
Phenol does not decompose \[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] to evolve \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]but picric acid does.
A. True
B. False
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Sodium bicarbonate (\[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]) is a weak base. In presence of acid \[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] dissociate and liberate \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]gas. Draw the structures of both phenol and picric acid and determine their acid strength.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium bicarbonate (\[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]) is a weak base when it reacts with acid it is converted into carbonic acid
(\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]). As carbonic acid is unstable it dissociates into \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]gas and water as follows:
\[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ }} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Now we will draw the structures of both phenol and picric acid and determine their acid strength as both are acidic in nature.
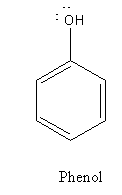
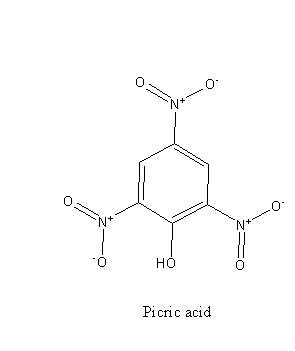
From the structure of phenol and picric acid we can say that picric acid is substituted phenol, there are three electron-withdrawing ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ groups bonded to the ring.
The acidic strength of substituted phenol is dependent on the nature of the substituent.
The electron-withdrawing group decreases the electron density of the phenol ring and stabilizes the negative charge and thus increases the acid strength.
In the case of the picric acid, the substituent is a nitro group (${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ ). It is an electron-withdrawing group so picric acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
As phenol is weak acid it cannot react with \[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] to evolve\[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\].
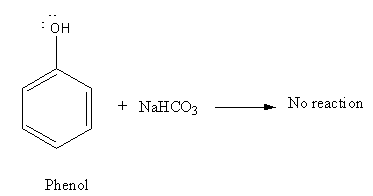
However, picric acid is stronger acid which reacts with base as shown below:
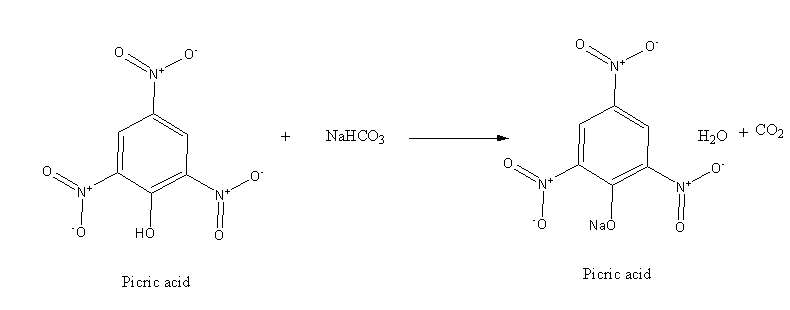
Hence, the given statement is true i.e, option ‘A’ is the correct answer.
Note: Ring activating groups that are electron-donating groups, decrease the strength of acid while a ring deactivating group increases the strength of the acid. So while determining acid strength it is necessary to determine whether the substituent is an electron-donating group or electron-withdrawing group.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium bicarbonate (\[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]) is a weak base when it reacts with acid it is converted into carbonic acid
(\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]). As carbonic acid is unstable it dissociates into \[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]gas and water as follows:
\[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ }} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Now we will draw the structures of both phenol and picric acid and determine their acid strength as both are acidic in nature.


From the structure of phenol and picric acid we can say that picric acid is substituted phenol, there are three electron-withdrawing ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ groups bonded to the ring.
The acidic strength of substituted phenol is dependent on the nature of the substituent.
The electron-withdrawing group decreases the electron density of the phenol ring and stabilizes the negative charge and thus increases the acid strength.
In the case of the picric acid, the substituent is a nitro group (${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ ). It is an electron-withdrawing group so picric acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
As phenol is weak acid it cannot react with \[{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] to evolve\[{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\].

However, picric acid is stronger acid which reacts with base as shown below:

Hence, the given statement is true i.e, option ‘A’ is the correct answer.
Note: Ring activating groups that are electron-donating groups, decrease the strength of acid while a ring deactivating group increases the strength of the acid. So while determining acid strength it is necessary to determine whether the substituent is an electron-donating group or electron-withdrawing group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




