
Compound ${C_4}{H_8}{O_2}$ exits in various structures as shown:
Which statement(s) is/are correct?
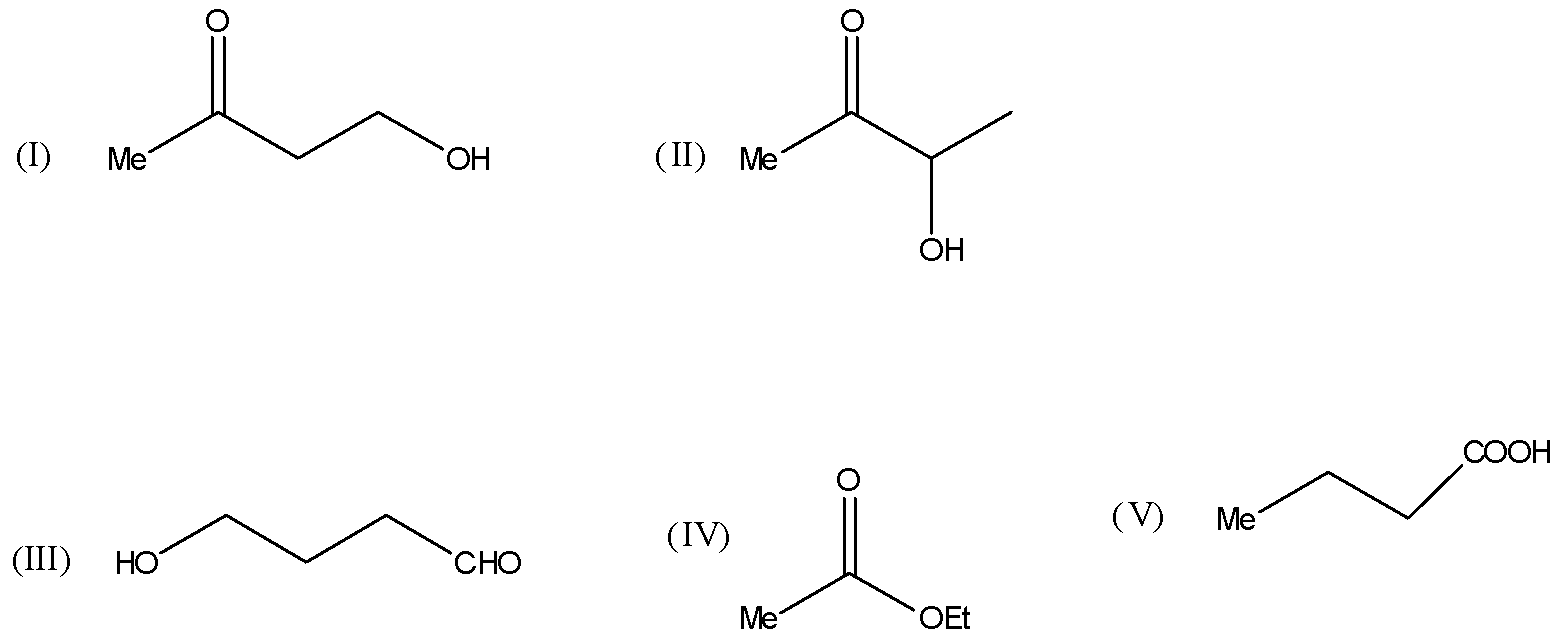
A) Compounds I and II give iodoform test: Compound I gives turbidity on heating with Lucas reagent, while compound II reduces Tollens’ reagent.
B) Compound III gives a silver mirror with ${[Ag{(N{H_3})_2}]^ \oplus }$ and does not react with NaOBr.
C) Compound IV on acid hydrolysis gives ${C_2}{H_5}COOH$ and MeOH.
D) Compound V on heating is decarboxylated to propane.

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Tollens’ test is given by all aldehydes and $\alpha $- hydroxy ketones. All alcohol shows turbidity with Lucas reagent. Iodoform test is given by the compounds having methyl ketone groups. Also, you should know that only $\beta $- keto acids undergo decarboxylation on heating.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given a compound having molecular formula, and its various structures are given. Let us discuss the statements given in options one by one:
A) Compounds I and II give iodoform test: Compound I gives turbidity on heating with Lucas reagent, while compound II reduces Tollens’ reagent.
