
Explain $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination.
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: When haloalkanes with $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ hydrogen atoms are boiled with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, they undergo the elimination of hydrogen halide $\text{ }\left( \text{HX} \right)\text{ }$ resulting in the formation of alkenes. These reactions are known as the dehydrohalogenation or $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination reactions. The major product is obtained by Saytzeff’s rule.
Complete Solution :
When haloalkanes with $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ hydrogen atoms are boiled with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, they undergo the elimination of hydrogen halide $\text{ }\left( \text{HX} \right)\text{ }$ resulting in the formation of alkenes. The general reaction of the dehydrohalogenation of the haloalkanes is as shown below:
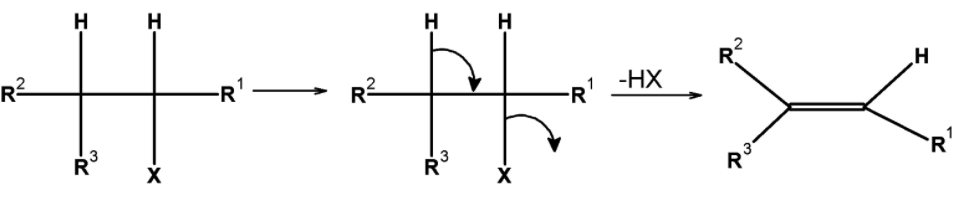
- These reactions are called the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination reactions because the hydrogen atom present at the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position of haloalkanes (i.e. at the carbon atom next to that which carries the halogen) is removed.
- These reactions are also known as the dehydrohalogenation reaction (removal of hydrogen halide) reactions. The elimination reaction occurs by the abstraction of a proton from a carbon atom next to the carbon bearing halogen atom and halide ion is also resulting in a new pi-bond.
- The 1-Bromobutane reacted with the alcoholic potassium hydroxide $\text{ KOH }$ .here, bromine (halogen group) is at the $\text{ }\alpha \text{ }$ position and hydrogen is at the $\text{ }\beta \text{ }$ position. when boiled with $\text{ KOH }$, hydrogen atom transfers its electron pair to the adjacent carbon-carbon bond, and bromide is removed from the molecule. This forms a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon atom and gives a1-butene as the product.
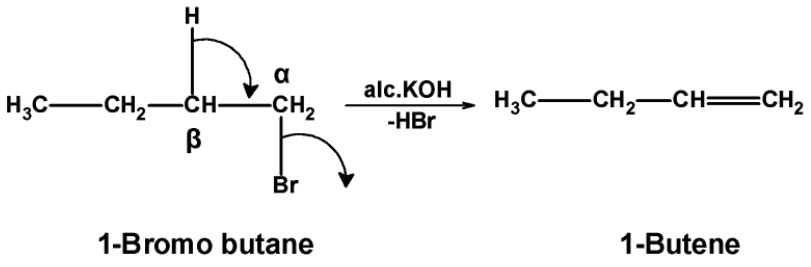
Thus, 1-Bromobutane on reaction with alcohol $\text{ KOH }$ gives 1-butene.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In the case of haloalkanes which has more than one $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position can eliminate the hydrogen halide in two different ways, then that alkene will be preferred in which carbon atoms joined by the double bond are maximum alkylated i.e. contain the largest number of alkyl groups. This rule is called Saytzeff’s rule. The rule gives the major product formed in the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination reaction. Here ,1-bromobutane has one $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position thus there would be only one major product.
Complete Solution :
When haloalkanes with $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ hydrogen atoms are boiled with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, they undergo the elimination of hydrogen halide $\text{ }\left( \text{HX} \right)\text{ }$ resulting in the formation of alkenes. The general reaction of the dehydrohalogenation of the haloalkanes is as shown below:

- These reactions are called the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination reactions because the hydrogen atom present at the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position of haloalkanes (i.e. at the carbon atom next to that which carries the halogen) is removed.
- These reactions are also known as the dehydrohalogenation reaction (removal of hydrogen halide) reactions. The elimination reaction occurs by the abstraction of a proton from a carbon atom next to the carbon bearing halogen atom and halide ion is also resulting in a new pi-bond.
- The 1-Bromobutane reacted with the alcoholic potassium hydroxide $\text{ KOH }$ .here, bromine (halogen group) is at the $\text{ }\alpha \text{ }$ position and hydrogen is at the $\text{ }\beta \text{ }$ position. when boiled with $\text{ KOH }$, hydrogen atom transfers its electron pair to the adjacent carbon-carbon bond, and bromide is removed from the molecule. This forms a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon atom and gives a1-butene as the product.

Thus, 1-Bromobutane on reaction with alcohol $\text{ KOH }$ gives 1-butene.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In the case of haloalkanes which has more than one $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position can eliminate the hydrogen halide in two different ways, then that alkene will be preferred in which carbon atoms joined by the double bond are maximum alkylated i.e. contain the largest number of alkyl groups. This rule is called Saytzeff’s rule. The rule gives the major product formed in the $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ elimination reaction. Here ,1-bromobutane has one $\text{ }\beta -\text{ }$ position thus there would be only one major product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




