
Among the following the branched chain polymer is:
(A) Polyvinyl chloride
(B) Bakelite
(C) Low density polythene
(D) High density polythene
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: This polymer has high branching and is formed by free radical addition and H abstraction process. Also it is formed under very high pressure and temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Branched chain polymers are those polymers which have a linear structure but have some branching as well.
Now let us talk about these 4 polymers individually.
-First we will see about polyvinyl chloride:
It is a synthetic plastic polymer. It is a linear shaped polymer made by the polymerisation of vinyl chloride ($C{H_2} = CH - Cl$) and is also thermoplastic in nature.
Its preparation reaction can be written as:
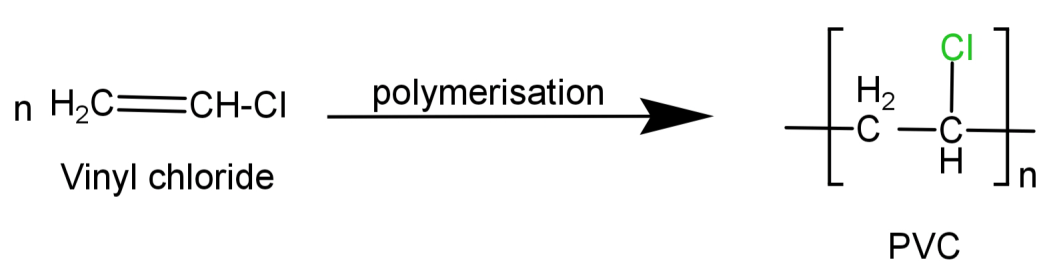
Since we can see that it is linear in shape (no branching present) it cannot be a branched chain polymer.
-About Bakelite:
It is a cross linked polymer and thermosetting type of polymer. It is formed using phenol (${C_6}{H_5}OH$) and formaldehyde ($HCHO$) monomers and hence is known as phenol-formaldehyde polymer. They are formed by the condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde in the