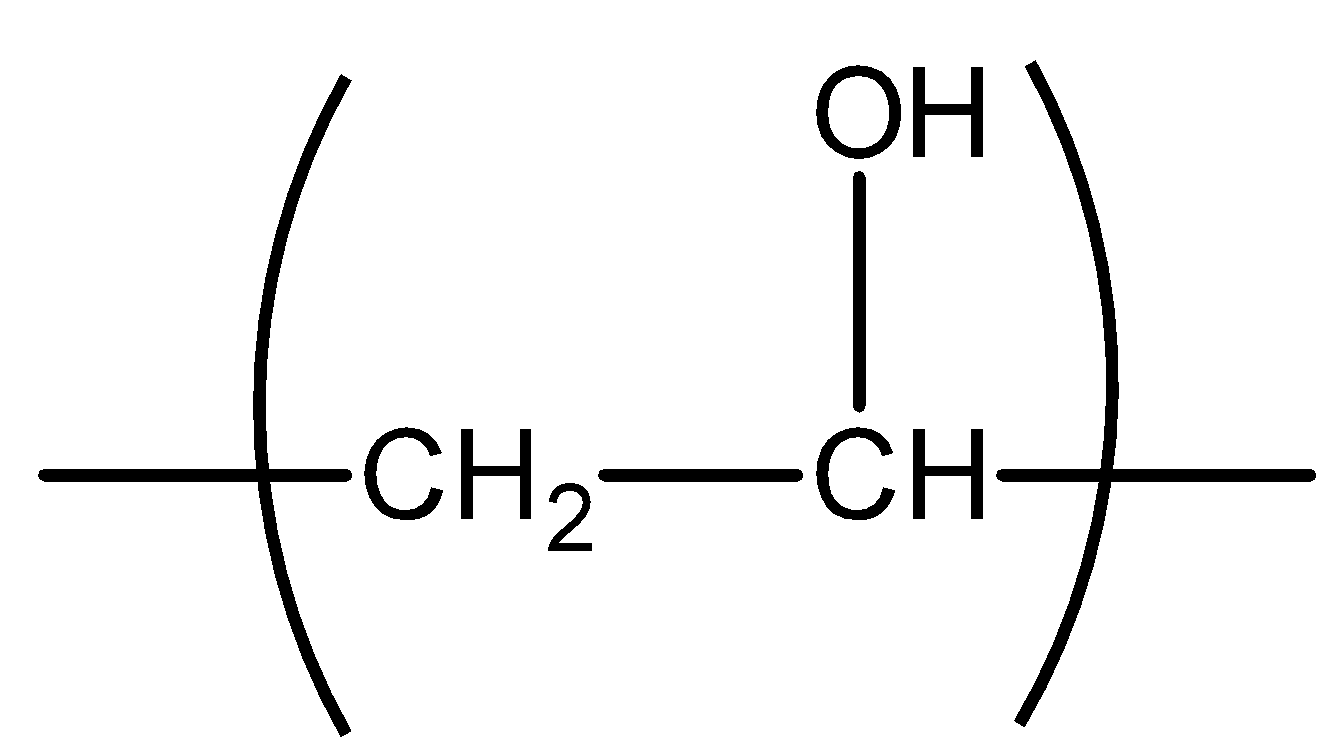
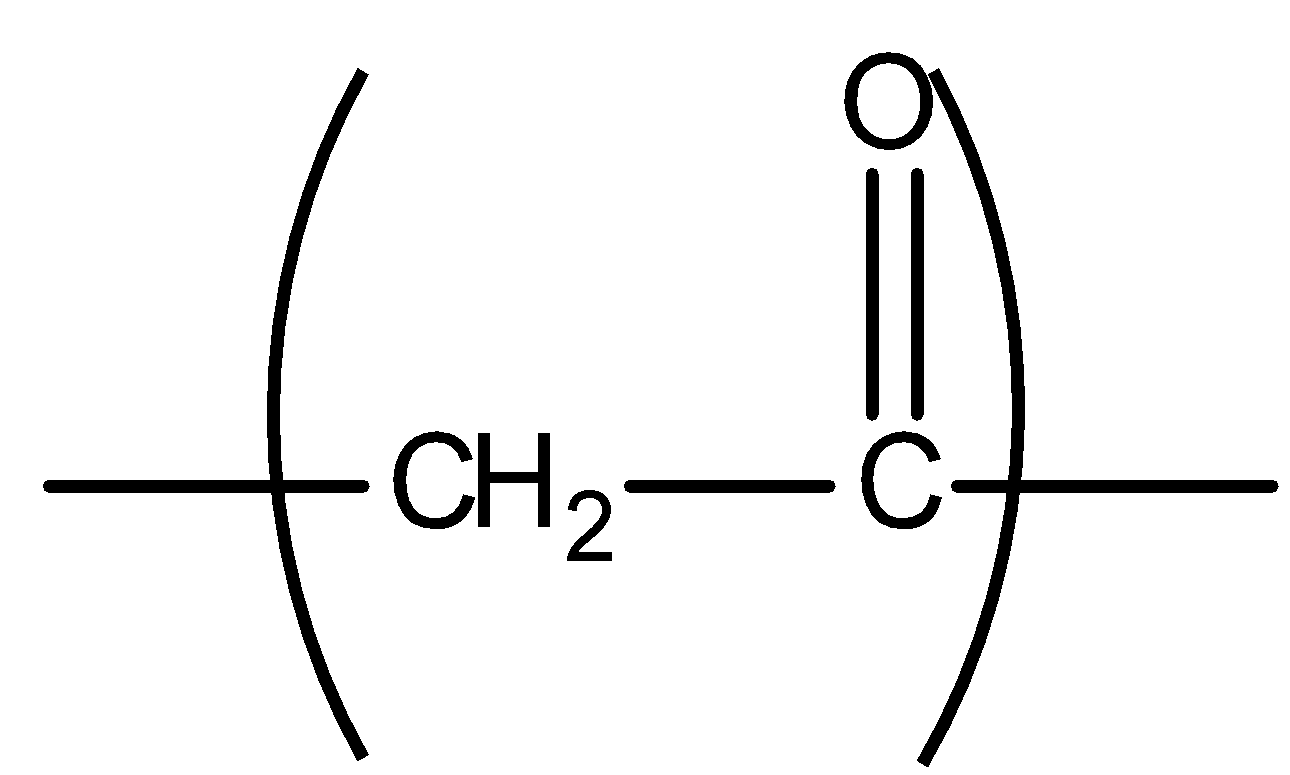
All the compounds having methyl ketone groups give iodoform tests. Ketogenic groups are as follows:
