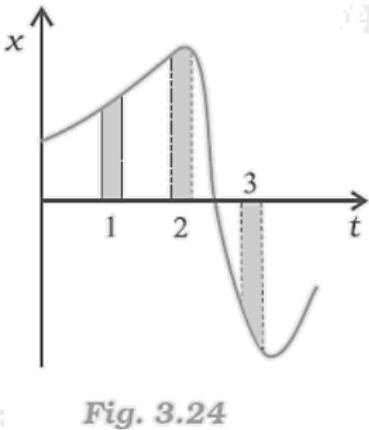
Ans: The average speed is greatest in interval 3 and least in interval 2. It is positive in intervals 1 & 2 and negative in interval 3.
The average speed of a particle shown in the x-t graph is given by the slope of the graph in a particular interval of time.
From the graph it is clear that the slope is maximum and minimum restively in intervals 3 and 2 respectively. Thus, the average speed of the particle is the greatest in interval 3 and is the least in interval 2. The sign of average velocity is positive in both intervals 1 and 2 as the slope is positive in these intervals. However, it is negative in interval 3 because the slope is negative in this interval.
18. Figure gives a speed-time graph of a particle in motion along a constant direction. Three equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average acceleration greatest in magnitude? In which interval is the average speed greatest? Choosing the positive direction as the constant direction of motion, give the signs of v and a in the three intervals. What are the accelerations at the points A, B, C and D?
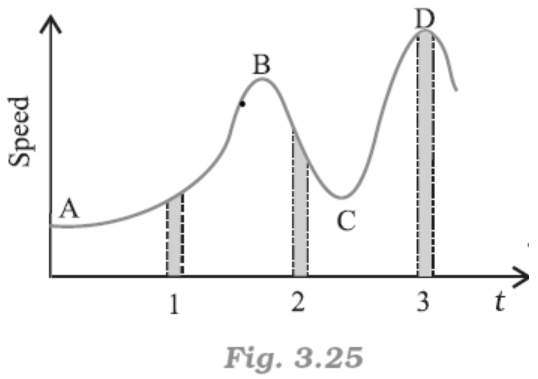
Ans: From the graph given in the question,
Average acceleration is greatest in interval \[2\].
Average speed is greatest in intervals of $3$.
v is positive for intervals \[1,\text{ }2\], and $3$.
a is positive for intervals $1$ and $3$ and negative in interval $2$
\[a\text{ }=\text{ }0\] at A, B, C, D
Acceleration is calculated as the slope of the speed-time graph. In the given case, it is given by the slope of the speed-time graph within the given interval of time.
As the slope of the given speed-time graph is maximum in interval \[2\], average acceleration will be the greatest in this interval.
From the time-axis, height of the curve gives the average speed of the particle. It is clear that the height is the greatest in interval 3. Thus, average speed of the particle is the greatest in the interval 3.
For interval 1:
The slope of the speed-time graph is positive. Hence, acceleration is positive. Similarly, the speed of the particle is positive in this interval.
In interval 2:
As slope of the speed-time graph is negative, acceleration is negative in this interval. However, speed is positive because it is a scalar quantity.
In interval 3:
As the slope of the speed-time graph is zero, acceleration is zero in this interval.
However, here the particle acquires some uniform speed. It is positive in this interval.
Points A, B, C, and D are all parallel to the time-axis. Thus, the slope is zero at these points.
Therefore, at points A, B, C, and D, acceleration of the particle is zero.
Motion in a Straight Line Chapter Summary - Class 11 NCERT Solutions
An object is said to be in motion if its position changes with time. The position of the object can be specified with reference to a conveniently chosen origin. For motion in a straight fine. position to the right of the origin is taken as positive and to the left as negative.
Path length is defined as the total length of the path traversed by an object.
Displacement is the change in position: $\Delta x=x_{2}-x_{1} $ Path length is greater or equal to the magnitude of the displacement between the same points.
An object is said to be in uniform motion in a straight line if its displacement is equal in equal intervals of time. Otherwise, the motion is said to be nonuniform
Average velocity is the displacement divided by the time Interval in which the displacement occurs: $ v\bar{}=\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}
On an x-t graph. The average velocity over a time Interval is the slope of the line connecting the initial and final positions corresponding to that interval.
Average Speed is the ratio of total path length traversed and the corresponding time Interval.
Instantaneous velocity or simply velocity is defined as the limit of the average velocity as the time interval $\Delta t$ becomes infinitesimally small
$v=\lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}v\bar{}=\lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}=\frac{dx}{dt}$The velocity at a particular instant is equal to the slope of the tangent drawn on position-time graph at that instant.
Average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the time interval during which the change occurs: $a\vec{}=\frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}$
Instantaneous acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the time interval at goes to zero:
$a=\lim_{\Delta \rightarrow t}a\vec{}=\lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}\frac{\Delta t}{\Delta v}=\frac{dv}{dt}$The acceleration of an object at a particular time is the slope of the velocity-time graph at that instant of time. For uniform motion. acceleration is zero and the x-t graph is a straight line inclined to the time axis and the v-t graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis. For motion with uniform acceleration. x - t graph is a parabola while the v-t graph is a straight line inclined to the time axis.
