
Describe the method of preparation of acetone in the laboratory and give the chemical equation with a labeled diagram?
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: There are many methods for the preparation of acetone in a laboratory. One can elaborate any one reaction like the dry distillation of anhydrous calcium acetate or the method which is currently used widely in the preparation of acetone which is by using the propylene.
Complete step by step answer:
1) Acetone is a very important chemical ingredient and used for many other purposes in the laboratory. Hence, its preparation method is also very important in order to get a higher yield of acetone.
2) There are many methods of preparation of acetone but we are going to discuss the method which is widely used nowadays in industries and has a higher yield of approximately $83\% $ which is cumene process.
3) In the cumene process, the acetone and phenol are produced by using benzene and propylene. In this reaction, a very small amount of radical initiator is used as a reagent in presence of atmospheric oxygen.
4) This is a widely used chemical method for the production of acetone as it uses very cheap raw material chemicals such as benzene and propylene which yields highly commercial products phenol and acetone.
5) The chemical reaction will be as follows,
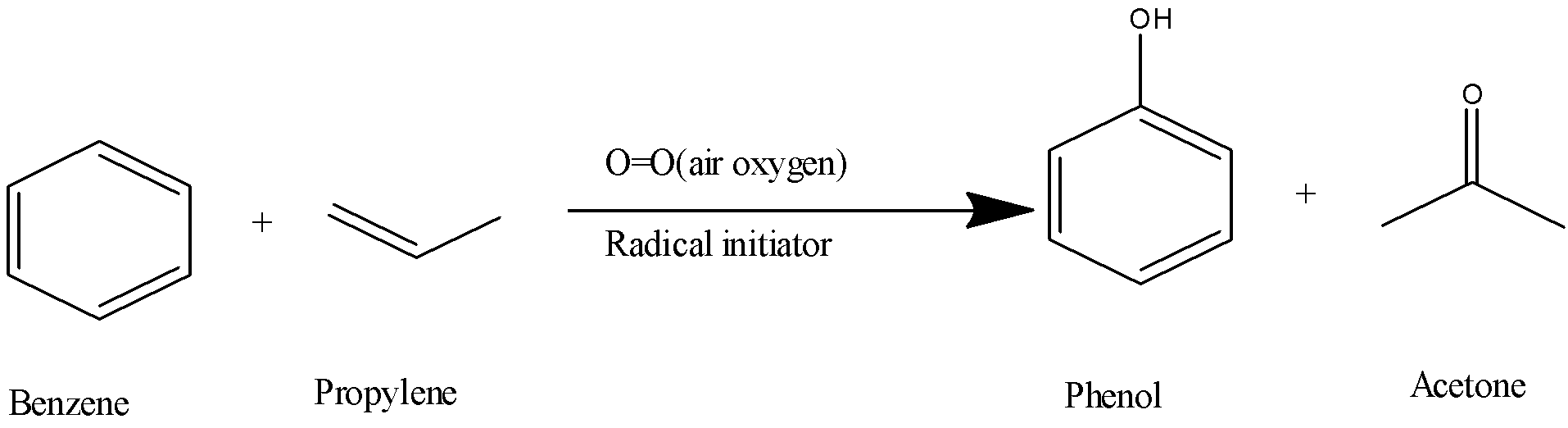
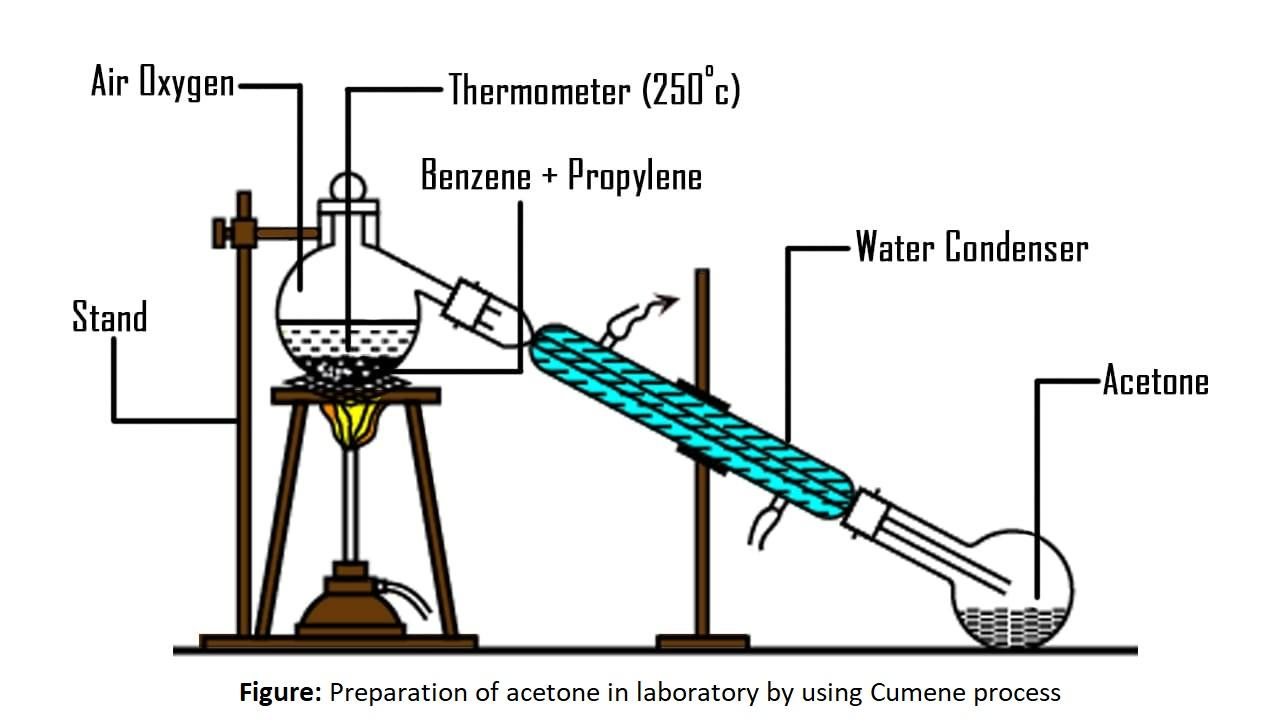
6) The labelled diagram for this reaction is as follows,
Additional information: Some alternative methods for the preparation of acetone are bellowed,
1) Acetone can also be prepared by dry distillation of calcium acetate which is shown below,
${\left( {C{H_3}COOH} \right)_2}Ca\xrightarrow{{Heat}}C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
2) Another method to prepare acetone is by doing dehydration of alcohol i.e. $2 - $propanol. Dehydration of alcohol will form the carbonyl group on the carbon atom which has an alcohol group on it.
$C{H_3} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{Cu/{{300}^0}C}}C{H_3} - CO - C{H_3}$
Note:
