
Draw a labelled diagram of a nucleosome, where is it found in the cell?
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: Nucleosomes carry information inherited epigenetically in the form of their core histones. The position of the nucleosome is not random in the genome. The position of each nucleosome in the cell is important because it determines the accessibility of DNA to regulatory proteins.
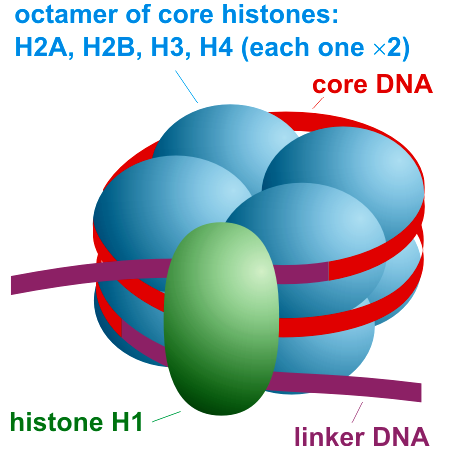
Complete step by step answer: In eukaryotes, a nucleosome is a basic structural unit of DNA packaging. Its structure consists of a segment of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins. It resembles a thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Every nucleosome is composed of less than two turns of DNA wound around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are called histone octamers. One histone octamer comprises two copies of each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Nucleosome positioning indicates the position of nucleosomes with respect to genomic DNA sequence. Nucleosome positioning is a dynamic process; it is sequencing-based mapping and approaches to identify the positions of individual nucleosomes at a specific time in a single cell. DNA is compacted into nucleosomes to fit in the cell nucleus. Along with nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is condensed by being folded into a series of complex structures which eventually forms a chromosome. Each human cell has around 30 million nucleosomes.
Additional information: Nucleosomes were first observed under the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins in 1974. Roger Kornberg gave the structure as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA.
Note: The linker histones such as H1 and its similar histone proteins are involved in chromatin compaction. They are at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble beads on a string of DNA under an electron microscope.
Complete step by step answer: In eukaryotes, a nucleosome is a basic structural unit of DNA packaging. Its structure consists of a segment of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins. It resembles a thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Every nucleosome is composed of less than two turns of DNA wound around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are called histone octamers. One histone octamer comprises two copies of each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Nucleosome positioning indicates the position of nucleosomes with respect to genomic DNA sequence. Nucleosome positioning is a dynamic process; it is sequencing-based mapping and approaches to identify the positions of individual nucleosomes at a specific time in a single cell. DNA is compacted into nucleosomes to fit in the cell nucleus. Along with nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is condensed by being folded into a series of complex structures which eventually forms a chromosome. Each human cell has around 30 million nucleosomes.

Additional information: Nucleosomes were first observed under the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins in 1974. Roger Kornberg gave the structure as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA.
Note: The linker histones such as H1 and its similar histone proteins are involved in chromatin compaction. They are at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble beads on a string of DNA under an electron microscope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




