
Draw a labelled diagram in the proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: In terms of biology, the word budding can be defined as a form of asexual reproduction. This process includes the development of an individual from a few propagative functional and structural points of the parent organism. In the case of some species, the buds may be produced from just about any end of the body of the organism. However, on the other hand, budding is constrained to specific areas.
Complete answer:
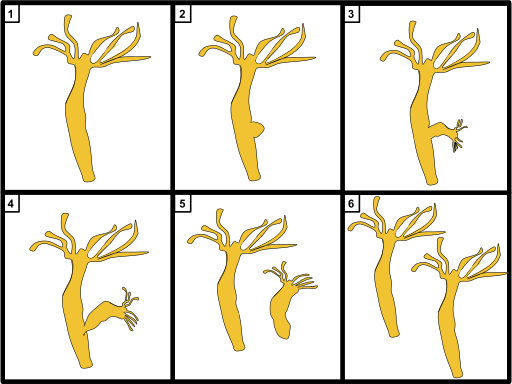
In the image:
1. Represents Hydra plant
2. Represents growth of hydra starts
3. Represents a new bud starts forming in the hydra
4. Represents that the bud growth is complete
5. Represents that the new bud detaches from the parent plant of hydra
6. Represents new hydra plants grows and cycle of budding in hydra finish
When we talk about organisms such as hydra, we can say that they use reformative cells for imitation in the procedure of budding.
In plants like a hydra, a bud-like structure progresses as an extension due to the reason of repeated division of the cell at one precise site. As we know, such plants like hydra make the buds grow on the surface of their bodies. Thus, we can say that in plants like a hydra, these buds progress into minute individuals. However, on the other hand, when these individuals get to fully mature, they get to detach from the paternal body. Besides, they turn out to be new independent individuals.
In short, these buds progress and advance into many tiny individuals. Also, at the time when they fully mature, they get separated from the parental body and turn out to be new autonomous individuals.
Note: The internal budding is called endodyogeny. It is the process of asexual reproduction. In general, this process is favored by many types of parasites, such as Toxoplasma gondii. This process normally comprises an uncommon procedure wherein the two offspring cells are formed interior to a mother cell and then is disbursed by the progenies well to their departure.
We need to note that the Endopolygeny is the section of the study of various organisms that reproduce at once through the process of internal budding.
Complete answer:

In the image:
1. Represents Hydra plant
2. Represents growth of hydra starts
3. Represents a new bud starts forming in the hydra
4. Represents that the bud growth is complete
5. Represents that the new bud detaches from the parent plant of hydra
6. Represents new hydra plants grows and cycle of budding in hydra finish
When we talk about organisms such as hydra, we can say that they use reformative cells for imitation in the procedure of budding.
In plants like a hydra, a bud-like structure progresses as an extension due to the reason of repeated division of the cell at one precise site. As we know, such plants like hydra make the buds grow on the surface of their bodies. Thus, we can say that in plants like a hydra, these buds progress into minute individuals. However, on the other hand, when these individuals get to fully mature, they get to detach from the paternal body. Besides, they turn out to be new independent individuals.
In short, these buds progress and advance into many tiny individuals. Also, at the time when they fully mature, they get separated from the parental body and turn out to be new autonomous individuals.
Note: The internal budding is called endodyogeny. It is the process of asexual reproduction. In general, this process is favored by many types of parasites, such as Toxoplasma gondii. This process normally comprises an uncommon procedure wherein the two offspring cells are formed interior to a mother cell and then is disbursed by the progenies well to their departure.
We need to note that the Endopolygeny is the section of the study of various organisms that reproduce at once through the process of internal budding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




