
What are the components of yeast artificial chromosomes?
Answer
476.1k+ views
Hint: Yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) is a vector used in cloning. YAC is derived from yeast or Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA which are then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. It is used for mapping and sequencing of genomes. These are the vectors that enable artificial chromosomes to be created and cloned into yeast.
Complete answer:
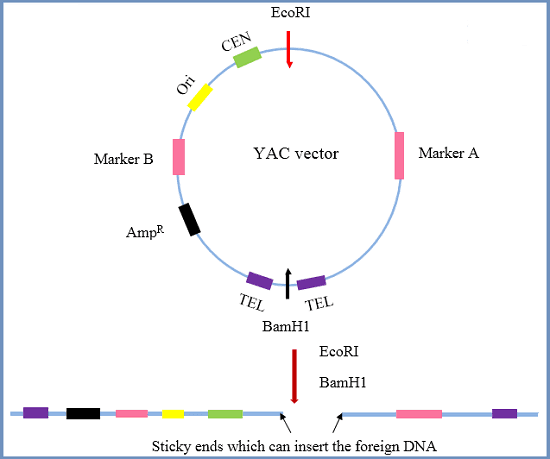
The primary components of a YAC are the ARS, centromere, and telomeres from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
ARSI: This sequence in YAC is an autonomously replicating sequence.
CEN: This represents the yeast centromere region. This ensures chromosome partitioning between two daughter cells and a selective marker gene.
TEL: TEL region provides the telomeres. They are not complete telomere sequences but once they go inside the yeast nucleus they act as seeding sequences in which telomeres build.
Additionally, selectable marker genes, such as antibiotic resistance and a visible marker, are utilized to select transformed yeast cells. Without these sequences, the chromosome will not be stable during extracellular replication, and would not be distinguishable from colonies without the vector.
Additional information:
Advantage of using YAC:
Yeast's artificial chromosome is capable of carrying a large DNA fragment.
It is used to clone and assemble the entire genome of an organism.
It is capable of cloning foreign DNA of 1 million base pairs.
Disadvantages of YAC:
They are very fragile and are highly prone to breakage.
They are unstable, the foreign DNA ligated are often deleted
The yield of DNA is not high.
Note:
Artificial chromosomes are man-made vectors and some examples of them are yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC) and bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC).
Vectors that are presently in use are engineered in such a way that they help in easy linking of foreign DNA and selection of recombinants from non- recombinant.
Following features are required to facilitate cloning into vector-
Origin of replication (ori), selectable markers, cloning sites.
Complete answer:
The primary components of a YAC are the ARS, centromere, and telomeres from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
ARSI: This sequence in YAC is an autonomously replicating sequence.
CEN: This represents the yeast centromere region. This ensures chromosome partitioning between two daughter cells and a selective marker gene.
TEL: TEL region provides the telomeres. They are not complete telomere sequences but once they go inside the yeast nucleus they act as seeding sequences in which telomeres build.
Additionally, selectable marker genes, such as antibiotic resistance and a visible marker, are utilized to select transformed yeast cells. Without these sequences, the chromosome will not be stable during extracellular replication, and would not be distinguishable from colonies without the vector.
Additional information:
Advantage of using YAC:
Yeast's artificial chromosome is capable of carrying a large DNA fragment.
It is used to clone and assemble the entire genome of an organism.
It is capable of cloning foreign DNA of 1 million base pairs.
Disadvantages of YAC:
They are very fragile and are highly prone to breakage.
They are unstable, the foreign DNA ligated are often deleted
The yield of DNA is not high.

Note:
Artificial chromosomes are man-made vectors and some examples of them are yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC) and bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC).
Vectors that are presently in use are engineered in such a way that they help in easy linking of foreign DNA and selection of recombinants from non- recombinant.
Following features are required to facilitate cloning into vector-
Origin of replication (ori), selectable markers, cloning sites.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




