
What is the meaning of the anti – parallel strands of a DNA molecule?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: The term ‘anti – parallel’ means strands that are extended in opposite directions but parallel in nature. According to the Watson & Crick Model, DNA which is present in the chromosomes of the cell has a double helix structure.
Complete answer:
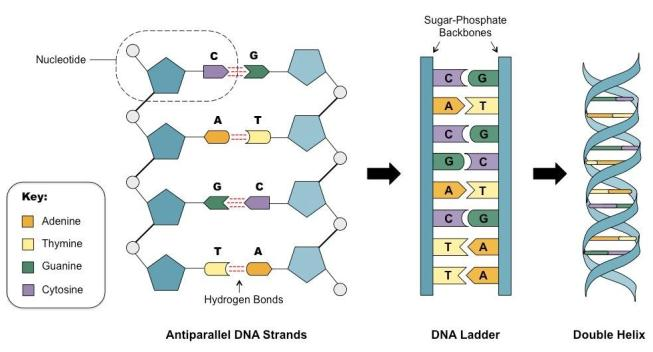
DNA i.e DeoxyRibonucleic Acid is the genetic material which passes from the parent to the offspring & carries morphological as well as genetic characteristics of the organisms. The double helix structure of a DNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains forming a ladder-like structure. The polynucleotide chains are anti – parallel to each other and the nitrogen bases are arranged through each chain.
The anti – parallel strands of a DNA molecule mean the phosphate group present in the start of two DNA strands are in opposite poles. The two strands are twisted to each other. One strand consists of the 3’ – 5’ linkage and the other strand has the opposite 5’ – 3’ linkage. [the 5’ – 3’ indicates 5 prime to 3 prime which is the number of carbons present in the DNA backbone]. The 5’ and 3’ consist of phosphate and hydroxyl groups respectively.
This opposite structural direction of the DNA molecules double helix model denotes the anti – parallel strands of a DNA molecule.
Note:
The double helix structure of DNA was invented by Watson & Crick thus known as the Watson-Crick model. The twisted anti – parallel strands have opposite linkage & contain nitrogen bases and pentose sugar. The purine groups are – Adenine & Guanine. The pyrimidine groups are – Thymine & Cytosine.
Complete answer:
DNA i.e DeoxyRibonucleic Acid is the genetic material which passes from the parent to the offspring & carries morphological as well as genetic characteristics of the organisms. The double helix structure of a DNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains forming a ladder-like structure. The polynucleotide chains are anti – parallel to each other and the nitrogen bases are arranged through each chain.
The anti – parallel strands of a DNA molecule mean the phosphate group present in the start of two DNA strands are in opposite poles. The two strands are twisted to each other. One strand consists of the 3’ – 5’ linkage and the other strand has the opposite 5’ – 3’ linkage. [the 5’ – 3’ indicates 5 prime to 3 prime which is the number of carbons present in the DNA backbone]. The 5’ and 3’ consist of phosphate and hydroxyl groups respectively.
This opposite structural direction of the DNA molecules double helix model denotes the anti – parallel strands of a DNA molecule.
Note:
The double helix structure of DNA was invented by Watson & Crick thus known as the Watson-Crick model. The twisted anti – parallel strands have opposite linkage & contain nitrogen bases and pentose sugar. The purine groups are – Adenine & Guanine. The pyrimidine groups are – Thymine & Cytosine.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




