
In the embryos of atypical dicot and grass, the true homologous structure is.
(a)Coleorhiza and coleoptile
(b)Coleoptile and scutellum
(c)Cotyledons and scutellum
(d)Hypocotyl and radicle
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: Liable on the number it, the seeds have been divided into two categories, which are monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous seeds. They are generally shield-shaped and are located laterally towards a side of the embryo axis.
Complete answer:
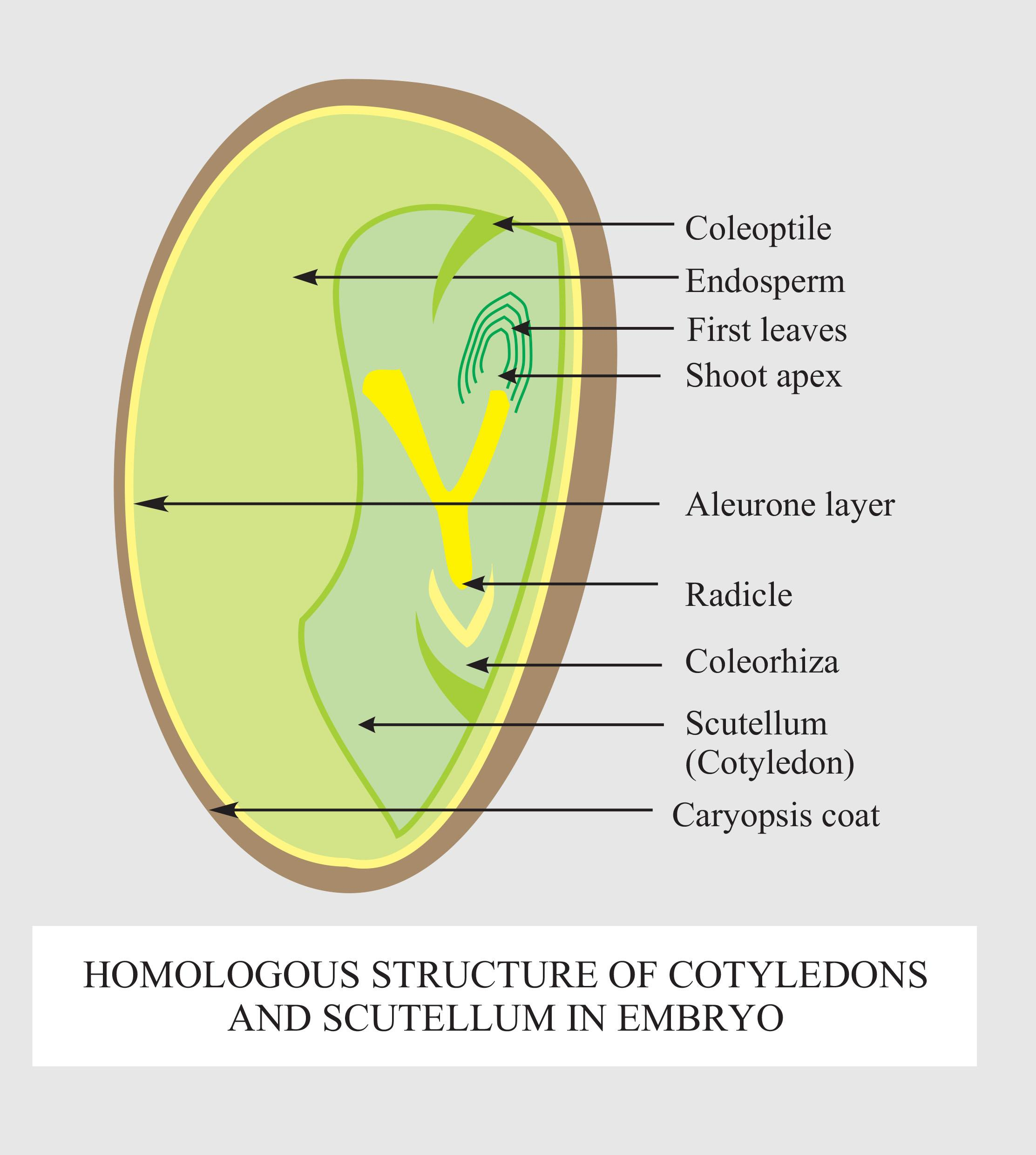
Cotyledon refers to the important part of the embryo present inside the seed. They are the first and the tender leaf emerges when the seed germinates. It is also called the storage unit of a seed, as it provides nutrients to the various parts of an embryo. Cotyledons of the standard dicot embryo are simple structures basically thick and swollen because of storage of food reserves, as they provide nutrients to the different parts of an embryo. The embryo of monocots made up of 1 large and shield-shaped cotyledon referred to as a scutellum present respecting one side (lateral) of the embryonal axis. E.g.: Grass family, Sorghum.
Additional Information: The reserve food in cotyledons is utilized to nurture the growing seedling. The embryo axis has two ends, which are the plumule and radicle. They are further enclosed within a protective cover called the seed coat. A structure known as hilum joins the seed to the fruit. Embryos of a monocotyledonous seed have just one large cotyledon called scutellum. The scutellum is usually shield-shaped and is found laterally towards the side of the embryo axis. As in dicotyledons, the embryo axis of monocotyledons have a shoot tip, plumule, surround during a sheath known as coleoptile and a root tip, radicle, enclosed in coleorhiza. In a monocotyledonous seed, the endosperm is roofed by a proteinous layer called the aleurone layer. Dicotyledons are also known as dicots. They are the groups into which all the flowering plants were equally divided. The name dicotyledons ask the seed to have two embryonic cotyledons. There are approximately 200,000 species of dicotyledons discovered till now.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cotyledons and scutellum’.
Note: The scutellum may also refer to the similarity of a narrow cotyledon in monocots. They are really thin with a high area and serve to absorb nutrients from the endosperm while germination. The number of cotyledons situated is one characteristic employed through botanists to classify the flowering plants.
Complete answer:
Cotyledon refers to the important part of the embryo present inside the seed. They are the first and the tender leaf emerges when the seed germinates. It is also called the storage unit of a seed, as it provides nutrients to the various parts of an embryo. Cotyledons of the standard dicot embryo are simple structures basically thick and swollen because of storage of food reserves, as they provide nutrients to the different parts of an embryo. The embryo of monocots made up of 1 large and shield-shaped cotyledon referred to as a scutellum present respecting one side (lateral) of the embryonal axis. E.g.: Grass family, Sorghum.
Additional Information: The reserve food in cotyledons is utilized to nurture the growing seedling. The embryo axis has two ends, which are the plumule and radicle. They are further enclosed within a protective cover called the seed coat. A structure known as hilum joins the seed to the fruit. Embryos of a monocotyledonous seed have just one large cotyledon called scutellum. The scutellum is usually shield-shaped and is found laterally towards the side of the embryo axis. As in dicotyledons, the embryo axis of monocotyledons have a shoot tip, plumule, surround during a sheath known as coleoptile and a root tip, radicle, enclosed in coleorhiza. In a monocotyledonous seed, the endosperm is roofed by a proteinous layer called the aleurone layer. Dicotyledons are also known as dicots. They are the groups into which all the flowering plants were equally divided. The name dicotyledons ask the seed to have two embryonic cotyledons. There are approximately 200,000 species of dicotyledons discovered till now.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cotyledons and scutellum’.
Note: The scutellum may also refer to the similarity of a narrow cotyledon in monocots. They are really thin with a high area and serve to absorb nutrients from the endosperm while germination. The number of cotyledons situated is one characteristic employed through botanists to classify the flowering plants.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




