
Acetanilide when treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives
\[1\]) o-Bromoacetanilide
\[2\]) N-Bromoacetanilide
\[3\]) p-Bromoacetanilide
\[4\]) m-Bromoacetanilide
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: We need to know that in organic chemistry benzene is one of the important compounds. It is one of the aromatic compounds. The molecular formula of benzene is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]. Aniline is one of the derivatives of benzene. The molecular formula of aniline is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_7}\]. The molecular formula of Acetanilide is \[{{\text{C}}_8}{\text{NO}}{{\text{H}}_9}\].
Complete answer:
The structural formula of aniline is

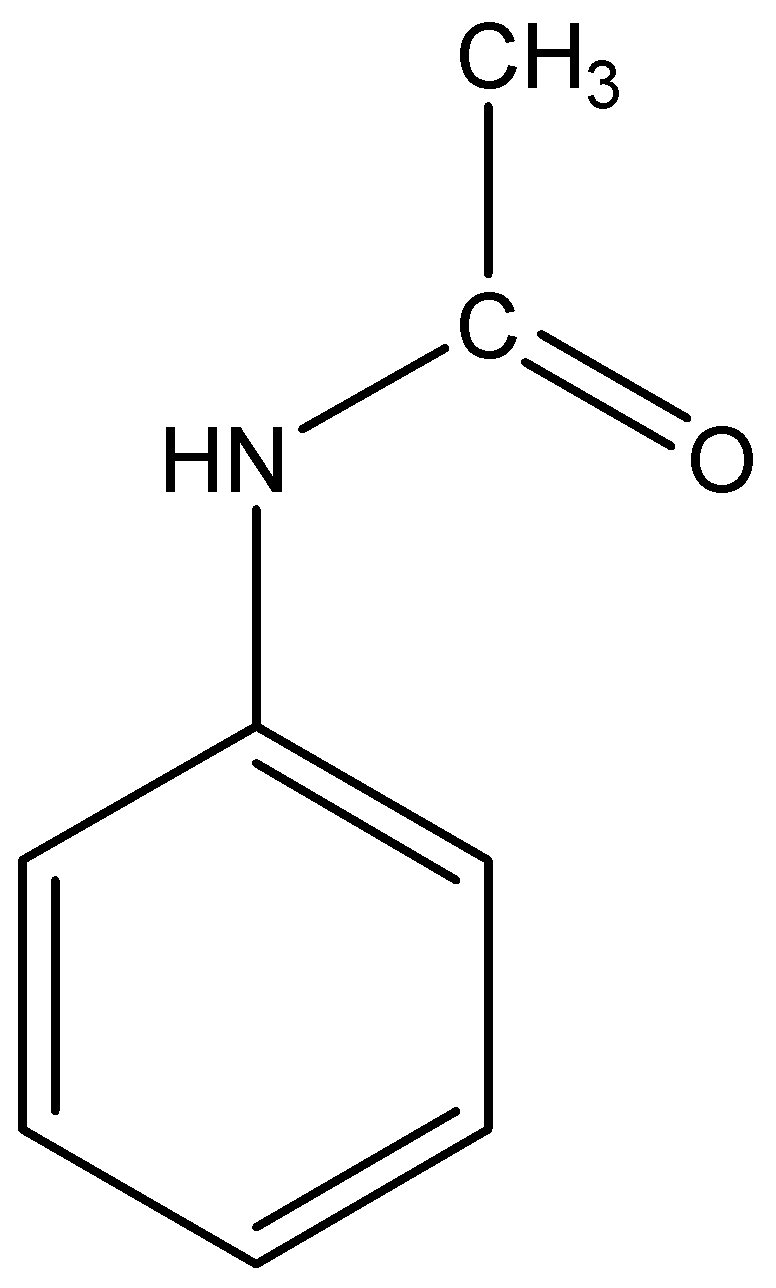
The structural formula of acetanilide is
Aniline when treated with bromine in acetic acid or water gives a product of 2,4,6- tribromo aniline. It is white precipitate.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,
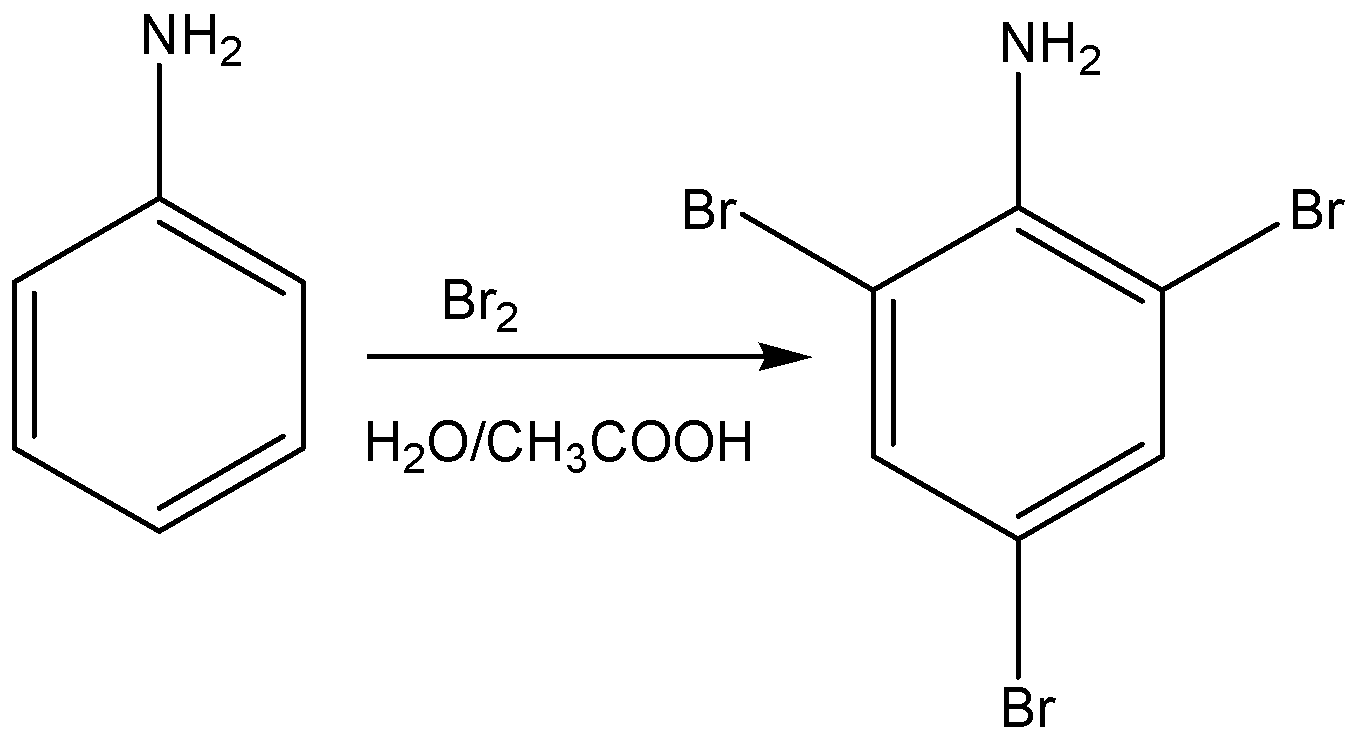
The structural formula of 2,4,6- tribromo aniline is