presence of an acid or a base catalyst and results in the formation of ortho and para-hydroxymethyl phenol derivatives. These further react with phenol to form a linear compound called novolac.
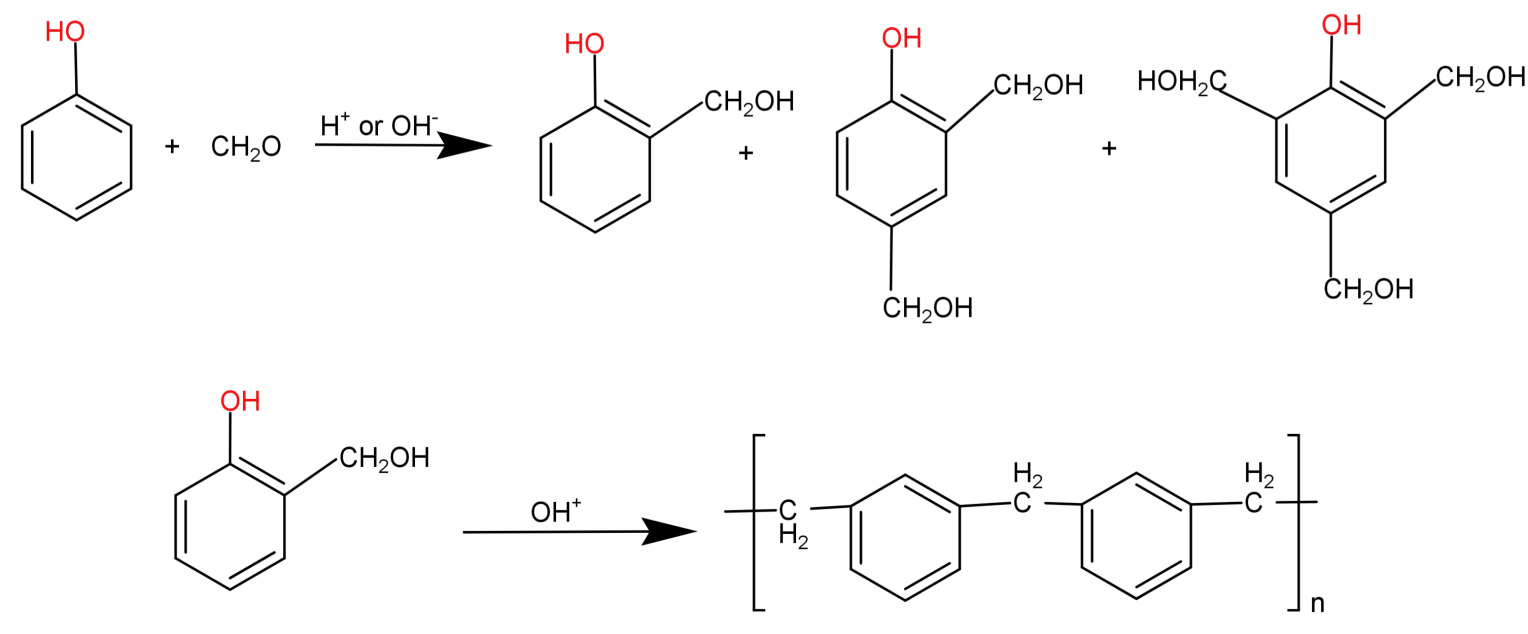
This novolac is further heated with formaldehyde to form a cross linked polymer called Bakelite.
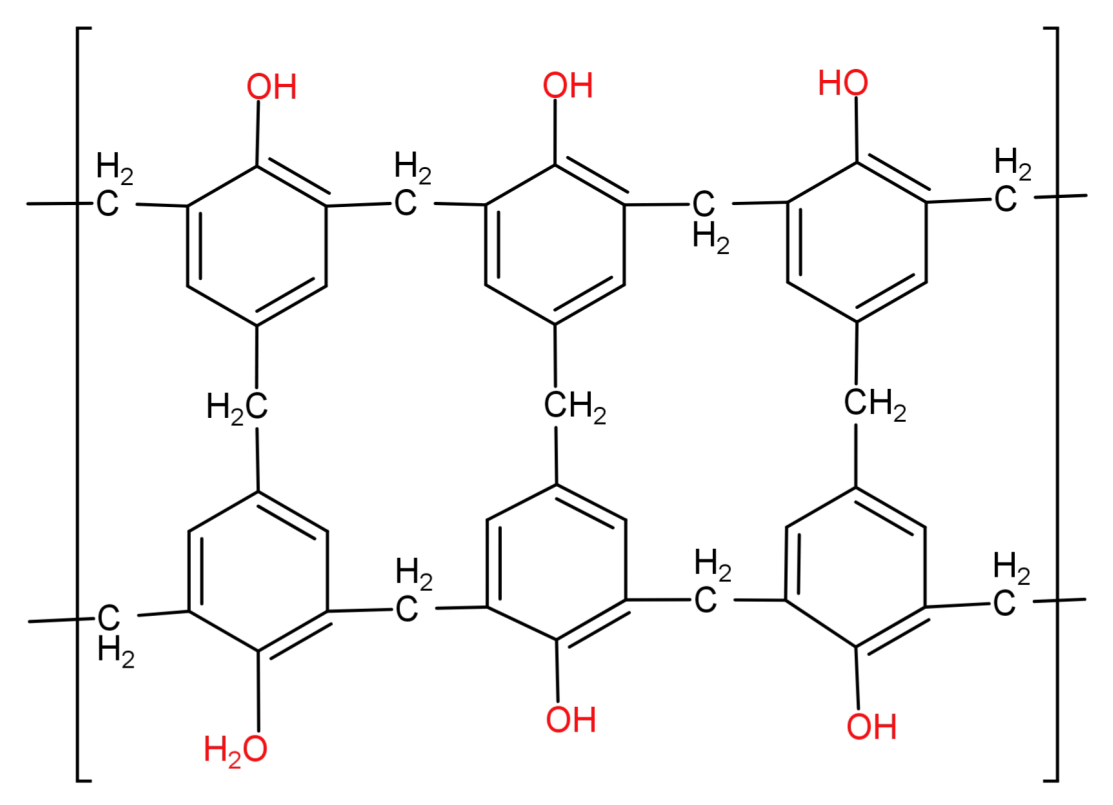
Since we can see that Bakelite has a cross linked 3D structure it cannot be a branched chain polymer.
-Low density polythene (LDP): It is formed by polymerisation of ethene ($C{H_2} = C{H_2}$) under high pressure of 1000-2000 atm and temperature of 350-570 K. This occurs in the presence of oxygen or a peroxide initiator catalyst. It has a highly branched structure. Although it is chemically inert and tough, it is quite flexible and a poor conductor of electricity. It is obtained by free radical addition and H atom abstraction.
-High density polythene (HDP): It is formed when ethene ($C{H_2} = C{H_2}$) undergoes addition polymerisation in a hydrocarbon solvent in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Its formation occurs at a temperature of 333-343 K and pressure of 6-7 atm. It is a linear structure polymer. Chemically it is inert and physically it is tough and hard.

