
In E-Z isomers, E isomer is that in which:
A) The smaller groups are on the same sides of the double bond.
B) The bulkier groups are on the same side of double bond
C) The smaller groups are on opposite side of double bond
D) The bulkier groups are on the opposite side of the double bond.
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: This nomenclature is used for alkenes where all the atoms attached are different in nature, it means when all atoms attached are different. We have to firstly assign them priority and then see that the same numbering groups are on the same side or different. There can be numbering or we can say them as smaller groups or bulkier groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have knowledge about cis and trans isomers in which the same groups which are on same side called as cis isomer and when same groups are on different sides then it will termed as trans isomer. Now a question arises: what is E and Z nomenclature. So, understand it as this that you are having an alkene in which all four bonds from two carbons are different and let them called as A, B, E and D thus it will have structure like this:
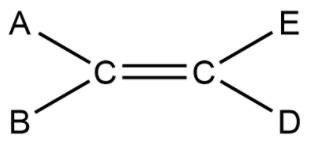
Now these groups that are attached are just for your understanding that all groups are different. Now we have groups in place of these and on the basis of their size we can assign them priority as a small group and bulky group. Note that when the small group that are attached on same side of the carbon atom that isomer is called Z (Zussamen) and when the groups are on opposite sides they are called as E (Entegagen) isomer.
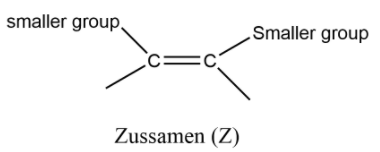
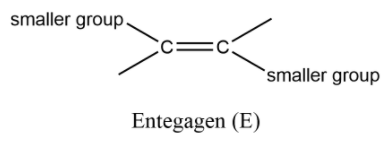
Note: : You can make it easy for you by considering the bulky groups on the same side and opposite sides. Now we can assign them priority by numbering them on the basis of atomic number. The group or atom having larger atomic number is termed as while the second atom or group is termed as . This same is assigned for the second carbon atom of alkene. If the same numbering groups get on the same side then it is Z otherwise it will be E.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have knowledge about cis and trans isomers in which the same groups which are on same side called as cis isomer and when same groups are on different sides then it will termed as trans isomer. Now a question arises: what is E and Z nomenclature. So, understand it as this that you are having an alkene in which all four bonds from two carbons are different and let them called as A, B, E and D thus it will have structure like this:

Now these groups that are attached are just for your understanding that all groups are different. Now we have groups in place of these and on the basis of their size we can assign them priority as a small group and bulky group. Note that when the small group that are attached on same side of the carbon atom that isomer is called Z (Zussamen) and when the groups are on opposite sides they are called as E (Entegagen) isomer.


Note: : You can make it easy for you by considering the bulky groups on the same side and opposite sides. Now we can assign them priority by numbering them on the basis of atomic number. The group or atom having larger atomic number is termed as while the second atom or group is termed as . This same is assigned for the second carbon atom of alkene. If the same numbering groups get on the same side then it is Z otherwise it will be E.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




