
How do amino acids behave in acidic and basic solutions?
Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint: Amino acid here in this, we will look at how amino acid behaves with acid and bases separately.
We know that amino acid contains a single group $N{H_2}$ and a single group \[ - COOH\]. It has a property of forming zwitterion ions, because of the presence of the above-mentioned group.
Complete answer:
It is basically the amino acid has both a basic amine group as well as an acidic carboxylic group
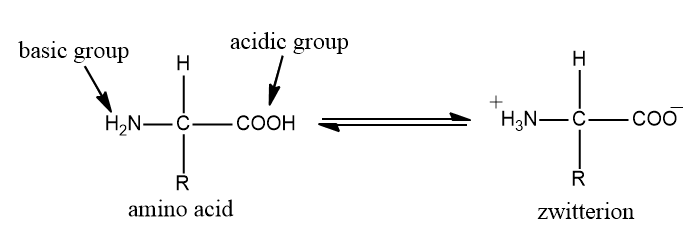
Adding base to amino acid solution
We will increase the pH of the solution of amino acid by adding hydroxide ions, the hydrogen ion will remove from the \[N{H_3}^ + \] group. If we run it under electrophoresis, it has negative charge.
Suppose we have an amino group under acidic condition and we slowly add alkali. So, when we add just the right amount of alkali, the more acidic hydrogen of the carboxylic group is removed instead of amino group hydrogen. And we get back zwitterion. the amino group will no longer have net positive or negative charge. This means, it wouldn’t move toward the cathode or anode during electrophoresis.
Amino in acidic condition,
if we decrease the pH by adding an acid to the solution, the \[ - COO\] part of zwitterion picks up the hydrogen ion. This time electrophoresis would move amino acid towards the cathode which is a negative electrode.
Note:
There is an internal transfer of a hydrogen ion from the carboxylic group to the amino group. This is the form that amino acids exist even in solid state. If you dissolve the amino acid in water, then this solution will contain this ion.
We know that amino acid contains a single group $N{H_2}$ and a single group \[ - COOH\]. It has a property of forming zwitterion ions, because of the presence of the above-mentioned group.
Complete answer:
It is basically the amino acid has both a basic amine group as well as an acidic carboxylic group

Adding base to amino acid solution
We will increase the pH of the solution of amino acid by adding hydroxide ions, the hydrogen ion will remove from the \[N{H_3}^ + \] group. If we run it under electrophoresis, it has negative charge.
Suppose we have an amino group under acidic condition and we slowly add alkali. So, when we add just the right amount of alkali, the more acidic hydrogen of the carboxylic group is removed instead of amino group hydrogen. And we get back zwitterion. the amino group will no longer have net positive or negative charge. This means, it wouldn’t move toward the cathode or anode during electrophoresis.
Amino in acidic condition,
if we decrease the pH by adding an acid to the solution, the \[ - COO\] part of zwitterion picks up the hydrogen ion. This time electrophoresis would move amino acid towards the cathode which is a negative electrode.
Note:
There is an internal transfer of a hydrogen ion from the carboxylic group to the amino group. This is the form that amino acids exist even in solid state. If you dissolve the amino acid in water, then this solution will contain this ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




