
Predict the products of the following reactions:
i. ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}} - {\text{C}} = {\text{O}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}}}$
ii. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{(b)}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{(a)KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{/KOH}}}} \\$
iii. ${\text{ph}} - {\text{COOH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/FeB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{3}}}}}$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: In the first reaction, acetone reacts with hydrazine. In the second reaction, toluene reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate and hydrogen ion or proton. In the third reaction, benzoic acid reacts with bromine in presence of the Lewis acid iron bromide.
Complete step by step solution:
i. In the first reaction, acetone reacts with hydrazine. Acetone hydrazone and water are formed in the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
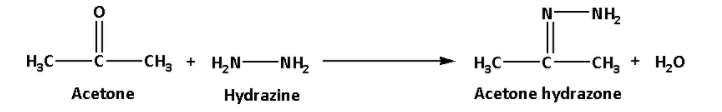
In the reaction, the nucleophile addition takes place and along with that a water molecule is eliminated. The reaction occurs in presence of a weak acid which acts as a catalyst. Thus, it is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Thus, the products of the reaction are acetone hydrazone.
ii. In the second reaction, toluene reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate and hydrogen ion or proton. Toluene on reaction with alkaline potassium permanganate forms potassium salt of benzoic acid. The potassium salt of benzoic acid on hydrolysis forms benzoic acid. In the reaction, the methyl group is converted to the carboxylic group.
The reaction is as follows:
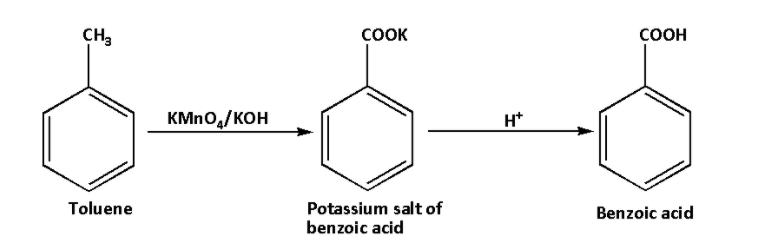
The potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent. The potassium hydroxide provides an alkaline medium because potassium permanganate is stable in alkaline medium only. Thus, alkaline potassium permanganate provides nascent oxygen and the oxidation of toluene occurs to produce benzoic acid.
Thus, the product of the reaction is benzoic acid.
iii. In the third reaction, benzoic acid reacts with bromine in presence of iron bromide. Benzoic acid in reaction with bromine in presence of iron bromide forms meta-bromobenzoic acid.
The reaction is as follows:
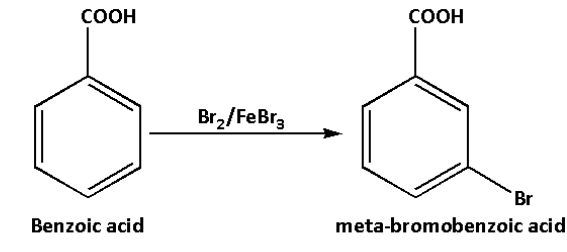
In the reaction, the bromine molecule reacts with iron bromide and donates its electron par to the iron bromide. As a result, a polar bromine-bromine bond is formed along with a more reactive electrophile.
The benzene ring then attacks this electrophile and thus, the benzene ring is brominated in the meta position to form meta-bromobenzoic acid.
Thus, the product of the reaction is meta-bromobenzoic acid.
Note:
Acetone hydrazone further condenses with acetone and forms azine. Alkaline potassium permanganate is a very good oxidising agent. It provides nascent oxygen and converts methyl group to carboxylic group. In the reaction of benzoic acid with bromine in the presence of iron bromide, iron bromide is a Lewis acid and it acts as a catalyst. Another Lewis acid aluminium bromide can also be used as a catalyst.
Complete step by step solution:
i. In the first reaction, acetone reacts with hydrazine. Acetone hydrazone and water are formed in the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:

In the reaction, the nucleophile addition takes place and along with that a water molecule is eliminated. The reaction occurs in presence of a weak acid which acts as a catalyst. Thus, it is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Thus, the products of the reaction are acetone hydrazone.
ii. In the second reaction, toluene reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate and hydrogen ion or proton. Toluene on reaction with alkaline potassium permanganate forms potassium salt of benzoic acid. The potassium salt of benzoic acid on hydrolysis forms benzoic acid. In the reaction, the methyl group is converted to the carboxylic group.
The reaction is as follows:

The potassium permanganate is a strong oxidising agent. The potassium hydroxide provides an alkaline medium because potassium permanganate is stable in alkaline medium only. Thus, alkaline potassium permanganate provides nascent oxygen and the oxidation of toluene occurs to produce benzoic acid.
Thus, the product of the reaction is benzoic acid.
iii. In the third reaction, benzoic acid reacts with bromine in presence of iron bromide. Benzoic acid in reaction with bromine in presence of iron bromide forms meta-bromobenzoic acid.
The reaction is as follows:

In the reaction, the bromine molecule reacts with iron bromide and donates its electron par to the iron bromide. As a result, a polar bromine-bromine bond is formed along with a more reactive electrophile.
The benzene ring then attacks this electrophile and thus, the benzene ring is brominated in the meta position to form meta-bromobenzoic acid.
Thus, the product of the reaction is meta-bromobenzoic acid.
Note:
Acetone hydrazone further condenses with acetone and forms azine. Alkaline potassium permanganate is a very good oxidising agent. It provides nascent oxygen and converts methyl group to carboxylic group. In the reaction of benzoic acid with bromine in the presence of iron bromide, iron bromide is a Lewis acid and it acts as a catalyst. Another Lewis acid aluminium bromide can also be used as a catalyst.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




