
What is the function of the spleen in the body?
Answer
502.8k+ views
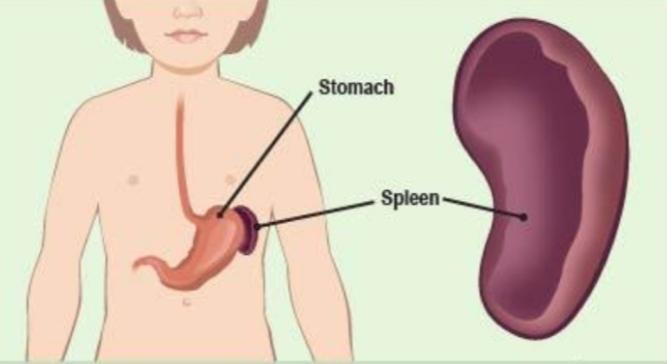
Hint: The spleen is a lymphoid organ that is situated in the left part of the abdomen. It is a purple colored organ that varies in size and shape among people. Usually, it is fish shaped and 4 inches long. The rig cage protects the spleen. It is present in all vertebrates.
Complete answer:
The spleen is a part of the lymphatic system that is located under the diaphragm. The lymphatic system helps in the removal of some substances, activating the white blood cells and generating an immune response. The spleen plays various important roles in the human body. It is primarily related to red blood cells and the lymphoid system. The functions of spleen are-
As a lymphoid organ, it is primarily involved in the filtration of blood and generates immune response. When foreign particles or pathogens enter the body, it activates the white blood cells to fight off with these pathogens. Thus, the spleen protects the body from a number of disease causing pathogens by detecting them.
The old and damaged red blood cells (RBCs) are destroyed in the spleen. For this reason, it is also called the graveyard of RBCs.
It also provides protection against some bacteria that cause pneumonia and meningitis.
It is involved in recycling of iron and acts as a blood reserve during hemorrhagic shock. The spleen stores RBCs, WBCs (white blood cells) and platelets.
In a foetus, it helps in the formation of all types of blood cells.
Note:
The spleen also has a clinical significance. It helps in the detection of certain diseases. For example- splenomegaly. Splenomegaly is a condition in which the spleen becomes enlarged. In children, viral infection is the most common cause of splenomegaly. In adults, it can be caused due to several diseases such as viral mononucleosis, leukemia, lymphoma etc.
Complete answer:
The spleen is a part of the lymphatic system that is located under the diaphragm. The lymphatic system helps in the removal of some substances, activating the white blood cells and generating an immune response. The spleen plays various important roles in the human body. It is primarily related to red blood cells and the lymphoid system. The functions of spleen are-
As a lymphoid organ, it is primarily involved in the filtration of blood and generates immune response. When foreign particles or pathogens enter the body, it activates the white blood cells to fight off with these pathogens. Thus, the spleen protects the body from a number of disease causing pathogens by detecting them.
The old and damaged red blood cells (RBCs) are destroyed in the spleen. For this reason, it is also called the graveyard of RBCs.
It also provides protection against some bacteria that cause pneumonia and meningitis.
It is involved in recycling of iron and acts as a blood reserve during hemorrhagic shock. The spleen stores RBCs, WBCs (white blood cells) and platelets.
In a foetus, it helps in the formation of all types of blood cells.

Note:
The spleen also has a clinical significance. It helps in the detection of certain diseases. For example- splenomegaly. Splenomegaly is a condition in which the spleen becomes enlarged. In children, viral infection is the most common cause of splenomegaly. In adults, it can be caused due to several diseases such as viral mononucleosis, leukemia, lymphoma etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