Now, compound I i.e.,
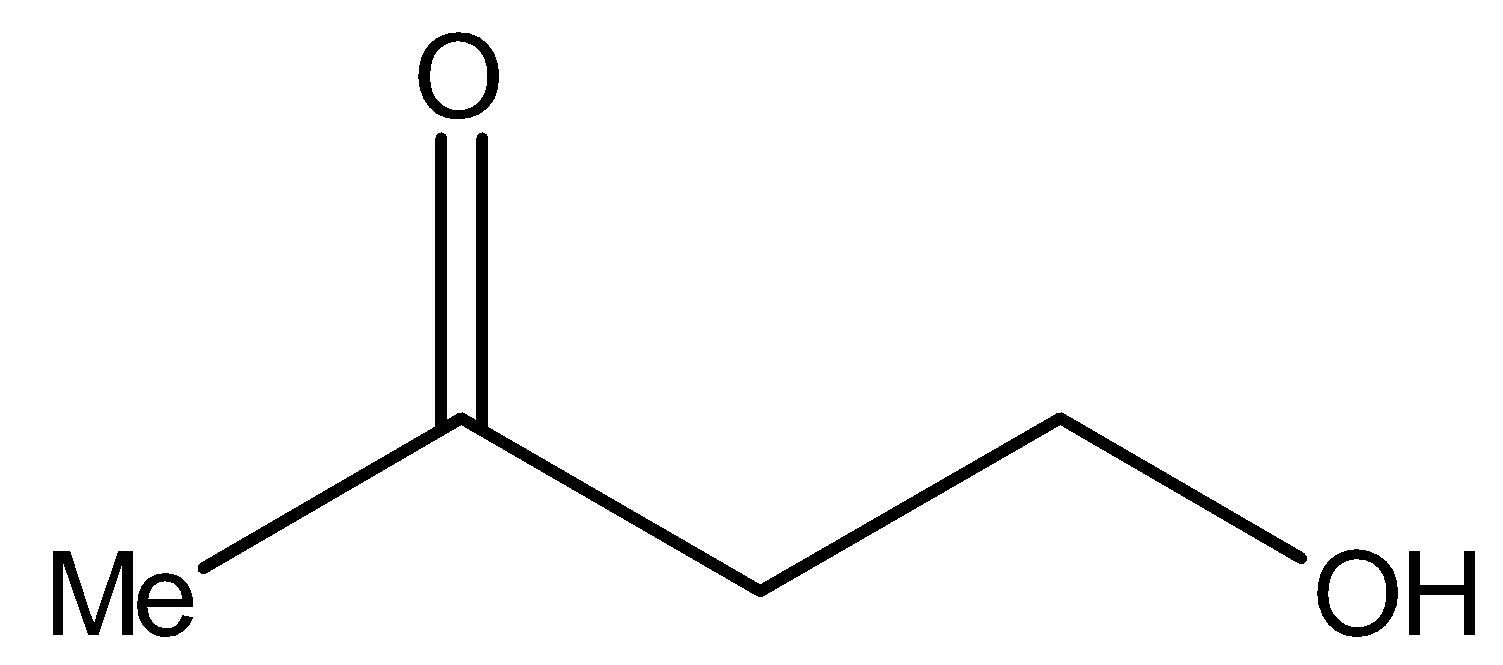
It contains methyl ketonic group ($ - C{H_2}CO - $). Therefore, it will give iodoform test.