But we want certain position bromination means we first do acylated aniline to get acetanilide. Acetanilide is treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide. This p-Bromoacetanilide undergoes hydrolysis to give p-Bromoaniline.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,

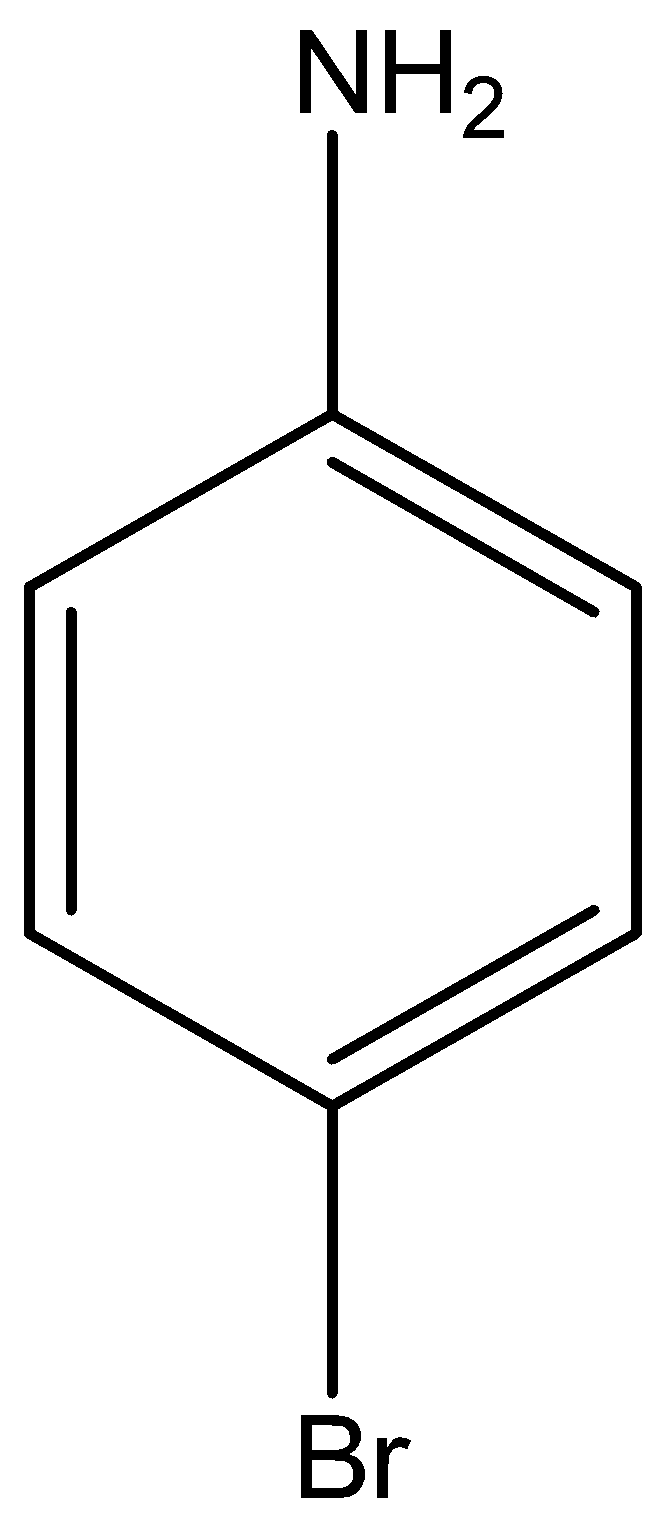
The structural formula of p-Bromo aniline is
Acetanilide is treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,
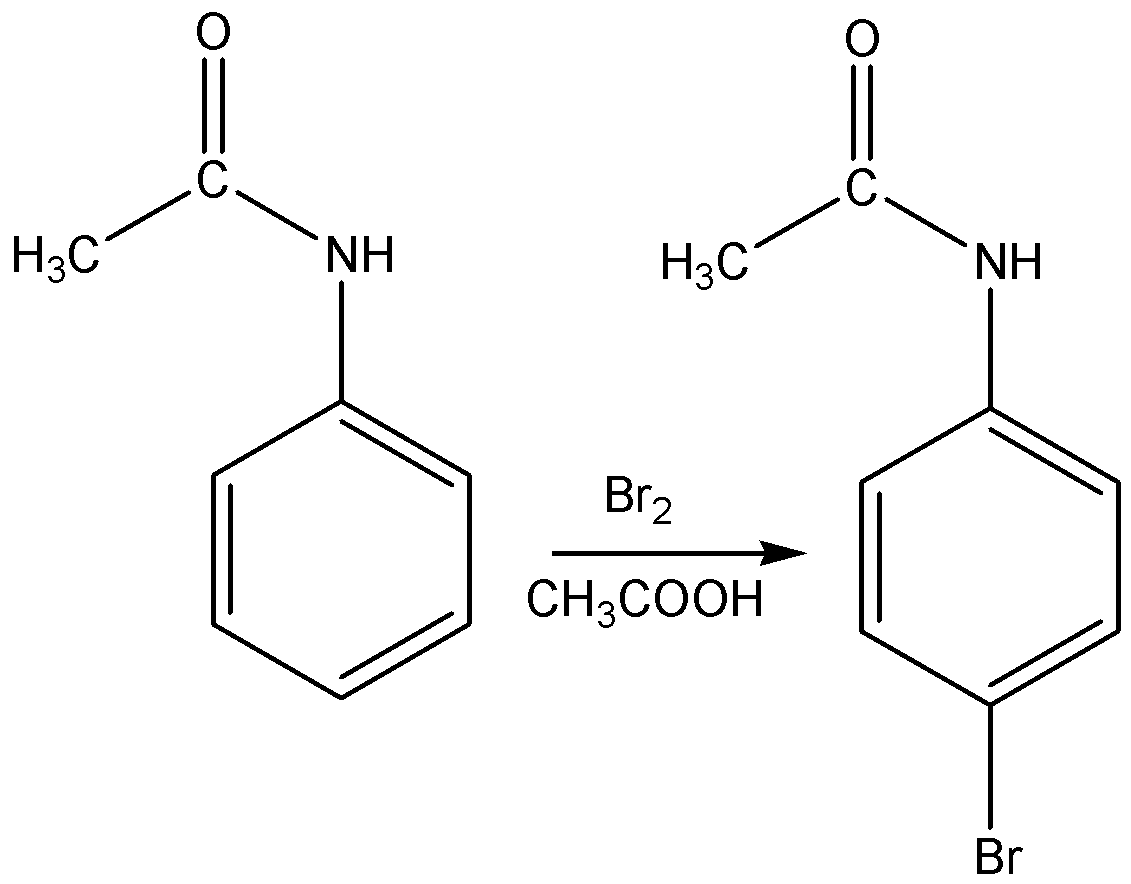
The structural formula of p-Bromoacetanilide is
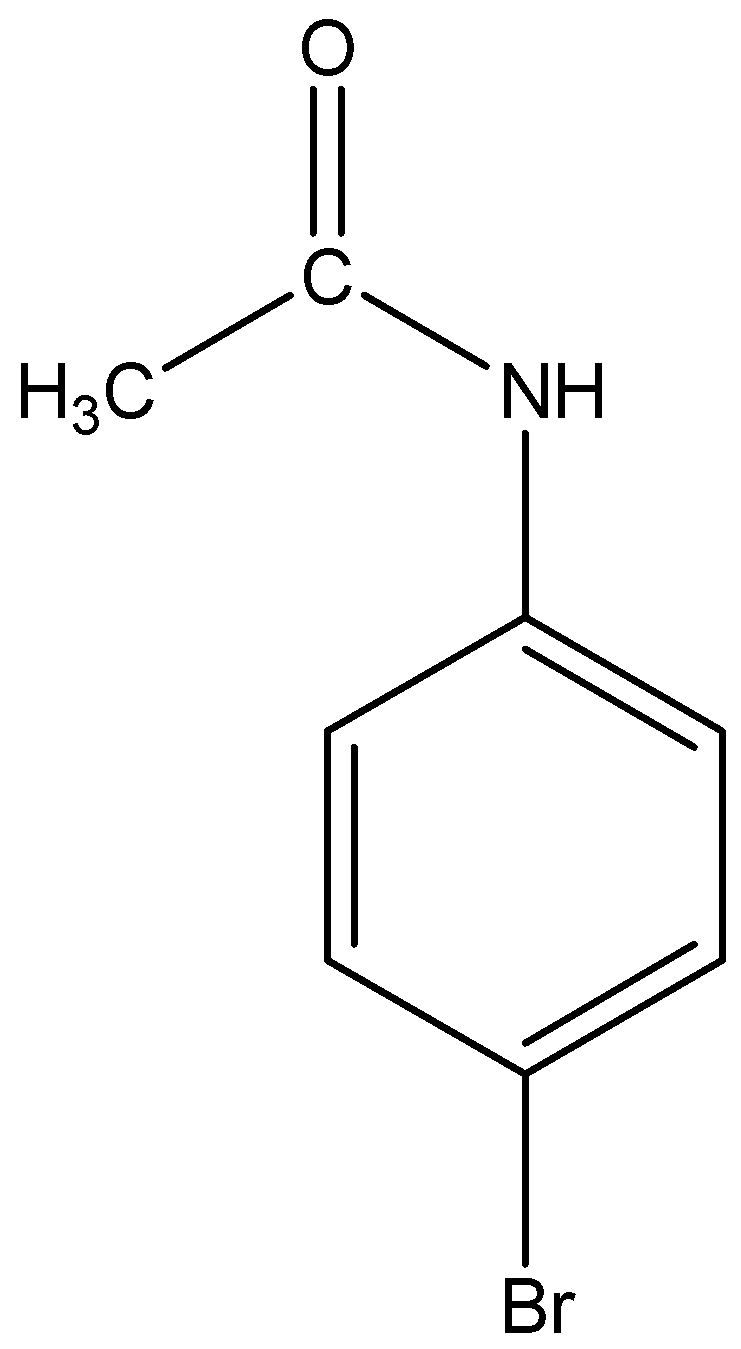
From the above discussion we know, acetanilide when treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide.
Hence, option \[3\] is correct.
Note:
Each mono-substituent moiety having three named positions in the ring. In the ring a nearby mono substituent group is called ortho position, that means two ortho positions are in the ring, because of the left and right side of the substituent group. The alternatively position of the substituent group in the ring is called meta position, here also two meta positions possible in the left and right side of the substituent group. Para position is nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitutions are attacked in ortho and para position in the ring.
Complete answer:
The structural formula of aniline is

The structural formula of acetanilide is

Aniline when treated with bromine in acetic acid or water gives a product of 2,4,6- tribromo aniline. It is white precipitate.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,

The structural formula of 2,4,6- tribromo aniline is

But we want certain position bromination means we first do acylated aniline to get acetanilide. Acetanilide is treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide. This p-Bromoacetanilide undergoes hydrolysis to give p-Bromoaniline.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,

The structural formula of p-Bromo aniline is

Acetanilide is treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide.
The reaction for the above discussion is given below,

The structural formula of p-Bromoacetanilide is

From the above discussion we know, acetanilide when treated with bromine in acetic acid mainly gives p-Bromoacetanilide.
Hence, option \[3\] is correct.
Note:
Each mono-substituent moiety having three named positions in the ring. In the ring a nearby mono substituent group is called ortho position, that means two ortho positions are in the ring, because of the left and right side of the substituent group. The alternatively position of the substituent group in the ring is called meta position, here also two meta positions possible in the left and right side of the substituent group. Para position is nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitutions are attacked in ortho and para position in the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




