
Singlet and triplet carbene are the same in _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
(A) Types of hybridisation
(B) Number of unshared electron pairs (for LP ${e^ - }$s)
(C) Number of $sigma$ - bonds
(D) Bond angle
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Carbene is a carbon species with insufficient bonding with 6 electrons in the valence orbit. Carbene consist of non-bonding electrons. Singlet and triplet carbene are two types of carbene which have different structures. But both have the same number of bond pairs.
Complete step by step answer:
A carbene is a neutral divalent carbon species that contains two electrons that are not shared with other two atoms. The general formula is ${\text{R = C:}}$ where R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. Methylene compounds are called carbene. The representation of the carbene is as follows:
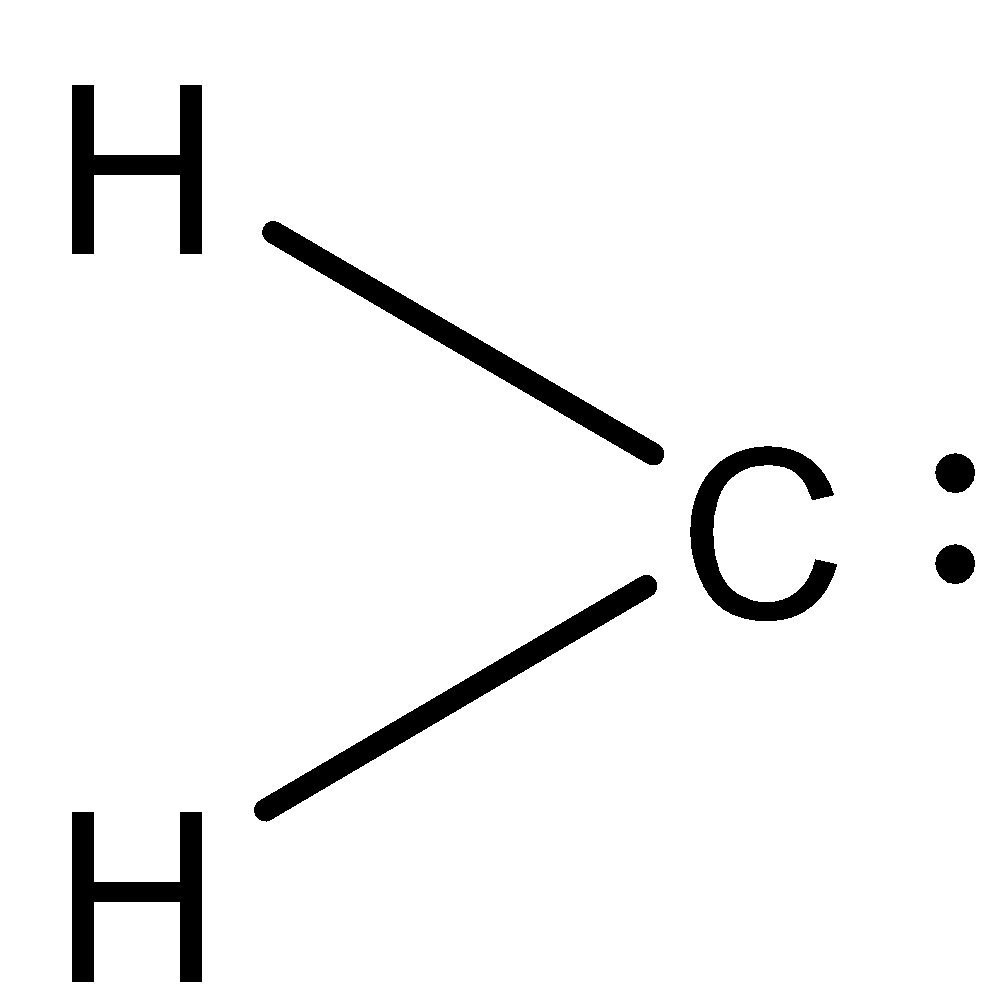
The carbon atom in this molecule has 6 electrons therefore it is an electron deficient species. Carbene therefore acts as an electrophile.