Similarly, compound II i.e.,
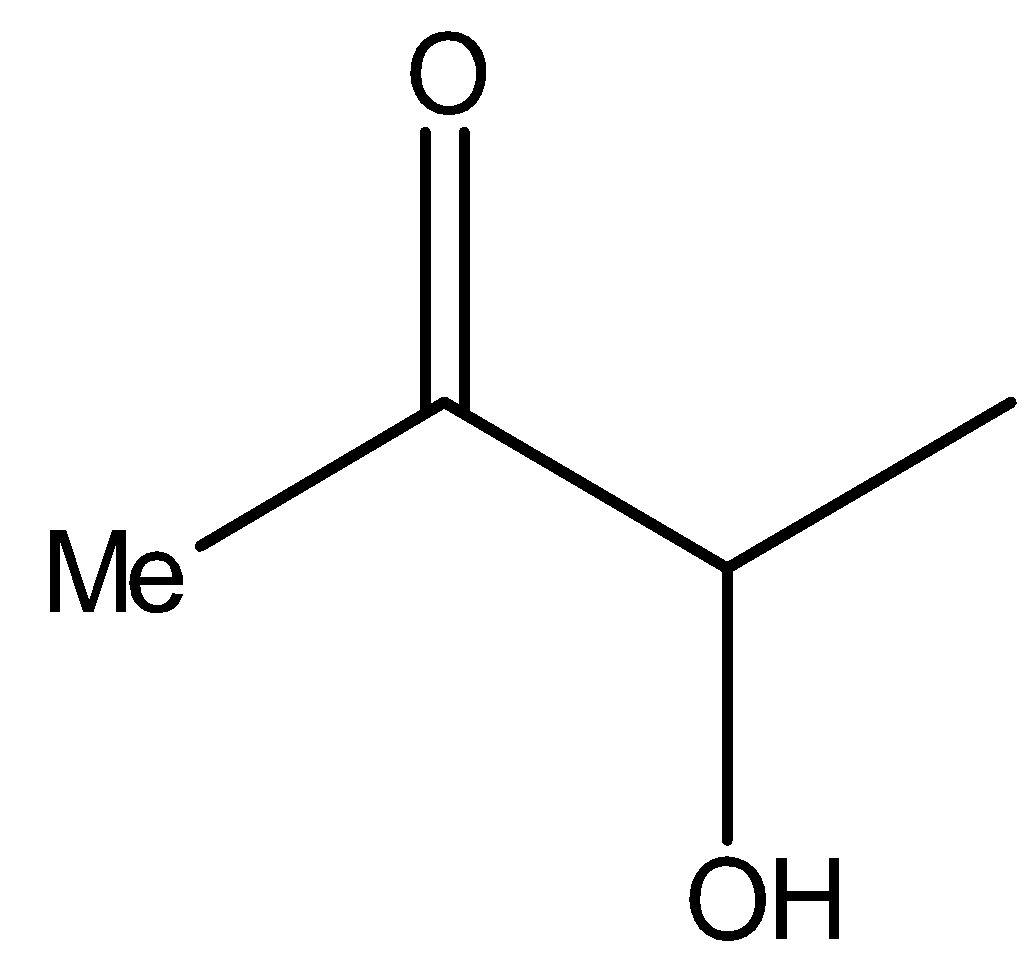
It also contains methyl ketone groups. Hence, compound II will also give iodoform test.
We know that alcohols give turbidity with Lucas reagent. Since compound I contains alcoholic groups (-OH), it will give turbidity with Lucas reagent.
All aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes reduce Tollens’ reagent and give a silver mirror. But ketones of special class i.e., $\alpha $- hydroxy ketones reduce Tollens’ reagent. General representation for $\alpha $- hydroxy ketones is:
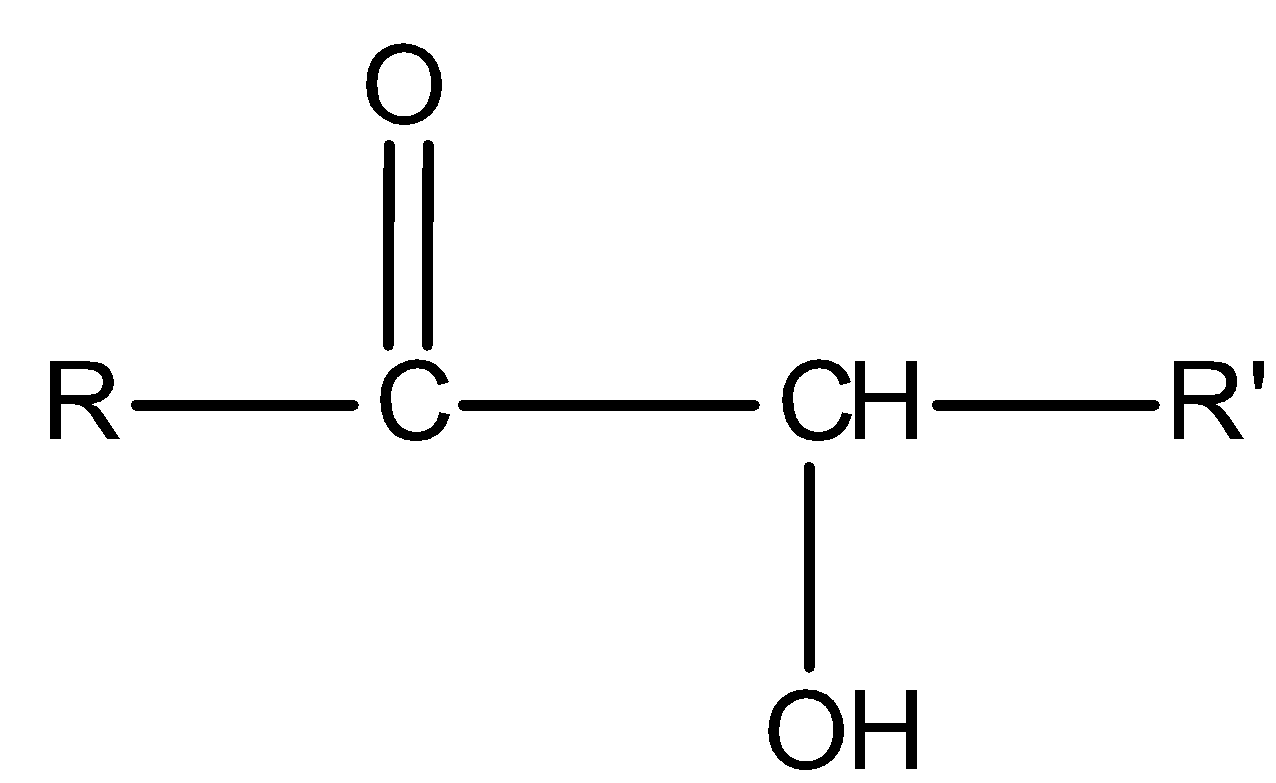
Now see the compound II,
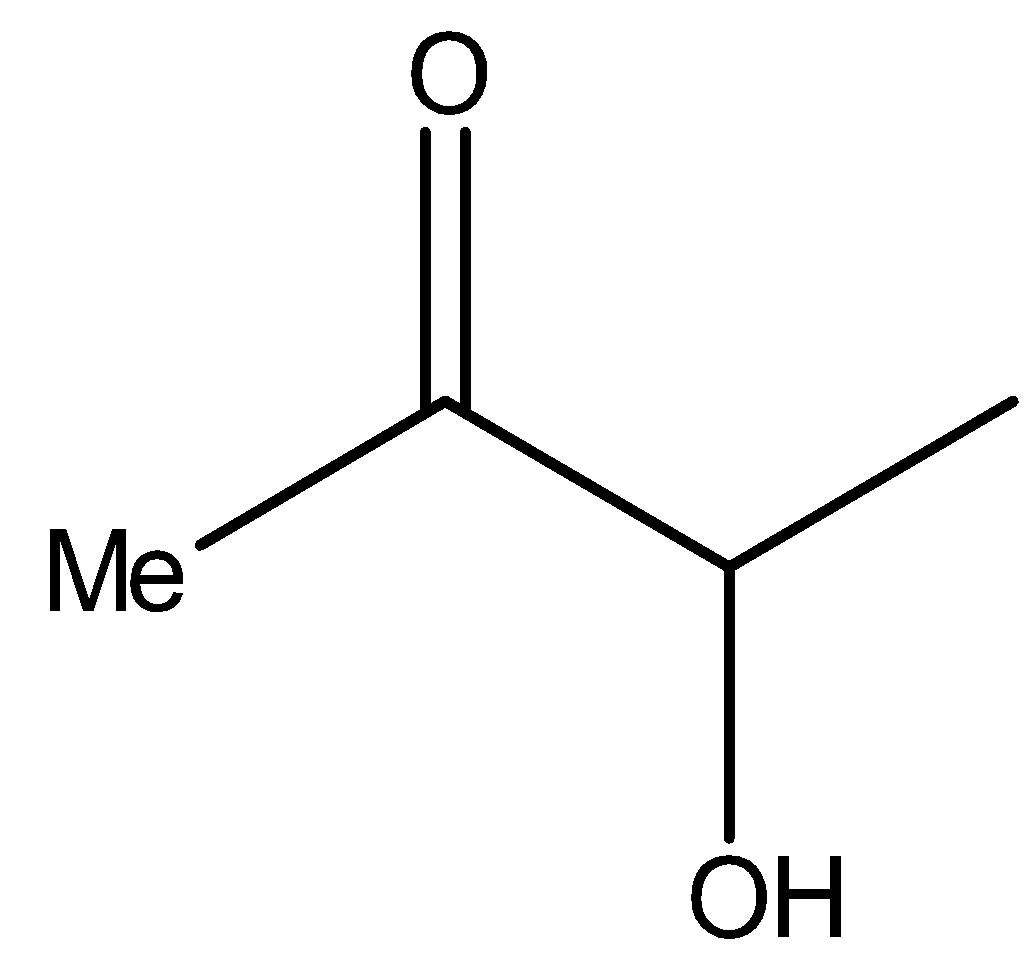
It is the same as the structure above, i.e., it is a $\alpha $- hydroxy ketone. Therefore, compound II will reduce Tollens’ reagent.
Thus, statement A is correct.
