
Phenol is heated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$. The product gives pink colour with alkali. The product is:
A) Phenolphthalein
B) Bakelite
C) Salicylic acid
D) Fluorescein
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Recall the name of a commonly used indicator which gives pink colour with alkali. It is also used in acid-base titrations. Proceed with the chemical reaction of phenol with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$. You should also know the structures of phenol and phthalic anhydride. Examine the characteristics of the product of the reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that when phenol is heated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$. The reaction of phenol with phthalic anhydride is an electrophilic substitution reaction. This reaction can be represented as:
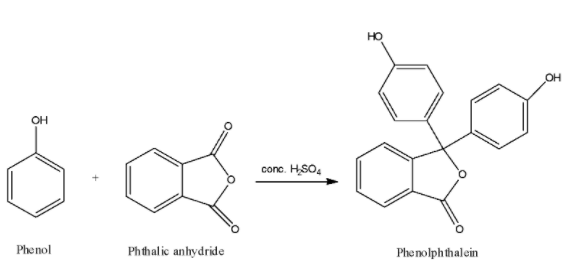
Therefore, when phenol is heated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$, the product we get is phenolphthalein. Phenolphthalein is commonly used in the acid-base titrations because of its unique characteristic of giving different colours in acidic medium and in basic medium. Phenolphthalein with acids or in acidic medium gives colourless solution whereas with base or alkali, phenolphthalein gives pink colour solution.
Therefore, the product which gives pink colour with alkali is phenolphthalein.
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: The chemical formula of phenolphthalein is ${C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_4}$. It is naturally a weak acid and is colourless. But it is used as an indicator in acid-base titrations because it gives a sharp or detectable colour change at the end point in the titration. Indicators don't change colour sharply at only one particular pH instead, they change colour over a narrow range of pH. The pH range at which phenolphthalein changes its colour from colourless (in acidic medium) to pink (in basic medium) is 8.3-10.0.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that when phenol is heated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$. The reaction of phenol with phthalic anhydride is an electrophilic substitution reaction. This reaction can be represented as:

Therefore, when phenol is heated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$, the product we get is phenolphthalein. Phenolphthalein is commonly used in the acid-base titrations because of its unique characteristic of giving different colours in acidic medium and in basic medium. Phenolphthalein with acids or in acidic medium gives colourless solution whereas with base or alkali, phenolphthalein gives pink colour solution.
Therefore, the product which gives pink colour with alkali is phenolphthalein.
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: The chemical formula of phenolphthalein is ${C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_4}$. It is naturally a weak acid and is colourless. But it is used as an indicator in acid-base titrations because it gives a sharp or detectable colour change at the end point in the titration. Indicators don't change colour sharply at only one particular pH instead, they change colour over a narrow range of pH. The pH range at which phenolphthalein changes its colour from colourless (in acidic medium) to pink (in basic medium) is 8.3-10.0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