The carbene is generated as follows:-
a) By heating diazomethane:
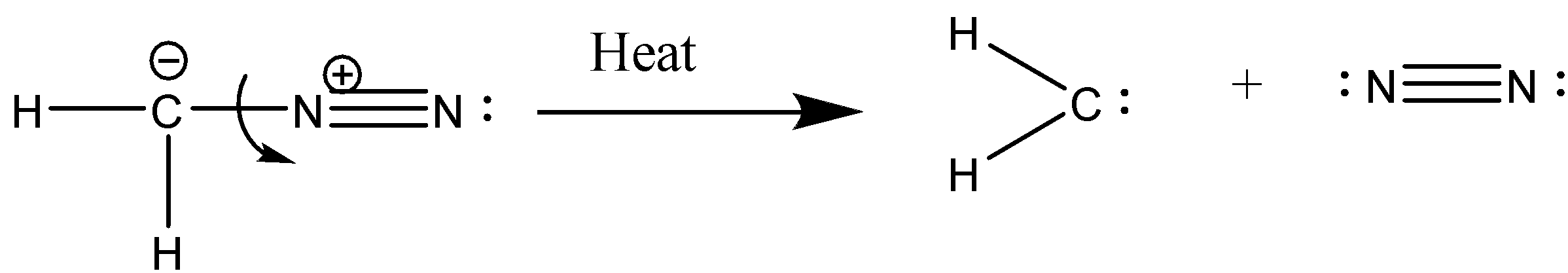
When diazomethane is heated it generates carbene by releasing nitrogen gas.
There are two classes of carbene, they are singlet and triplet carbenes.
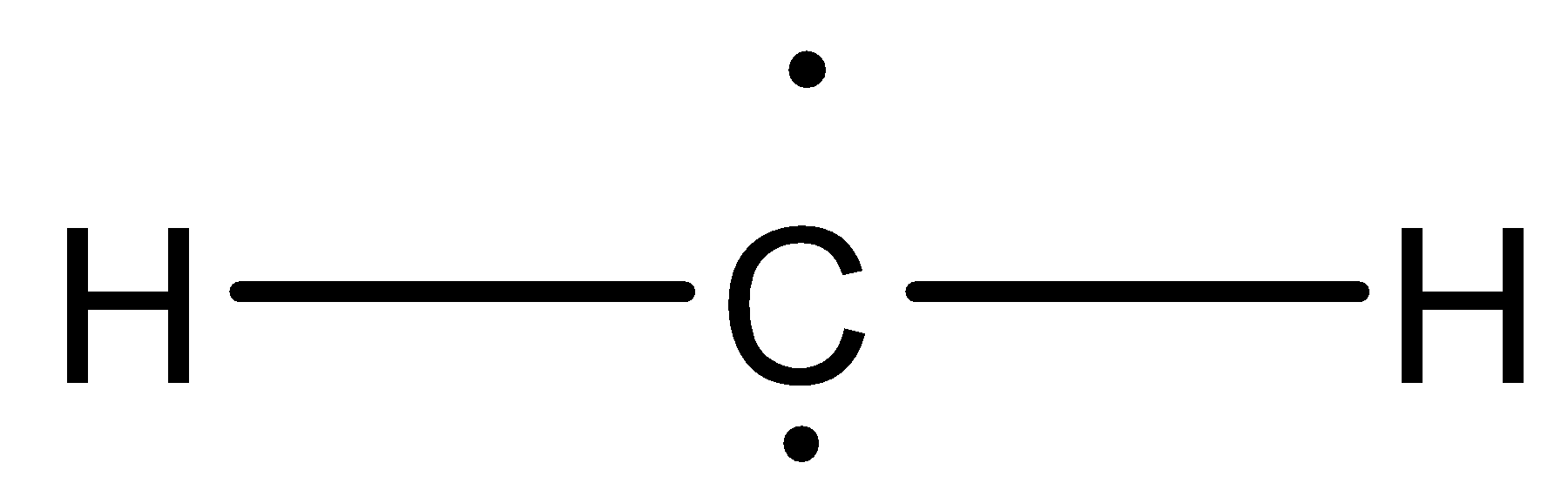
1) Singlet carbene: Singlet carbenes are spin paired. This molecule has ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybrid structure. The two electrons are in the same orbital. In case of singlet carbene electrons are paired. This carbene is therefore diamagnetic. It consists of three ${e^ - }$ pairs. Geometry of molecules is bent.
Structure is planar. Shape is bent. Geometry/shape of molecule is determined by the number of bond pairs in the molecule.