B) Compound III gives a silver mirror with ${[Ag{(N{H_3})_2}]^ \oplus }$ and does not react with NaOBr.
Compound III is:
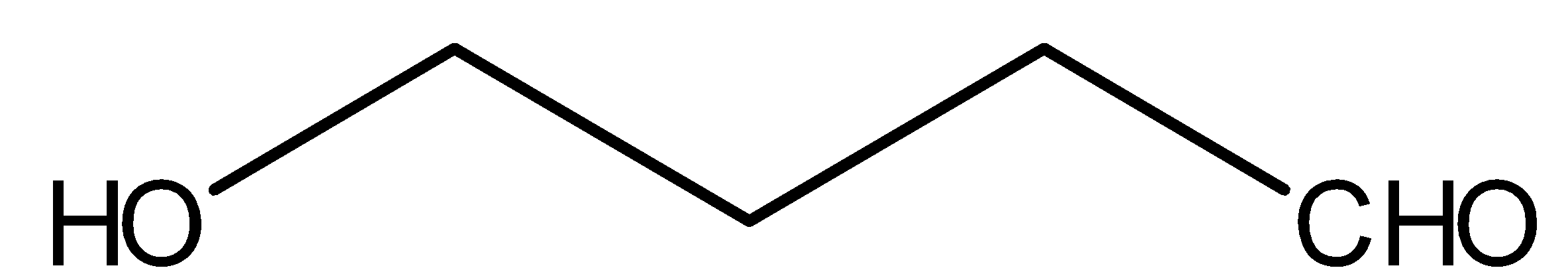
This above compound is an aldehyde, therefore it will reduce Tollene’s reagent and will give silver mirror. Tollen’s reagent is ${[Ag{(N{H_3})_2}]^ \oplus }$. NaOBr is nothing but combination of NaOH and $B{r_2}$. Methyl ketones gives react with NaOBr. But compound III does not have methyl ketonic group therefore, it will not react with NaOBr.
Thus, statement B is correct.
C) Compound IV on acid hydrolysis gives ${C_2}{H_5}COOH$ and MeOH.
