Physical Features Of India Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science Geography Contemporary India Chapter 2 Physical Features Of India (2025-26)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science Geography Contemporary India Chapter 2 Physical Features Of India (2025-26)
1. What does Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of India explain in NCERT?
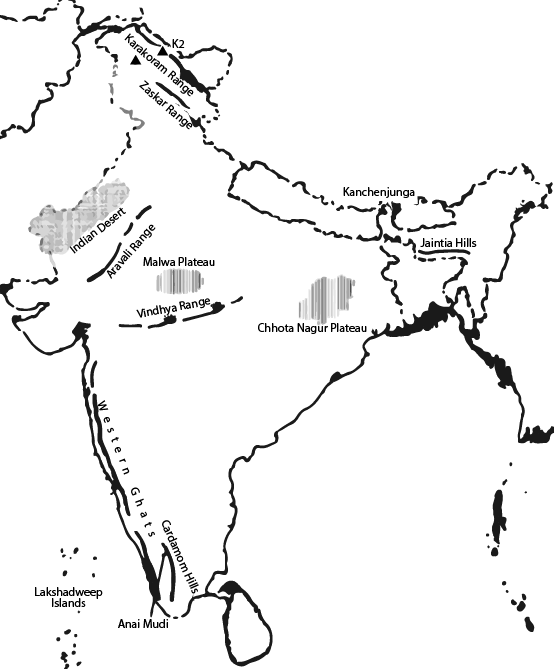
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 – Physical Features of India explains the major landforms of the country, such as the Himalayan Mountains, Northern Plains, Peninsular Plateau, Indian Desert, Coastal Plains, and Islands. On Vedantu, NCERT Solutions explain these features exactly as described in the NCERT textbook.
2. What types of questions can students expect from Physical Features of India Class 9?
From physical features of India Class 9, students can expect descriptive questions, short notes, and comparison-based questions related to India’s physiographic divisions. Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions help students understand how such textbook questions are answered as per NCERT standards.
3. Are Physical Features of India Class 9 questions and answers strictly NCERT-based?
Yes, physical features of India Class 9 questions and answers available on Vedantu are fully based on the NCERT textbook. The answers follow NCERT definitions, maps, and explanations without adding extra reference material.
4. Which physiographic divisions are covered in Class 9 Geography Chapter 2?
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 covers six major physiographic divisions of India:
The Himalayan Mountains
The Northern Plains
The Peninsular Plateau
The Indian Desert
The Coastal Plains
The Islands
All these topics are clearly explained in Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions.
5. How do NCERT Solutions help in answering Geography Class 9 Chapter 2 questions?
Geography Class 9 Chapter 2 question answers help students learn how to write clear, structured answers using NCERT language. On Vedantu, solutions follow the textbook approach, which is useful for CBSE exam preparation.
6. Do Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions include all exercise questions of Chapter 2?
Yes, Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 include complete answers to all in-text and exercise questions given in the NCERT textbook, without skipping any question.
7. How are terms like bhabar and plains explained in NCERT Solutions?
In Class 9 Geography Chapter 2, terms such as bhabar, plains, plateaus, and deserts are explained clearly using NCERT descriptions. Vedantu presents these explanations in a student-friendly manner while staying textbook-focused.
8. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 exam preparation?
Yes, practising NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 on Vedantu is sufficient for school exams, as CBSE questions are framed directly from the NCERT textbook.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video