
A) Draw a typical illuminated p-n junction solar cell.
B) LED converts ______ energy to light.
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: For solving part A of the question, you could give a brief description about the solar cell and then draw the diagram. Also, give a short description about what happens when a solar cell is illuminated. For the B part, you could recall the working of a LED and then determine what helps it to glow to get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A) Let us first give a brief description on the structure and working of a solar cell. We have a p-type silicon wafer on which a small layer of n-type silicon is grown. We have a metal finger electrode deposited on top of the n-Si layer which acts as the front contact. The other side of the p-type is coated with metal and it acts as the back contact. So, basically the structure of typical p-n junction solar cell is like this,
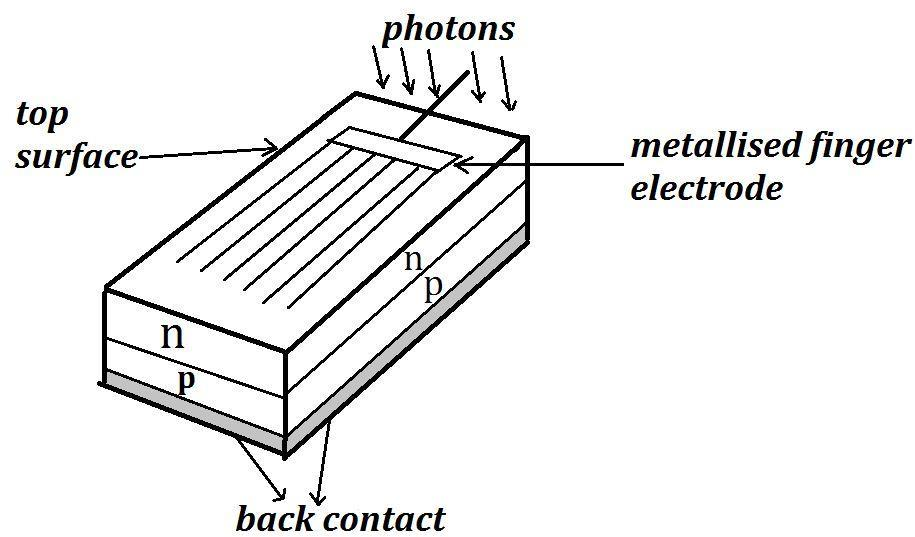
When light falls on the solar cell it generates an emf as the result of 3 processes, namely, generation, separation and collection. Light with $h\nu > {{E}_{g}}$ generates electron-hole pair close to the junction. Electrons move to n-side and holes move to p-side due to the electric field of the depletion region. The front contact collects the electrons reaching n-side and back contact collects holes reaching the p-side resulting in n-side being negative and p-side being positive giving rise to photo-voltage.
When we connect an extra load to the solar cell, photocurrent ${{I}_{L}}$ flows through the load. A typical illuminated p-n junction solar cell is represented as,
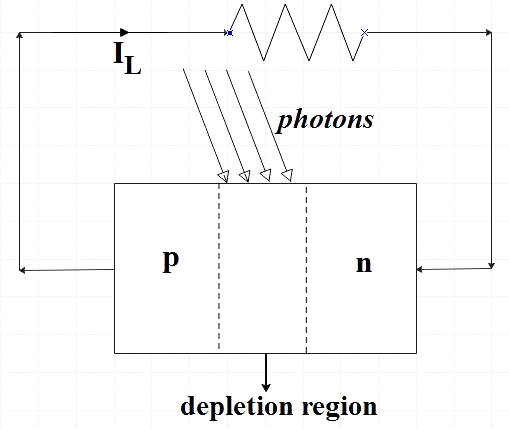
Since the solar cell supplies current to the load, the I-V characteristics is given by,
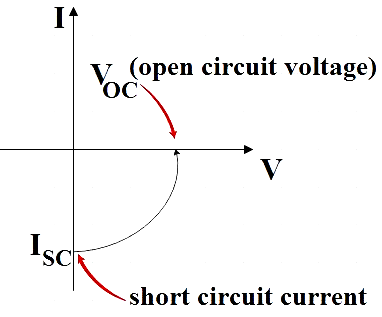
B) LED converts electrical energy to light.
Let us look at what happens for an LED light to glow. The light emitting diode (LED) is a heavily doped p-n junction. When the diode is forward biased, electrons are sent from $n\to p$ and holes are sent from $p\to n$, resulting in the increase in concentration of minority carriers at the junction boundary. These excess minority carriers recombine with majority charge carriers near the junction. This recombination results in energy release in the form of photons. Since all these processes occur under biased conditions, we could say that LED converts electrical energy to light.
Note: In questions like this where you are asked to draw a diagram, adding a brief description about the same makes your answer look perfect. Give importance to the details in such questions, that is, for example in this question make sure that your diagram is that of a typical ‘illuminated’ p-n junction solar cell. In the second part, though it is a fill in the blank question, adding a brief justification to your answer makes your answer complete.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A) Let us first give a brief description on the structure and working of a solar cell. We have a p-type silicon wafer on which a small layer of n-type silicon is grown. We have a metal finger electrode deposited on top of the n-Si layer which acts as the front contact. The other side of the p-type is coated with metal and it acts as the back contact. So, basically the structure of typical p-n junction solar cell is like this,

When light falls on the solar cell it generates an emf as the result of 3 processes, namely, generation, separation and collection. Light with $h\nu > {{E}_{g}}$ generates electron-hole pair close to the junction. Electrons move to n-side and holes move to p-side due to the electric field of the depletion region. The front contact collects the electrons reaching n-side and back contact collects holes reaching the p-side resulting in n-side being negative and p-side being positive giving rise to photo-voltage.
When we connect an extra load to the solar cell, photocurrent ${{I}_{L}}$ flows through the load. A typical illuminated p-n junction solar cell is represented as,

Since the solar cell supplies current to the load, the I-V characteristics is given by,

B) LED converts electrical energy to light.
Let us look at what happens for an LED light to glow. The light emitting diode (LED) is a heavily doped p-n junction. When the diode is forward biased, electrons are sent from $n\to p$ and holes are sent from $p\to n$, resulting in the increase in concentration of minority carriers at the junction boundary. These excess minority carriers recombine with majority charge carriers near the junction. This recombination results in energy release in the form of photons. Since all these processes occur under biased conditions, we could say that LED converts electrical energy to light.
Note: In questions like this where you are asked to draw a diagram, adding a brief description about the same makes your answer look perfect. Give importance to the details in such questions, that is, for example in this question make sure that your diagram is that of a typical ‘illuminated’ p-n junction solar cell. In the second part, though it is a fill in the blank question, adding a brief justification to your answer makes your answer complete.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




