
Why is the angle of dip at the magnetic equator zero degree?
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: Whenever the magnetic field lines go parallel with the earth’s equator to be precise the magnetic equator, the angle of dip has a fixed value, we need to know that value according to the question. The angle of dip is the angle that the Earth’s magnetic field lines make with the horizontal. This angle of dip varies at each and every point as it passes from one magnetic pole to another.
Complete step-by-step answer:
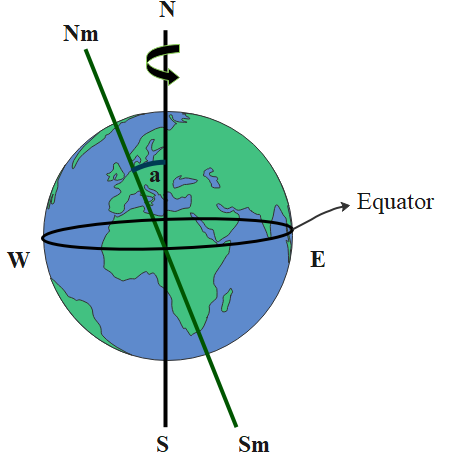
Here in the diagram, the circular object represents the earth and the line that is passing vertically through the middle of the earth is the representation of the geographic north pole and south pole (represented as ‘N’ and ‘S’ respectively), but in the case of the earth, the magnetic north pole and the south pole (represented by ‘Ns’ and ‘Sm’ respectively) of the earth passes diagonally making an angle represented by ‘a’ of magnitude 11.3$^ \circ $with the actual line of poles. The line that is visually horizontally passing through the middle of the earth is the line of the equator. The other two sides of the earth are west and east are represented by ‘W’ and ‘E’ respectively.
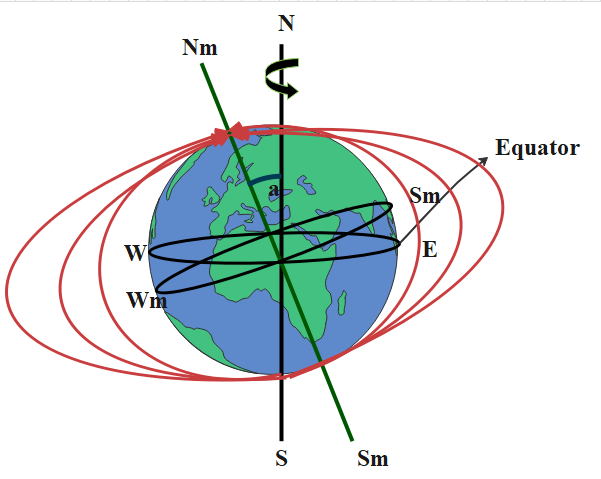
Now, we see that lines are passing from the magnetic north to the magnetic south pole of the earth. Those lines make a certain angle with the earth’s horizon; this angle is known as angle of dip. And ‘Wm’ and ‘Em’ are the magnetic meridians of the earth. So when the magnetic field lines pass through one pole to another pole at one point the magnetic meridian and the field lines would be parallel and the angle of dip at that time would be ${0^ \circ }$.
Note: There are two types of representation poles of the earth, one is the geographical poles and the other one is the magnetic poles. The geographical poles have different equators and the magnetic poles have a different equator.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Here in the diagram, the circular object represents the earth and the line that is passing vertically through the middle of the earth is the representation of the geographic north pole and south pole (represented as ‘N’ and ‘S’ respectively), but in the case of the earth, the magnetic north pole and the south pole (represented by ‘Ns’ and ‘Sm’ respectively) of the earth passes diagonally making an angle represented by ‘a’ of magnitude 11.3$^ \circ $with the actual line of poles. The line that is visually horizontally passing through the middle of the earth is the line of the equator. The other two sides of the earth are west and east are represented by ‘W’ and ‘E’ respectively.

Now, we see that lines are passing from the magnetic north to the magnetic south pole of the earth. Those lines make a certain angle with the earth’s horizon; this angle is known as angle of dip. And ‘Wm’ and ‘Em’ are the magnetic meridians of the earth. So when the magnetic field lines pass through one pole to another pole at one point the magnetic meridian and the field lines would be parallel and the angle of dip at that time would be ${0^ \circ }$.
Note: There are two types of representation poles of the earth, one is the geographical poles and the other one is the magnetic poles. The geographical poles have different equators and the magnetic poles have a different equator.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




