
Show how $\sqrt{5}$ can be shown in the number line.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: We denote the points representing 0 and 2 in the number line as $O$ and $A$. We construct a right angled triangle OAB such that $\angle OAB$ is the right angle and $AB=1$ unit. We use the Pythagoras theorem and find $OB=\sqrt{5}$ units. We take an arc OB from the point of O and cut the number line at the point G. G represents $\sqrt{5}$ in the number line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know from Pythagora's theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle the square of hypotenuse is sum of squares of other two sides.” If $h$ is the length of hypotenuse and $p,b$ are the lengths of other two sides, then we have
\[{{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\]
If we can find a length of $\sqrt{5}$ and take an arc of that length from point 0 in the number line we can show the position of $\sqrt{5}$. Let us choose the hypotenuse as $h=\sqrt{5}$. So we have${{h}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}=5$. We can choose two perfect squares ${{p}^{2}}=4,{{b}^{2}}=1$ such that${{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}=5$. Then we have $p=2,b=1$.
We denote the point representing 0 and 2 in the number line as $O$ and $A$. The line segment $OA$ will be our choice for $p=2$.We draw the right angle at the point of A and construct the right angle triangle $\Delta OAB$ such that $AB=1$unit. The line segment $OB$ will be our choice for $p=1$. \[\]
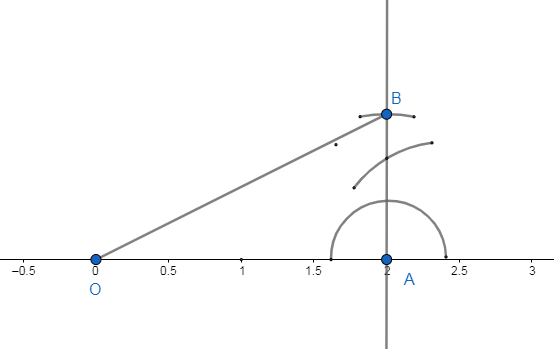
We see that in the above right angled triangle OAB is the hypotenuse $h=OB$. So by Pythagoras theorem we have,
\[\begin{align}
& O{{B}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{2}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}=\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
We take the arc $OB=\sqrt{5}$ from O and cut the number line at the point G. G will represent the number $\sqrt{5}$ in the number line.\[\]
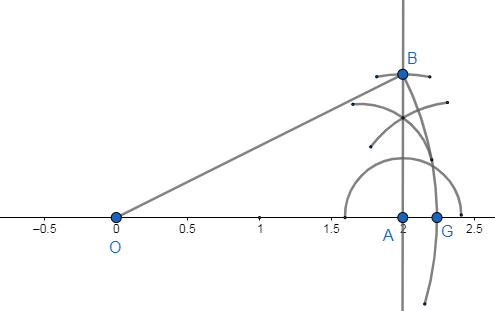
Note: We note that $\sqrt{5}$ is an irrational number which means $\sqrt{5}$ cannot be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$where $p$ is any integer and $q$ is a non-zero integer. We can alternative solve by choosing ${{p}^{2}}=2,{{b}^{2}}=3$ but or that we need to construct right angled triangles with hypotenuse of length $\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3}$units.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know from Pythagora's theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle the square of hypotenuse is sum of squares of other two sides.” If $h$ is the length of hypotenuse and $p,b$ are the lengths of other two sides, then we have
\[{{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\]
If we can find a length of $\sqrt{5}$ and take an arc of that length from point 0 in the number line we can show the position of $\sqrt{5}$. Let us choose the hypotenuse as $h=\sqrt{5}$. So we have${{h}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}=5$. We can choose two perfect squares ${{p}^{2}}=4,{{b}^{2}}=1$ such that${{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}=5$. Then we have $p=2,b=1$.
We denote the point representing 0 and 2 in the number line as $O$ and $A$. The line segment $OA$ will be our choice for $p=2$.We draw the right angle at the point of A and construct the right angle triangle $\Delta OAB$ such that $AB=1$unit. The line segment $OB$ will be our choice for $p=1$. \[\]

We see that in the above right angled triangle OAB is the hypotenuse $h=OB$. So by Pythagoras theorem we have,
\[\begin{align}
& O{{B}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{2}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}=\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
We take the arc $OB=\sqrt{5}$ from O and cut the number line at the point G. G will represent the number $\sqrt{5}$ in the number line.\[\]

Note: We note that $\sqrt{5}$ is an irrational number which means $\sqrt{5}$ cannot be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$where $p$ is any integer and $q$ is a non-zero integer. We can alternative solve by choosing ${{p}^{2}}=2,{{b}^{2}}=3$ but or that we need to construct right angled triangles with hypotenuse of length $\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3}$units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




