
Lossen rearrangement
Beckmann rearrangement


Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Lossen rearrangement is the arrangement of hydroxamate ester into isocyanate. is known as isocyanate. Hydrolysis of isocyanate gives primary amine. Beckmann rearrangement is the rearrangement of oxime into an amide. $ - {\text{C(O}})N - $ is known as an amide. Amide reacts with bromine in presence of potassium hydroxide to give primary amine is known as the Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Complete answer:
Lossen rearrangement is used for the preparation of isocyanate from hydroxamate ester. The isocyanate is used for the preparation of amine.
The Lossen rearrangement is shown as follows:
From the hydroxamate ester base abstract proton so nitrogen gets a negative charge. The negative charge is delocalized to form a double bond with attached carbon so an alkyl group from carbon shifts to the nitrogen, and isocyanate forms.
Hydrolysis of carbon-nitrogen double bond takes place, so the carbonyl group converts into a carboxylic group. Then base abstract protons from the carboxylic group and the bond shifting leads to the removal of the carbon dioxide. So, the primary amine forms.
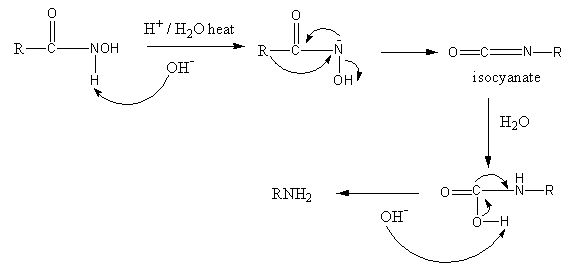
Beckmann rearrangement
Beckmann rearrangement gives amides from oximes. Ketoximes give secondary amides and aldoxime gives primary amides. The reaction is catalysed by acid.
Hydroxy groups of oxime get protonated in presence of acid, so a water molecule removes and nitrogen gets a negative charge. The negatively charged nitrogen attack on alkyl groups of attached carbon, so carbon-nitrogen triple bond forms. Then base attacks on carbon forming an enol form of amide. The enol form tautomerism to give amide.

The amide can be converted into primary amine by reacting the amide with bromine and sodium hydroxide. The reaction of conversion of primary amide into primary amine in presence of bromine with potassium hydroxide is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Here, the amide formed by Beckmann rearrangement is secondary. Secondary amide does not give Hoffmann bromamide reaction. So, ${\text{RC(O)NHR}}$ will not react with ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{KOH}}$.
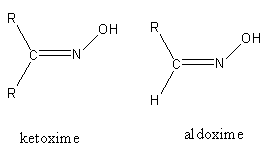
Note: Lossen rearrangement, Beckmann rearrangement and Hofmann reaction, all are used for the preparation of primary amine. Hoffmann bromamide reaction is used for the preparation of primary amine only. The structure of aldoxime and ketoxime is as follows:
Complete answer:
Lossen rearrangement is used for the preparation of isocyanate from hydroxamate ester. The isocyanate is used for the preparation of amine.
The Lossen rearrangement is shown as follows:
From the hydroxamate ester base abstract proton so nitrogen gets a negative charge. The negative charge is delocalized to form a double bond with attached carbon so an alkyl group from carbon shifts to the nitrogen, and isocyanate forms.
Hydrolysis of carbon-nitrogen double bond takes place, so the carbonyl group converts into a carboxylic group. Then base abstract protons from the carboxylic group and the bond shifting leads to the removal of the carbon dioxide. So, the primary amine forms.

Beckmann rearrangement
Beckmann rearrangement gives amides from oximes. Ketoximes give secondary amides and aldoxime gives primary amides. The reaction is catalysed by acid.
Hydroxy groups of oxime get protonated in presence of acid, so a water molecule removes and nitrogen gets a negative charge. The negatively charged nitrogen attack on alkyl groups of attached carbon, so carbon-nitrogen triple bond forms. Then base attacks on carbon forming an enol form of amide. The enol form tautomerism to give amide.

The amide can be converted into primary amine by reacting the amide with bromine and sodium hydroxide. The reaction of conversion of primary amide into primary amine in presence of bromine with potassium hydroxide is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Here, the amide formed by Beckmann rearrangement is secondary. Secondary amide does not give Hoffmann bromamide reaction. So, ${\text{RC(O)NHR}}$ will not react with ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{KOH}}$.
Note: Lossen rearrangement, Beckmann rearrangement and Hofmann reaction, all are used for the preparation of primary amine. Hoffmann bromamide reaction is used for the preparation of primary amine only. The structure of aldoxime and ketoxime is as follows:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




