
What happens when two diodes are in parallel.
Answer
494.7k+ views
Hint: A diode is an electrical component with two terminals that conducts electricity predominantly in one direction. On one end, it has a lot of resistance and on the other, it has a lot of resistance. Let's take a closer look at what a diode is in this post. Diodes are used to restrict the voltage in circuits as well as to convert AC to DC. To get the most out of diodes, semiconductors like silicon and germanium are employed. Despite the fact that they both transfer electricity in the same direction, the manner in which they do so differs. Diodes come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its own set of uses.
Complete answer:
The terms "parallel connection" and "two common points" refer to how the components are linked across each other. The current varies by component, but the voltage drop is constant.
When diodes are linked in series, the same pattern emerges. Carrying capacity is currently increasing. On both sides of the resulting diode, there is no conduction. For steady state circumstances, diodes of the same kind with the same voltage drops can be utilised. The reverse blocking voltages of the parallel diodes would be the same in this scenario. When utilising diodes with the same forward voltage drops, there are a few things to keep in mind:
The heat sinks on the diodes should be the same.
When cooling is required, they should all be chilled at the same time.
The below figure showing two diodes connected in parallel:
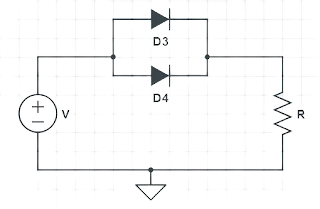
The current carrying capability of the diodes rises when they are linked in parallel. If the load current is higher than a single diode's current rating, several diodes can be linked in parallel to raise the forward current rating. Because the diodes have differing forward bias characteristics, current will not flow uniformly through them if they are linked in parallel.
Note :
A diode's most frequent purpose is to allow an electric current to flow in one direction (the forward direction of the diode) while blocking it in the opposing direction (the reverse direction). As a result, the diode may be thought of as an electrical check valve. Rectification is the term for this unidirectional characteristic, which is utilised to convert alternating current (ac) to direct current (dc) (dc). Diodes and other rectifier types can be employed to extract modulation from radio signals in radio receivers.
Complete answer:
The terms "parallel connection" and "two common points" refer to how the components are linked across each other. The current varies by component, but the voltage drop is constant.
When diodes are linked in series, the same pattern emerges. Carrying capacity is currently increasing. On both sides of the resulting diode, there is no conduction. For steady state circumstances, diodes of the same kind with the same voltage drops can be utilised. The reverse blocking voltages of the parallel diodes would be the same in this scenario. When utilising diodes with the same forward voltage drops, there are a few things to keep in mind:
The heat sinks on the diodes should be the same.
When cooling is required, they should all be chilled at the same time.
The below figure showing two diodes connected in parallel:

The current carrying capability of the diodes rises when they are linked in parallel. If the load current is higher than a single diode's current rating, several diodes can be linked in parallel to raise the forward current rating. Because the diodes have differing forward bias characteristics, current will not flow uniformly through them if they are linked in parallel.
Note :
A diode's most frequent purpose is to allow an electric current to flow in one direction (the forward direction of the diode) while blocking it in the opposing direction (the reverse direction). As a result, the diode may be thought of as an electrical check valve. Rectification is the term for this unidirectional characteristic, which is utilised to convert alternating current (ac) to direct current (dc) (dc). Diodes and other rectifier types can be employed to extract modulation from radio signals in radio receivers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




