
What causes Chromatic aberration?
A) Marginal rays
B) Central rays
C) Difference in radii of curvature of its surfaces
D) Variation of focal length of lens with color
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: White light consists of seven colors as propounded by Newton's disc experiment. Each of these colors have a different speed and hence they deviate at different measures when passing from one medium to another.
Chromatic aberration is the phenomenon in which different colors of the light deviate through different measures when incident on a lens. This is a type of optical defect. This has several consequences as listed:
Fringes (unwanted) are observed
White objects appear colored
Objects appear blurry
The lens maker’s formula relates the refractive index and the focal length of the lens which in turn relate the wavelength of the light to the focal length.
Mathematically the lens maker’s formula is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu - 1)(\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}})$
Where f is the focal length of the lens, $\mu $ is the refractive index and ${R_1}\,,{R_2}$ are the radii of curvatures for the spherical surfaces.
Complete step by step answer:
Chromatic aberration is the failure of the lens to focus all the colors to the same convergence point. Different colors converge at different points. This is also known as Chromatic distortion.
This aberration is seen as the fringes along the boundaries of the object. These are the bright and dark fringes.
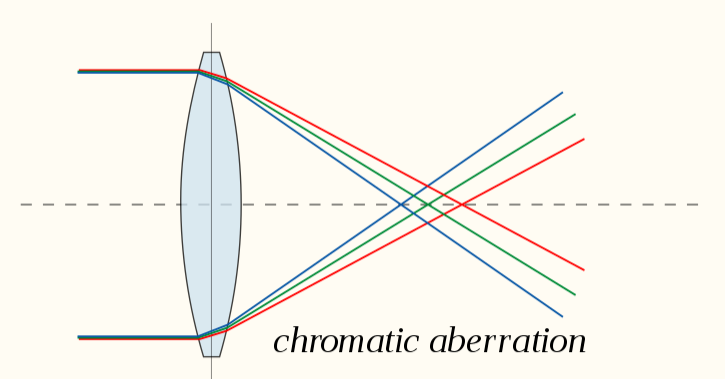
Each color of light cannot be focused on the same point since the refractive index of the lens is different for different wavelengths. Since the focal length of the lens is dependent on the wavelength of the incident light, for different colors there will be different foci for the same lens.
So, we can say that the cause of chromatic aberration is the variation of focal length of lens with color.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: A consequence of chromatic aberration is that the white objects appear to be colored and a bit blurred. To remove the chromatic aberration, we use two lenses kept in close contact, a process known as achromatization. This should be noted that it is not necessary to keep the focal length of the two lenses to be the same but the dimensions of the lenses should be largely kept the same.
Chromatic aberration is the phenomenon in which different colors of the light deviate through different measures when incident on a lens. This is a type of optical defect. This has several consequences as listed:
Fringes (unwanted) are observed
White objects appear colored
Objects appear blurry
The lens maker’s formula relates the refractive index and the focal length of the lens which in turn relate the wavelength of the light to the focal length.
Mathematically the lens maker’s formula is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu - 1)(\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}})$
Where f is the focal length of the lens, $\mu $ is the refractive index and ${R_1}\,,{R_2}$ are the radii of curvatures for the spherical surfaces.
Complete step by step answer:
Chromatic aberration is the failure of the lens to focus all the colors to the same convergence point. Different colors converge at different points. This is also known as Chromatic distortion.
This aberration is seen as the fringes along the boundaries of the object. These are the bright and dark fringes.

Each color of light cannot be focused on the same point since the refractive index of the lens is different for different wavelengths. Since the focal length of the lens is dependent on the wavelength of the incident light, for different colors there will be different foci for the same lens.
So, we can say that the cause of chromatic aberration is the variation of focal length of lens with color.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: A consequence of chromatic aberration is that the white objects appear to be colored and a bit blurred. To remove the chromatic aberration, we use two lenses kept in close contact, a process known as achromatization. This should be noted that it is not necessary to keep the focal length of the two lenses to be the same but the dimensions of the lenses should be largely kept the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