The area under the velocity-time curve between times t1 and t2 is equal to the displacement of the object during that interval of time.
For objects in uniformly accelerated rectilinear motion. the five quantities, displacement x, time taken t. Initial velocity v0, final velocity v and acceleration a are related by a set of simple equations called kinematic equations of motion:
v=v0+at
x=v0t+$\frac{1}{2}$at2
v2=$v_{0}^{2}$+2ax
For Uniform Motion
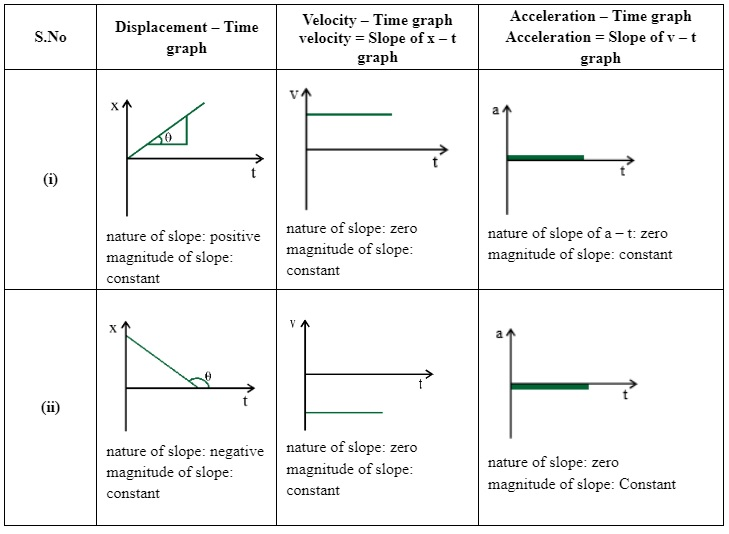
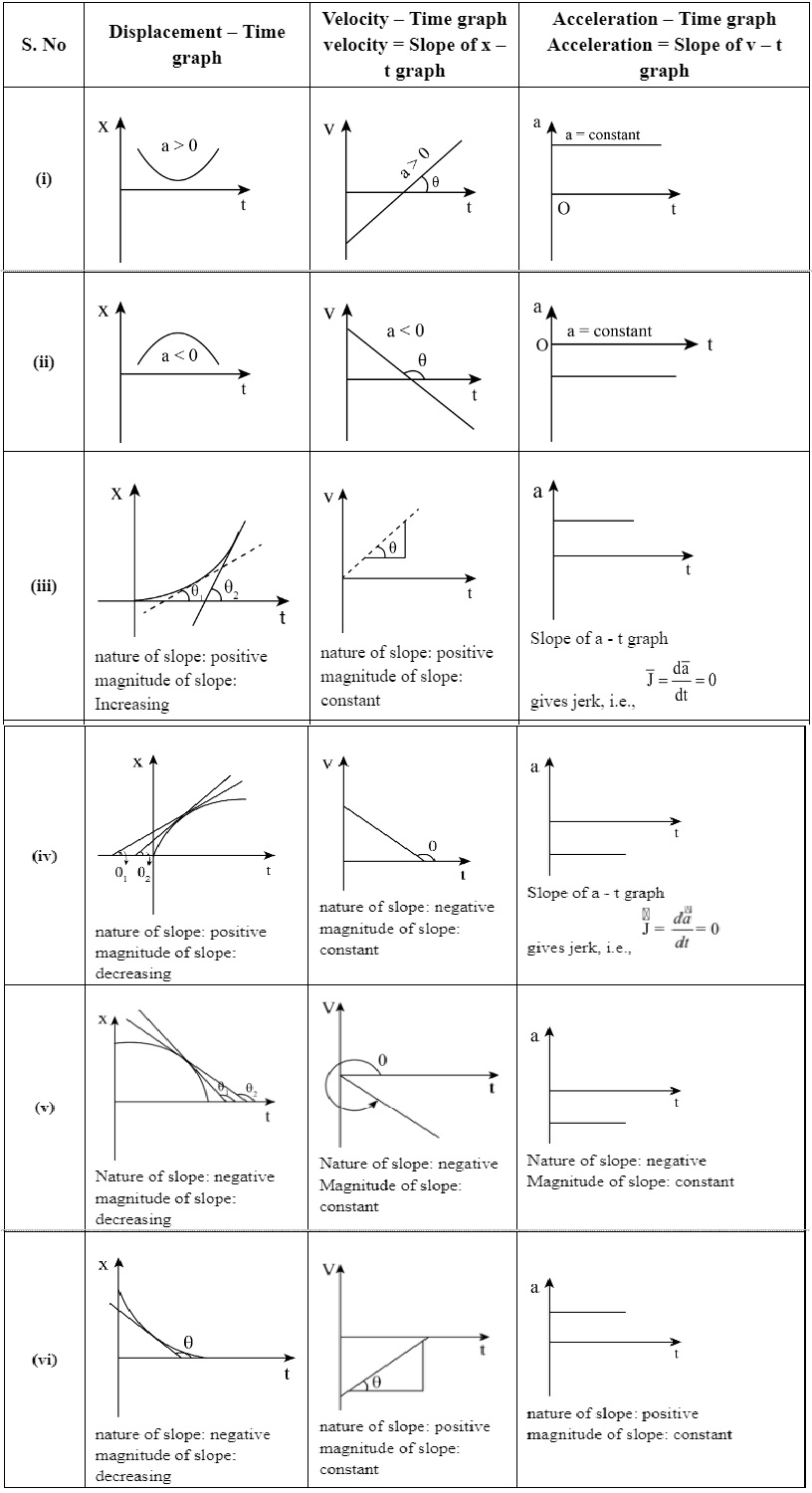
For Non-Uniform Motion
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Motion in a Straight Line | 3.2 Position, Path Length and Displacement |
3.3 Average Velocity and Average Speed | |
3.7 Relative Velocity | |
Exercises 3.5, 3.7–3.9 and 3.23–3.28 | |
Appendix 3.1 |
Conclusion
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Exercise Solutions on Motion In A Straight Line provided by Vedantu are comprehensive, and helps students understand motion and the different kinds of motion. This chapter explores different types of motion, including uniform motion, non-uniform motion, and uniformly accelerated motion. In Ch 2 physics class 11 ncert solutions we learn how to solve problems involving these concepts using various equations relating to distance, time, speed, velocity, and acceleration. These concepts are essential for mastering the topic and are often tested in exams. From previous year's question papers, typically around 2–3 questions are asked from this chapter. These questions test students' grasp of theoretical concepts as well as their problem-solving skills.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 2
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 2 Motion in a Straight Line |
1 | |
2 | |
3 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S. No | NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter-wise List |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | Chapter 6 - Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Solutions |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 |
CBSE Class 11 Physics Study Materials
S.No. | Study Materials for Class 11 Physics |
|---|---|
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in a Straight Line (2025-26)
1. What is motion in straight line class 11?
Motion in a straight line refers to the movement of an object along a single dimension where the particle's position can be described by a single coordinate. This type of motion involves concepts like displacement, velocity, acceleration, and equations of motion, forming the foundation of kinematics in physics.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for motion in a straight line help students understand kinematics concepts?
NCERT Solutions provide step-by-step explanations for all textbook problems, breaking down complex kinematic equations and graph interpretations into manageable parts. Students often struggle with connecting mathematical formulas to real-world motion scenarios.