So, the correct option is: (C) Low density polythene.
Note: The high density polymer is linear and still it has a high density because the linear chains of polyethene are bonded to each other by very strong forces and so are closely packed, while on the other hand low density polymer has higher branching and so the intermolecular forces (dipole induced dipole attraction) are weaker. This also makes the LDP weaker than HDP with lesser tensile strength.
Complete step by step answer:
Branched chain polymers are those polymers which have a linear structure but have some branching as well.
Now let us talk about these 4 polymers individually.
-First we will see about polyvinyl chloride:
It is a synthetic plastic polymer. It is a linear shaped polymer made by the polymerisation of vinyl chloride ($C{H_2} = CH - Cl$) and is also thermoplastic in nature.
Its preparation reaction can be written as:

Since we can see that it is linear in shape (no branching present) it cannot be a branched chain polymer.
-About Bakelite:
It is a cross linked polymer and thermosetting type of polymer. It is formed using phenol (${C_6}{H_5}OH$) and formaldehyde ($HCHO$) monomers and hence is known as phenol-formaldehyde polymer. They are formed by the condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde in the presence of an acid or a base catalyst and results in the formation of ortho and para-hydroxymethyl phenol derivatives. These further react with phenol to form a linear compound called novolac.

This novolac is further heated with formaldehyde to form a cross linked polymer called Bakelite.

Since we can see that Bakelite has a cross linked 3D structure it cannot be a branched chain polymer.
-Low density polythene (LDP): It is formed by polymerisation of ethene ($C{H_2} = C{H_2}$) under high pressure of 1000-2000 atm and temperature of 350-570 K. This occurs in the presence of oxygen or a peroxide initiator catalyst. It has a highly branched structure. Although it is chemically inert and tough, it is quite flexible and a poor conductor of electricity. It is obtained by free radical addition and H atom abstraction.

-High density polythene (HDP): It is formed when ethene ($C{H_2} = C{H_2}$) undergoes addition polymerisation in a hydrocarbon solvent in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Its formation occurs at a temperature of 333-343 K and pressure of 6-7 atm. It is a linear structure polymer. Chemically it is inert and physically it is tough and hard.

So, the correct option is: (C) Low density polythene.
Note: The high density polymer is linear and still it has a high density because the linear chains of polyethene are bonded to each other by very strong forces and so are closely packed, while on the other hand low density polymer has higher branching and so the intermolecular forces (dipole induced dipole attraction) are weaker. This also makes the LDP weaker than HDP with lesser tensile strength.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




