
For the preparation of chloroethane
A. HCl gas is passed through ethanol.
B. ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine.
C. Ethyl sulphide is treated with hydrogen chloride.
D. Any of the above methods can be employed.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:To prepare chloroethane from ethanol, reduction of alcohol group is required. Ethanol gives nucleophilic substitution with hydrochloric acid. But this reaction requires a catalyst. Thionyl forms ethoxide ion and dimethyl amine or pyridine helps to generate a chloride nucleophile.
Complete answer:
Alcohol gives nucleophilic substitution with hydrochloric acid. But this reaction requires a catalyst such as zinc chloride. The tertiary alcohol is more reactive for this reaction than the primary alcohol. Ethanol is the primary alcohol and the catalyst is also not present, so chloroethane cannot be prepared by passing the hydrochloric gas through ethanol.
Reaction, when ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine, is as follows:
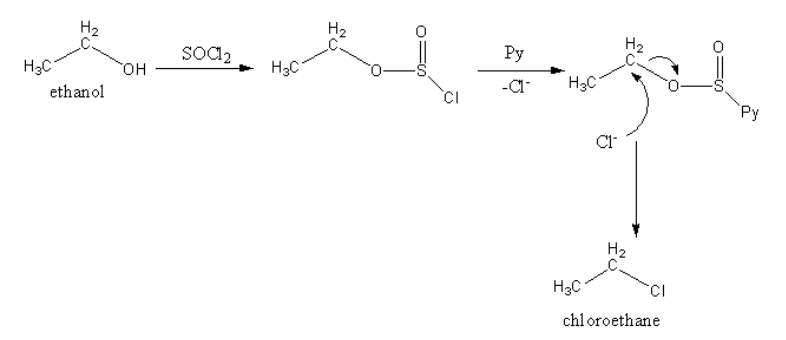
Ethyl sulphide on treating with hydrogen chloride does not give chloroethane.
So, for the preparation of chloroethane, ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine.
Therefore, option (B) ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine, is correct.
Note:
The reaction of an alcohol with thionyl chloride to generate alkyl halide is known as the Darzens process. The reaction of an alcohol with hydrochloric acid in presence of a catalyst such as zinc chloride is known as the Lucas test. This test is used to differentiate alcohols. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, so a carbocation generates during the reaction so, the rate of reaction depends upon the stability of the carbocation. Thus Lucas tests differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Complete answer:
Alcohol gives nucleophilic substitution with hydrochloric acid. But this reaction requires a catalyst such as zinc chloride. The tertiary alcohol is more reactive for this reaction than the primary alcohol. Ethanol is the primary alcohol and the catalyst is also not present, so chloroethane cannot be prepared by passing the hydrochloric gas through ethanol.
Reaction, when ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine, is as follows:

Ethyl sulphide on treating with hydrogen chloride does not give chloroethane.
So, for the preparation of chloroethane, ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine.
Therefore, option (B) ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride in the presence of dimethyl amine or pyridine, is correct.
Note:
The reaction of an alcohol with thionyl chloride to generate alkyl halide is known as the Darzens process. The reaction of an alcohol with hydrochloric acid in presence of a catalyst such as zinc chloride is known as the Lucas test. This test is used to differentiate alcohols. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, so a carbocation generates during the reaction so, the rate of reaction depends upon the stability of the carbocation. Thus Lucas tests differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




