
DNA strands are antiparallel because of
A. H-bonds
B. Phosphodiester bonds
C. Disulfide bonds
D. Peptide bonds
Answer
606.6k+ views
Hint: The bonds resulting in the antiparallel polarity of DNA double-strand are usually formed between a highly electronegative atom and an element of group 1. It can either form triple or double bonds between nitrogenous bases.
Complete answer:
The DNA polymerases that replicate DNA and transcribe RNA from DNA can read the template strand only in the 3' to 5' direction to synthesize in the 5' to 3' directions. The main reason for this antiparallel nature of the DNA is stability. The phosphodiester bond links the phosphate group to the hydroxyl group of the sugar molecule, due to which the DNA polymer has two free ends, the 3’ end and the 5’end. Now only if these two strands are present in an anti-parallel fashion, the stability obtained will be maximum. The strands can also be parallel but, in that case, no triple hydrogen bond between guanine and cytosine nitrogenous bases will occur and this will make it less stable. DNA replication will also be impossible if the strands are not arranged in anti-parallel fashion. Further stacking of base pairs occurs in anti-parallel conditions and this results in base stacking interactions which provide further stability.
Additional Information:
Some structural features of DNA are:
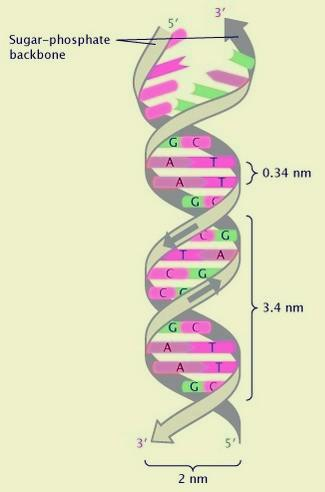
- Nucleotides are composed of sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Many nucleotides join together by a phosphodiester bond to form a polynucleotide structure.
- Three types of bonds are present in DNA. N-glycosidic bonds are present between the nitrogenous base and pentose sugar. The phosphodiester bond is formed between 5’ carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide and 3’ carbon of another sugar of the next nucleotide. Hydrogen bonds are present between nitrogenous bases in a base pair. Three hydrogen bonds are present between guanine and cytosine. Two hydrogen bonds are present between adenine and thymine.
- The polynucleotide chain has sugar and phosphate backbone and bases are present at right angles to it.
So, the correct answer is, “DNA strands are antiparallel because of H-bonds.”
Note: The main reason why DNA strands are antiparallel is due to the high level of stability achieved in an antiparallel configuration. DNA can also exist in parallel configuration but the base pairing will be different (reverse Watson and Crick base pairing) and stability will be less. But in this question, the most appropriate answer would be hydrogen bonds.
Complete answer:
The DNA polymerases that replicate DNA and transcribe RNA from DNA can read the template strand only in the 3' to 5' direction to synthesize in the 5' to 3' directions. The main reason for this antiparallel nature of the DNA is stability. The phosphodiester bond links the phosphate group to the hydroxyl group of the sugar molecule, due to which the DNA polymer has two free ends, the 3’ end and the 5’end. Now only if these two strands are present in an anti-parallel fashion, the stability obtained will be maximum. The strands can also be parallel but, in that case, no triple hydrogen bond between guanine and cytosine nitrogenous bases will occur and this will make it less stable. DNA replication will also be impossible if the strands are not arranged in anti-parallel fashion. Further stacking of base pairs occurs in anti-parallel conditions and this results in base stacking interactions which provide further stability.
Additional Information:
Some structural features of DNA are:

- Nucleotides are composed of sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Many nucleotides join together by a phosphodiester bond to form a polynucleotide structure.
- Three types of bonds are present in DNA. N-glycosidic bonds are present between the nitrogenous base and pentose sugar. The phosphodiester bond is formed between 5’ carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide and 3’ carbon of another sugar of the next nucleotide. Hydrogen bonds are present between nitrogenous bases in a base pair. Three hydrogen bonds are present between guanine and cytosine. Two hydrogen bonds are present between adenine and thymine.
- The polynucleotide chain has sugar and phosphate backbone and bases are present at right angles to it.
So, the correct answer is, “DNA strands are antiparallel because of H-bonds.”
Note: The main reason why DNA strands are antiparallel is due to the high level of stability achieved in an antiparallel configuration. DNA can also exist in parallel configuration but the base pairing will be different (reverse Watson and Crick base pairing) and stability will be less. But in this question, the most appropriate answer would be hydrogen bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




