
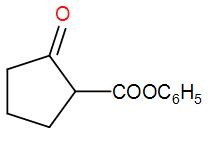
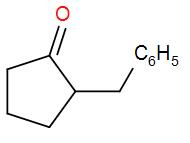
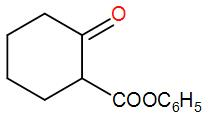
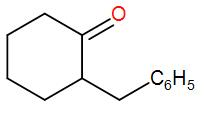
A Dieckmann condensation of diethyl adipate was carried out by heating with sodium ethoxide. One equivalent of benzyl bromide was added, and the resulting mixture was then refluxed in 5% HCl for several hours and extracted with ether. What compound has been prepared by this procedure?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: This is an Intramolecular Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution. In Dieckmann condensation the products are cyclic \[\beta \] – ketoesters and the favoured formation is of the more stable 5 or 6 membered rings. The acyl carbon has a double bond oxygen and an alkyl group, it is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from oxoacids including inorganic acids.
Complete step by step answer:
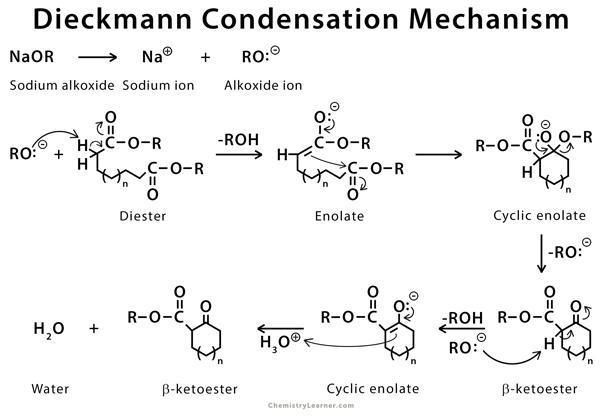
- We can use diester compounds to give an intramolecular Claisen condensation which is also known as Diekmann condensation.
- We use this reaction to form a carbon-carbon bond between two tethered ester groups using an alkoxide base in alcohol to make a cyclic \[\beta \]-keto ester.
- One ester group of the reactant must have an $\alpha $-hydrogen which is abstracted by the base to form an enolate and alcohol.
- The enolate ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of the other ester molecule, to regenerate the base an -OR group is released, and the final product formed is a \[\beta \] – keto ester.
- Now for better understanding let’s see the reaction mechanism:
Sodium ethoxide removes the alpha proton to form enolate ion
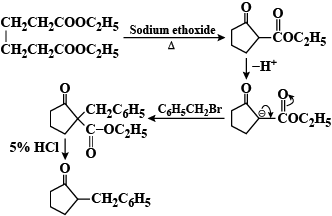
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
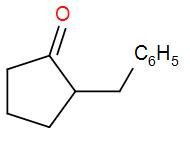
Note: -The most used reagent is alkoxide in Diekmann condensation.
-Remember that enolate ions are good nucleophiles and ester carbonyl carbon atoms are electrophilic.
- Nucleophiles are those reactants which are electron rich and provide a pair of electrons but on contrary electrophiles are electron deficient and accept a pair of electrons to achieve stability.
Complete step by step answer:
- We can use diester compounds to give an intramolecular Claisen condensation which is also known as Diekmann condensation.
- We use this reaction to form a carbon-carbon bond between two tethered ester groups using an alkoxide base in alcohol to make a cyclic \[\beta \]-keto ester.
- One ester group of the reactant must have an $\alpha $-hydrogen which is abstracted by the base to form an enolate and alcohol.
- The enolate ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of the other ester molecule, to regenerate the base an -OR group is released, and the final product formed is a \[\beta \] – keto ester.
- Now for better understanding let’s see the reaction mechanism:
Sodium ethoxide removes the alpha proton to form enolate ion


So, the correct answer is “Option B”.

Note: -The most used reagent is alkoxide in Diekmann condensation.
-Remember that enolate ions are good nucleophiles and ester carbonyl carbon atoms are electrophilic.
- Nucleophiles are those reactants which are electron rich and provide a pair of electrons but on contrary electrophiles are electron deficient and accept a pair of electrons to achieve stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




