
How can we calculate the Buoyant force on an object?
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: We need to understand what is the Buoyant force, what are the reasons for this force to be acting on a body and to what extent it can act on a body. These will give us the solution to the methods to calculate the buoyant force acting on a body.
Complete Solution:
The Buoyancy or the buoyant force is a phenomenon experienced by an object which is placed in a fluid medium. It is defined as the upward force experienced by a body due to the molecules in the surface of the fluid in which the object is placed.
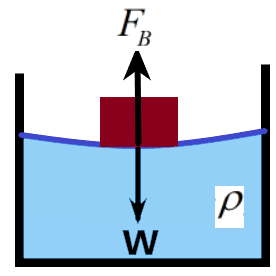
We can understand from the definition that the Buoyant force is opposing the gravitational force. The upward force is due to the pressure exerted by the fluid molecules on the object that is kept in the fluid. The force of buoyancy is dependent on the density of the fluid medium balancing the weight of the object placed in it.
The buoyant force will be balancing the gravitational force to the extent that the body is floating. In the case of sinking, the buoyant force was insufficient to hold the object up.
The Buoyant force is given as –
\[{{F}_{B}}=-\rho gV\]
Where \[\rho \] is the density of the fluid medium, g is the acceleration due to gravity and V is the volume of the fluid.
This way we can calculate the force of Buoyancy experienced by an object in a fluid medium such as air or water.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The Buoyant force as given in the problem is applicable only when the object placed in the fluid medium is either completely floating or partially floating. In case of partial floating, the buoyancy and the gravitational force and equal and opposite and thus remain balanced.
Complete Solution:
The Buoyancy or the buoyant force is a phenomenon experienced by an object which is placed in a fluid medium. It is defined as the upward force experienced by a body due to the molecules in the surface of the fluid in which the object is placed.

We can understand from the definition that the Buoyant force is opposing the gravitational force. The upward force is due to the pressure exerted by the fluid molecules on the object that is kept in the fluid. The force of buoyancy is dependent on the density of the fluid medium balancing the weight of the object placed in it.
The buoyant force will be balancing the gravitational force to the extent that the body is floating. In the case of sinking, the buoyant force was insufficient to hold the object up.
The Buoyant force is given as –
\[{{F}_{B}}=-\rho gV\]
Where \[\rho \] is the density of the fluid medium, g is the acceleration due to gravity and V is the volume of the fluid.
This way we can calculate the force of Buoyancy experienced by an object in a fluid medium such as air or water.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The Buoyant force as given in the problem is applicable only when the object placed in the fluid medium is either completely floating or partially floating. In case of partial floating, the buoyancy and the gravitational force and equal and opposite and thus remain balanced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




