
In which stage of development, the embryonic cells form the germinal layers by the movement?
A.Morula
B.Blastula
C.Gastrula
D.Neurula
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Human embryonic development is characterized by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is termed a fetus. The germinal stage refers to the time from fertilization through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus.
Complete answer:Gastrulation is a phase early in the embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula is a single-layered hollow sphere of cells which are reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body e.g. dorsal-ventral and the anterior-posterior, and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut.
In triploblastic organisms, the gastrula is a three-layered structure. These three germ layers are known as the ectoderm which forms the outer layer, mesoderm which is the middle layer, and the inner layer is known as the endoderm. In diploblastic organisms, such as Cnidaria and Ctenophora, the gastrula is made up of only two layers the ectoderm and the endoderm. The two layers are also sometimes known as the hypoblast and epiblast.
Hence, the correct option is (c) Gastrula.
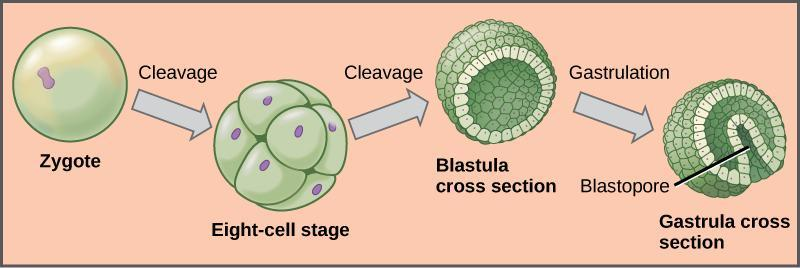
Note:Gastrulation takes place after cleavage and the formation of the blastula. Gastrulation is followed by organogenesis, where individual organs develop within the newly formed germ layers. Each layer gives rise to specific tissues and organs in the developing embryo.
Complete answer:Gastrulation is a phase early in the embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula is a single-layered hollow sphere of cells which are reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body e.g. dorsal-ventral and the anterior-posterior, and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut.
In triploblastic organisms, the gastrula is a three-layered structure. These three germ layers are known as the ectoderm which forms the outer layer, mesoderm which is the middle layer, and the inner layer is known as the endoderm. In diploblastic organisms, such as Cnidaria and Ctenophora, the gastrula is made up of only two layers the ectoderm and the endoderm. The two layers are also sometimes known as the hypoblast and epiblast.
Hence, the correct option is (c) Gastrula.

Note:Gastrulation takes place after cleavage and the formation of the blastula. Gastrulation is followed by organogenesis, where individual organs develop within the newly formed germ layers. Each layer gives rise to specific tissues and organs in the developing embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