Acidic hydrolysis $({H^ + }/{H_2}O)$ of compound IV:
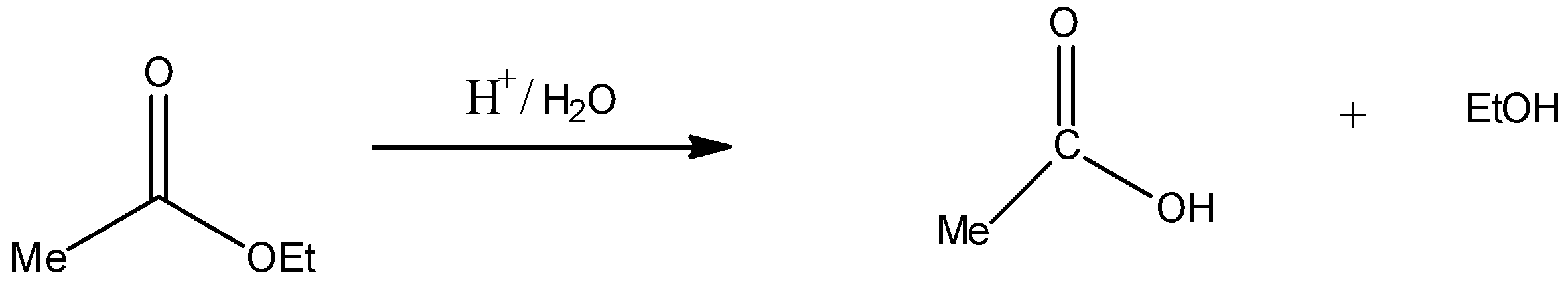
Thus, compound IV on acid hydrolysis gives $MeCOOH$ and EtOH. Hence, statement C is incorrect.
D) Compound V on heating is decarboxylated to propane.
Compound V is:
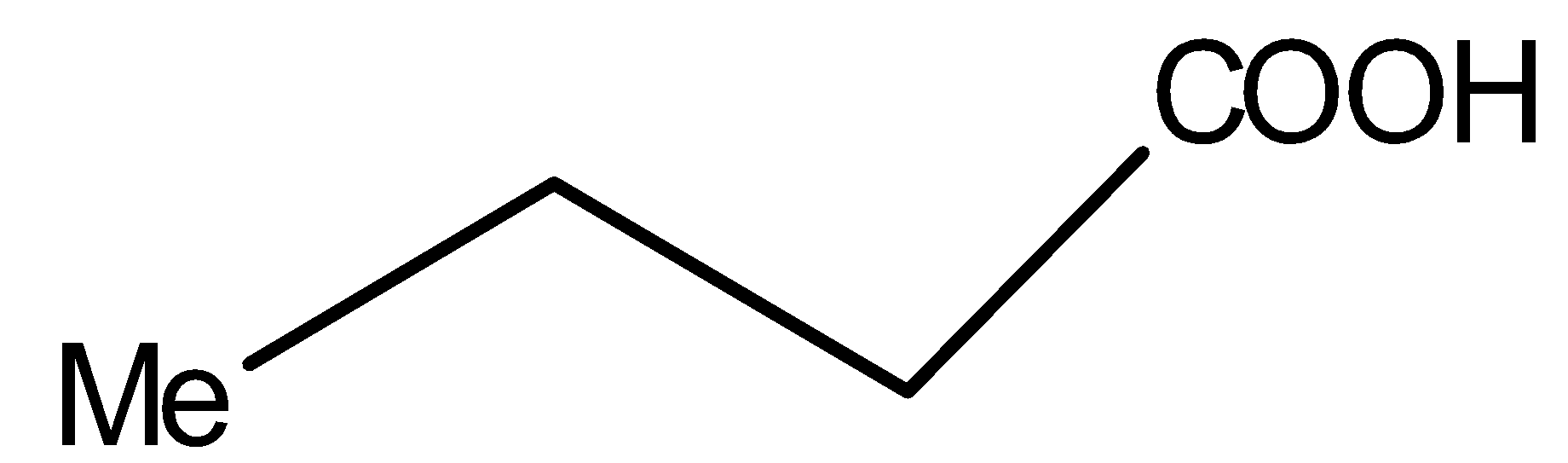
You must know that only $\beta $- keto acids under decarboxylation. General representation of $\beta $- keto acids is:
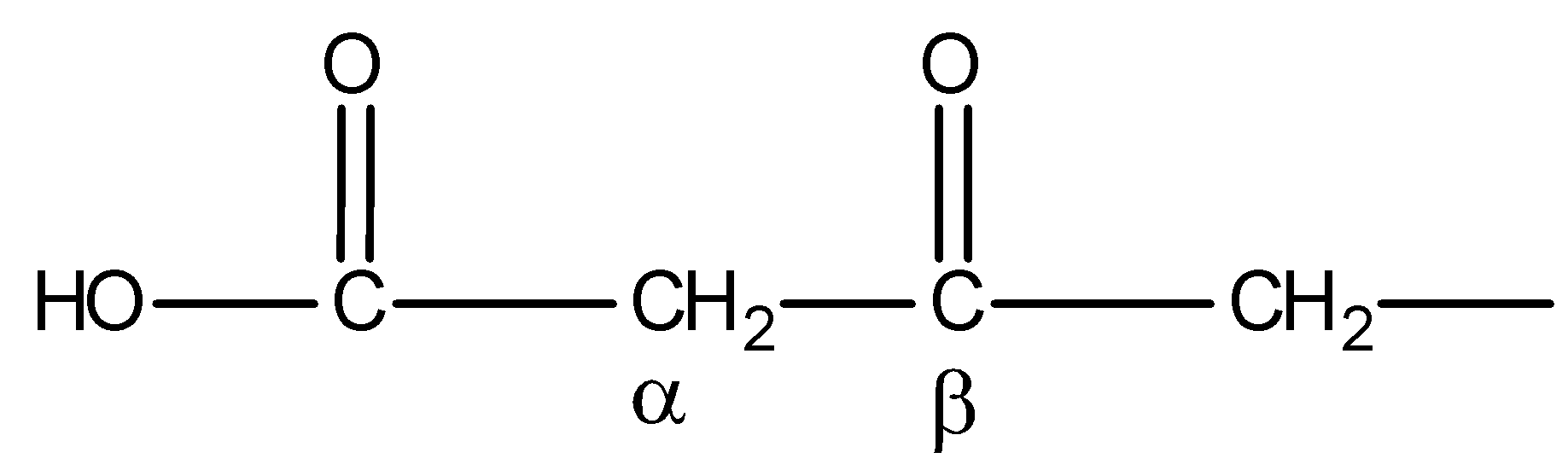
But compound IV is not $\beta $- keto acid. Thus, on heating, it will not undergo decarboxylation. Hence, statement D is incorrect.
Therefore, among all the given statements, statement A and B are correct. Thus, option A and B are the answers.
Note: Lucas reagent is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride $(ZnC{l_2})$ in conc. hydrochloric acid. Lucas reagent is used to distinguish the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. All alcohols show turbidity with Lucas reagent but they differ in the time taken for showing the turbidity.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given a compound having molecular formula, and its various structures are given. Let us discuss the statements given in options one by one:
A) Compounds I and II give iodoform test: Compound I gives turbidity on heating with Lucas reagent, while compound II reduces Tollens’ reagent.
All the compounds having methyl ketone groups give iodoform tests. Ketogenic groups are as follows:


Now, compound I i.e.,

It contains methyl ketonic group ($ - C{H_2}CO - $). Therefore, it will give iodoform test.
Similarly, compound II i.e.,

It also contains methyl ketone groups. Hence, compound II will also give iodoform test.
We know that alcohols give turbidity with Lucas reagent. Since compound I contains alcoholic groups (-OH), it will give turbidity with Lucas reagent.
All aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes reduce Tollens’ reagent and give a silver mirror. But ketones of special class i.e., $\alpha $- hydroxy ketones reduce Tollens’ reagent. General representation for $\alpha $- hydroxy ketones is:

Now see the compound II,

It is the same as the structure above, i.e., it is a $\alpha $- hydroxy ketone. Therefore, compound II will reduce Tollens’ reagent.
Thus, statement A is correct.
B) Compound III gives a silver mirror with ${[Ag{(N{H_3})_2}]^ \oplus }$ and does not react with NaOBr.
Compound III is:

This above compound is an aldehyde, therefore it will reduce Tollene’s reagent and will give silver mirror. Tollen’s reagent is ${[Ag{(N{H_3})_2}]^ \oplus }$. NaOBr is nothing but combination of NaOH and $B{r_2}$. Methyl ketones gives react with NaOBr. But compound III does not have methyl ketonic group therefore, it will not react with NaOBr.
Thus, statement B is correct.
C) Compound IV on acid hydrolysis gives ${C_2}{H_5}COOH$ and MeOH.
Acidic hydrolysis $({H^ + }/{H_2}O)$ of compound IV:

Thus, compound IV on acid hydrolysis gives $MeCOOH$ and EtOH. Hence, statement C is incorrect.
D) Compound V on heating is decarboxylated to propane.
Compound V is:

You must know that only $\beta $- keto acids under decarboxylation. General representation of $\beta $- keto acids is:

But compound IV is not $\beta $- keto acid. Thus, on heating, it will not undergo decarboxylation. Hence, statement D is incorrect.
Therefore, among all the given statements, statement A and B are correct. Thus, option A and B are the answers.
Note: Lucas reagent is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride $(ZnC{l_2})$ in conc. hydrochloric acid. Lucas reagent is used to distinguish the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. All alcohols show turbidity with Lucas reagent but they differ in the time taken for showing the turbidity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




