
A cube of edge ‘k’ is divided into ‘n’ equal cubes. Determine the edge of the new cube.
A. $ \sqrt {nk} $
B. $ \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} $
C. $ \sqrt[3]{{nk}} $
D. $ \dfrac{{\sqrt[3]{n}}}{k} $
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Let the edge of each of the smaller cubes is a. Find the volume of the larger cube with edge k and volume of the smaller cube with edge a. The sum of volumes of all the n smaller cubes will be equal to the volume of the larger cube. Equate the volume of the larger cube with the volume of n smaller cubes and find the length of edge of the new cube in terms of k and n.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Volume of a cube is $ {l^3} $ , where l is the length of the edge of the cube.
We are given that a cube of edge ‘k’ is divided into ‘n’ equal cubes.
We have to determine the edge of the new cube.
Let the edge of the new cube is a.
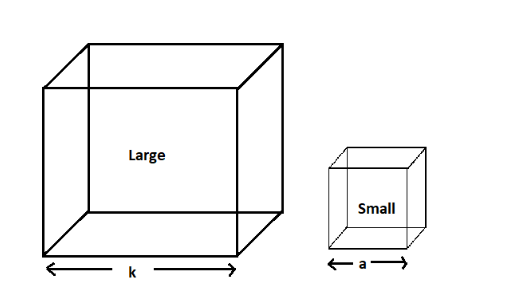
Volume of the larger cube with edge k is $ k \times k \times k = {k^3}cube.units $
Volume of each of the smaller cubes with edge a is $ a \times a \times a = {a^3}cube.units $
The larger cube is divided into n smaller cubes.
Therefore, the volume of all the smaller cubes must sum up to the volume of the larger cube.
$
\Rightarrow {a^3} + {a^3} + {a^3} + ......ntimes = {k^3} \\
\Rightarrow n \times {a^3} = {k^3} \\
\Rightarrow {a^3} = \dfrac{{{k^3}}}{n} \\
\Rightarrow a = \sqrt[3]{{\dfrac{{{k^3}}}{n}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt[3]{{{k^3}}}}}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} \\
\therefore a = \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} \\
$
Therefore, the length of edge of the new cube is $ \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} $
The correct answer is Option B, $ \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: A cube is a three dimensional shape with 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. A cuboid is also a three dimensional shape which has 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. But all the edges are equal in a cube but not in a cuboid. The volumes of cube and cuboid are different. So do not confuse the formula of volume of cube with volume of cuboid. And when a larger cube is divided into n smaller cubes then each smaller cube will have the same edge length, same volume and same area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Volume of a cube is $ {l^3} $ , where l is the length of the edge of the cube.
We are given that a cube of edge ‘k’ is divided into ‘n’ equal cubes.
We have to determine the edge of the new cube.
Let the edge of the new cube is a.

Volume of the larger cube with edge k is $ k \times k \times k = {k^3}cube.units $
Volume of each of the smaller cubes with edge a is $ a \times a \times a = {a^3}cube.units $
The larger cube is divided into n smaller cubes.
Therefore, the volume of all the smaller cubes must sum up to the volume of the larger cube.
$
\Rightarrow {a^3} + {a^3} + {a^3} + ......ntimes = {k^3} \\
\Rightarrow n \times {a^3} = {k^3} \\
\Rightarrow {a^3} = \dfrac{{{k^3}}}{n} \\
\Rightarrow a = \sqrt[3]{{\dfrac{{{k^3}}}{n}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt[3]{{{k^3}}}}}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} \\
\therefore a = \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} \\
$
Therefore, the length of edge of the new cube is $ \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} $
The correct answer is Option B, $ \dfrac{k}{{\sqrt[3]{n}}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: A cube is a three dimensional shape with 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. A cuboid is also a three dimensional shape which has 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. But all the edges are equal in a cube but not in a cuboid. The volumes of cube and cuboid are different. So do not confuse the formula of volume of cube with volume of cuboid. And when a larger cube is divided into n smaller cubes then each smaller cube will have the same edge length, same volume and same area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