The radical initiator used in the above reaction starts the reaction by activating the benzene ring for the reaction. Benzene is a very stable compound that does not take part in reaction very easily, so we have to use a proper catalyst to initiate the reaction which in the above case a radical initiator is used. The atmospheric oxygen acts as an oxidizing agent.
Complete step by step answer:
1) Acetone is a very important chemical ingredient and used for many other purposes in the laboratory. Hence, its preparation method is also very important in order to get a higher yield of acetone.
2) There are many methods of preparation of acetone but we are going to discuss the method which is widely used nowadays in industries and has a higher yield of approximately $83\% $ which is cumene process.
3) In the cumene process, the acetone and phenol are produced by using benzene and propylene. In this reaction, a very small amount of radical initiator is used as a reagent in presence of atmospheric oxygen.
4) This is a widely used chemical method for the production of acetone as it uses very cheap raw material chemicals such as benzene and propylene which yields highly commercial products phenol and acetone.
5) The chemical reaction will be as follows,

6) The labelled diagram for this reaction is as follows,

Additional information: Some alternative methods for the preparation of acetone are bellowed,
1) Acetone can also be prepared by dry distillation of calcium acetate which is shown below,
${\left( {C{H_3}COOH} \right)_2}Ca\xrightarrow{{Heat}}C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
2) Another method to prepare acetone is by doing dehydration of alcohol i.e. $2 - $propanol. Dehydration of alcohol will form the carbonyl group on the carbon atom which has an alcohol group on it.
$C{H_3} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{Cu/{{300}^0}C}}C{H_3} - CO - C{H_3}$
Note:
The radical initiator used in the above reaction starts the reaction by activating the benzene ring for the reaction. Benzene is a very stable compound that does not take part in reaction very easily, so we have to use a proper catalyst to initiate the reaction which in the above case a radical initiator is used. The atmospheric oxygen acts as an oxidizing agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