Students can solve similar problems independently after reviewing solutions.
These comprehensive solutions bridge the gap between theoretical concepts and practical problem-solving skills essential for physics mastery.
3. What are the 4 formulas for linear motion?
The four kinematic equations for uniform acceleration are: v = u + at (velocity-time relation), s = ut + ½at² (position-time relation), v² = u² + 2as (velocity-displacement relation), and s = (u + v)t/2 (average velocity relation). These equations connect displacement, initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration, and time.
4. Can students access motion in a straight line class 11 pdf materials for offline study?
Students can download comprehensive study materials including NCERT Solutions, chapter notes, and practice questions in PDF format from Vedantu for convenient offline access.
5. What does uniform acceleration mean in straight line motion?
Uniform acceleration occurs when an object's velocity changes by equal amounts in equal time intervals. The acceleration remains constant throughout the motion, making it possible to use kinematic equations. Examples include free fall under gravity and motion of vehicles with constant throttle.
6. How do velocity-time graphs represent different types of motion?
Velocity-time graphs visually represent motion characteristics where the slope indicates acceleration and the area under the curve represents displacement. Graphical interpretation helps students understand motion patterns more intuitively than equations alone.
7. What is relative velocity in one-dimensional motion?
Relative velocity is the velocity of one object as observed from another moving object. In straight line motion, it's calculated as the vector difference of individual velocities. When objects move in the same direction, relative velocity decreases; when opposite, it increases proportionally.
8. Why are sign conventions important in kinematic problems?
Sign conventions establish consistent directional references, typically choosing positive direction as rightward or upward motion and negative for opposite directions. Incorrect sign usage leads to wrong numerical answers and conceptual confusion in physics problems.
9. What are common examples of straight line motion in daily life?
Examples of straight line motion include a car moving on a straight road, a ball thrown vertically upward, an elevator moving between floors, a train on straight tracks, and objects in free fall.
10. How do class 11 Physics motion in a straight line NCERT solutions address numerical problems?
NCERT Solutions provide systematic approaches to numerical problems, showing proper formula selection, unit conversions, and mathematical calculations with clear reasoning. Numerical proficiency builds confidence and prepares students for competitive examinations requiring quick problem-solving skills.

























