
How will you convert:
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanal to propan-2-ol
Answer
521k+ views
Hint: - (i )In conversion of propene to propan-1-ol, oxidation reaction takes place. Oxidation reaction is the reaction in which oxygen is added to a compound. To convert propene to propan-1-ol, we will use the method of reaction of propene with peroxide.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Reaction of alkene with hydrogen halide in presence of peroxide results Anti Markovnikov’s addition. Anti Markovnikov’s addition states that in reaction of alkene with hydrogen halide, hydrogen is added to the carbon atom of the double bond which is bonded to least number of hydrogen atoms and the halide atom is boned to the another carbon atom of double bond.

The produced alkyl halide reacts with KOH followed by heating produces propan-1-ol.
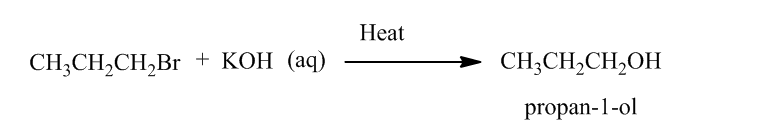
Note:
The other method to produce propan-1-ol from propene is hydroboration oxidation reaction. In this reaction, reaction of diborane $\left( {{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$with propene produces trialkyl boranes (addition product). Then, the oxidation trialkyl boranes to alcohol takes place by ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}$(peroxide) in presence of a base $\left( {{\rm{NaOH}}} \right)$.
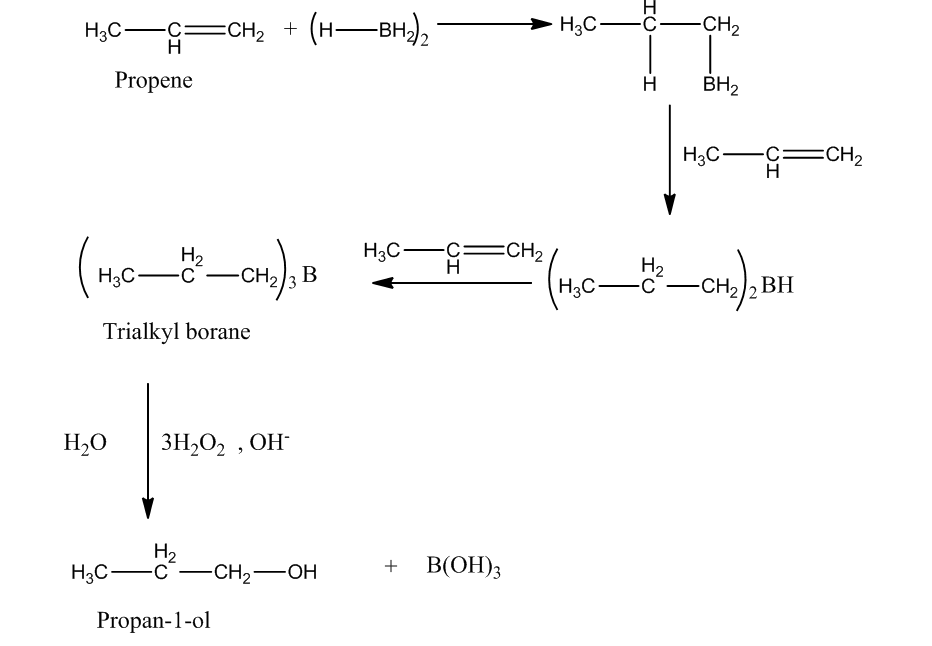
(ii)
Hint:
In conversion of ethanal to propan-2-ol, the carbon atom increases by one. So, we will use Grignard reagent so, that, parent chain can be increased by one carbon atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
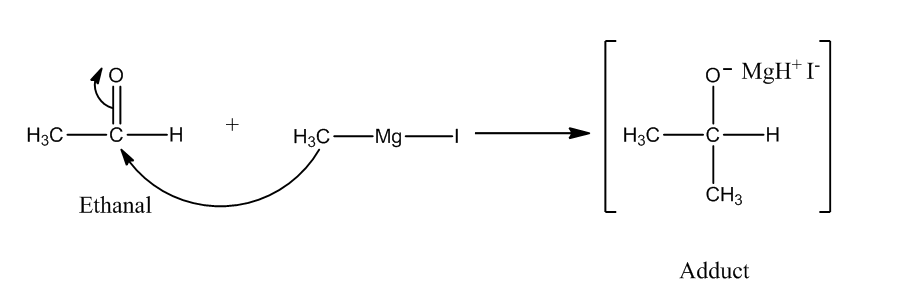
The reaction of Grignard reagent with carbonyl compounds produces alcohol. We need one more carbon atom than the original reactant. So, we have to use ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{MgI}}$ as the Grignard reagent.
Step 1: The nucleophilic attack of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group produces an adduct.
Step2: Hydrolysis of adduct produces an alcohol.
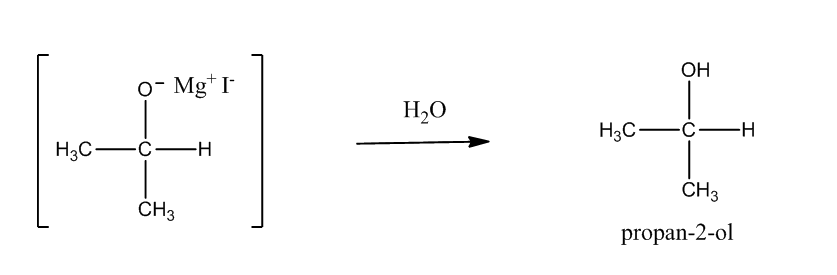
Note: It is possible to get confused in taking Grignard reagent for the conversion of ethanal to propan-2-ol. You have to observe the number of carbon atoms in reactant and the product. In the given question, one more carbon atom is present in product than the reactant. So, Grignard reagent has only one carbon atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Reaction of alkene with hydrogen halide in presence of peroxide results Anti Markovnikov’s addition. Anti Markovnikov’s addition states that in reaction of alkene with hydrogen halide, hydrogen is added to the carbon atom of the double bond which is bonded to least number of hydrogen atoms and the halide atom is boned to the another carbon atom of double bond.

The produced alkyl halide reacts with KOH followed by heating produces propan-1-ol.

Note:
The other method to produce propan-1-ol from propene is hydroboration oxidation reaction. In this reaction, reaction of diborane $\left( {{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$with propene produces trialkyl boranes (addition product). Then, the oxidation trialkyl boranes to alcohol takes place by ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}$(peroxide) in presence of a base $\left( {{\rm{NaOH}}} \right)$.

(ii)
Hint:
In conversion of ethanal to propan-2-ol, the carbon atom increases by one. So, we will use Grignard reagent so, that, parent chain can be increased by one carbon atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The reaction of Grignard reagent with carbonyl compounds produces alcohol. We need one more carbon atom than the original reactant. So, we have to use ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{MgI}}$ as the Grignard reagent.
Step 1: The nucleophilic attack of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group produces an adduct.

Step2: Hydrolysis of adduct produces an alcohol.

Note: It is possible to get confused in taking Grignard reagent for the conversion of ethanal to propan-2-ol. You have to observe the number of carbon atoms in reactant and the product. In the given question, one more carbon atom is present in product than the reactant. So, Grignard reagent has only one carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