Singlet carbene is the name given according to the total spin. One electron carries a spin of -1/2 if it rotates anticlockwise and +1/2 if it rotates clockwise. If the electrons are paired then one will have spin of +1/2 while the other will have -1/2.
$S = + \dfrac{1}{2} - \dfrac{1}{2} = 0$
By using the value of spin of electrons we can find the value of total spin as follows:
${\text{Total spin = 2S + 1}}$
${\text{Total spin = 2}} \times {\text{0 + 1 = 1}}$. Since the value of total spin comes out to be one, thus the name singlet is given to this type of carbene.
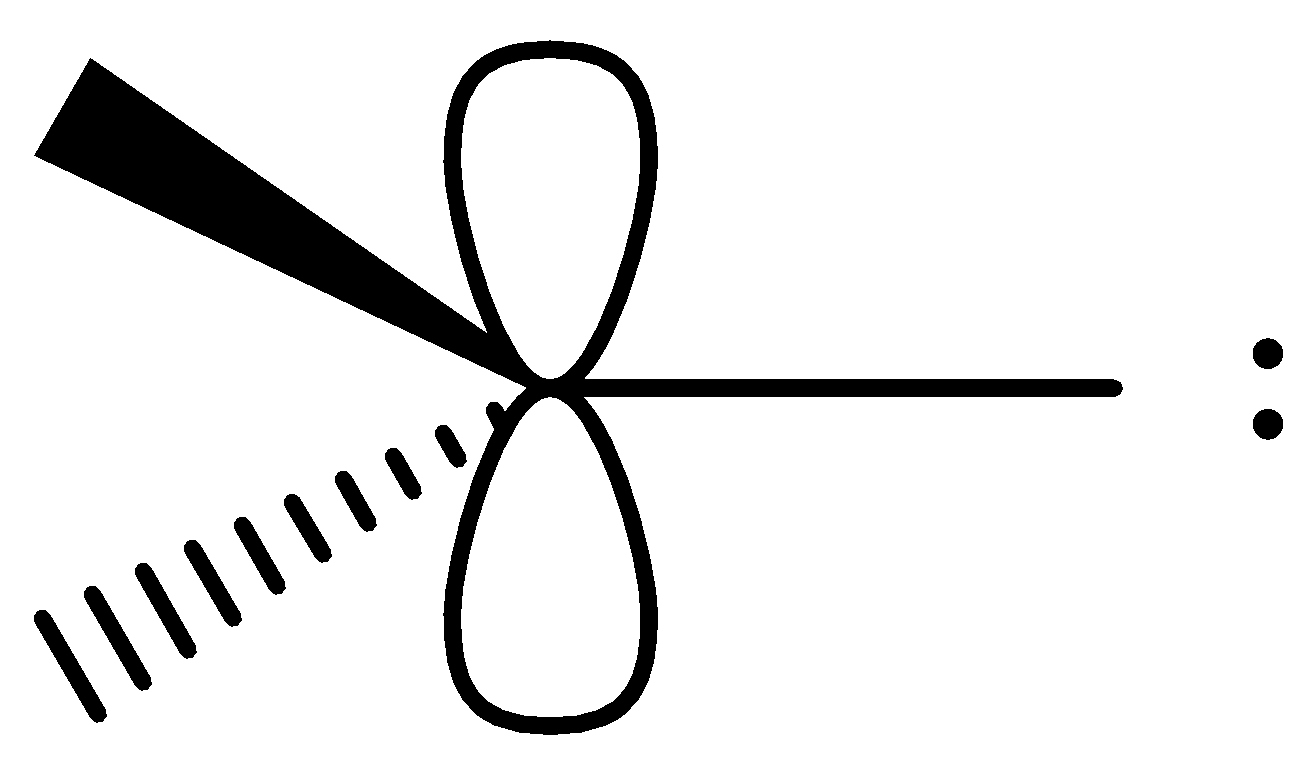
2) Triplet carbene – It is represented as follows
Two electrons which are non-bonded are present in different orbitals. These two electrons are unpaired. Therefore, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Hybridisation of triplet carbene: For this molecule, there is a need of 4 orbitals. Among them, two bond pairs will require hybrid orbitals. The molecules will form a $\sigma $ bond. The two single electrons are in atomic orbitals. So there is a need for two atomic orbitals. Accordingly the hybridisation is sp. Shape will be linear.
Orbital diagram is as follows:
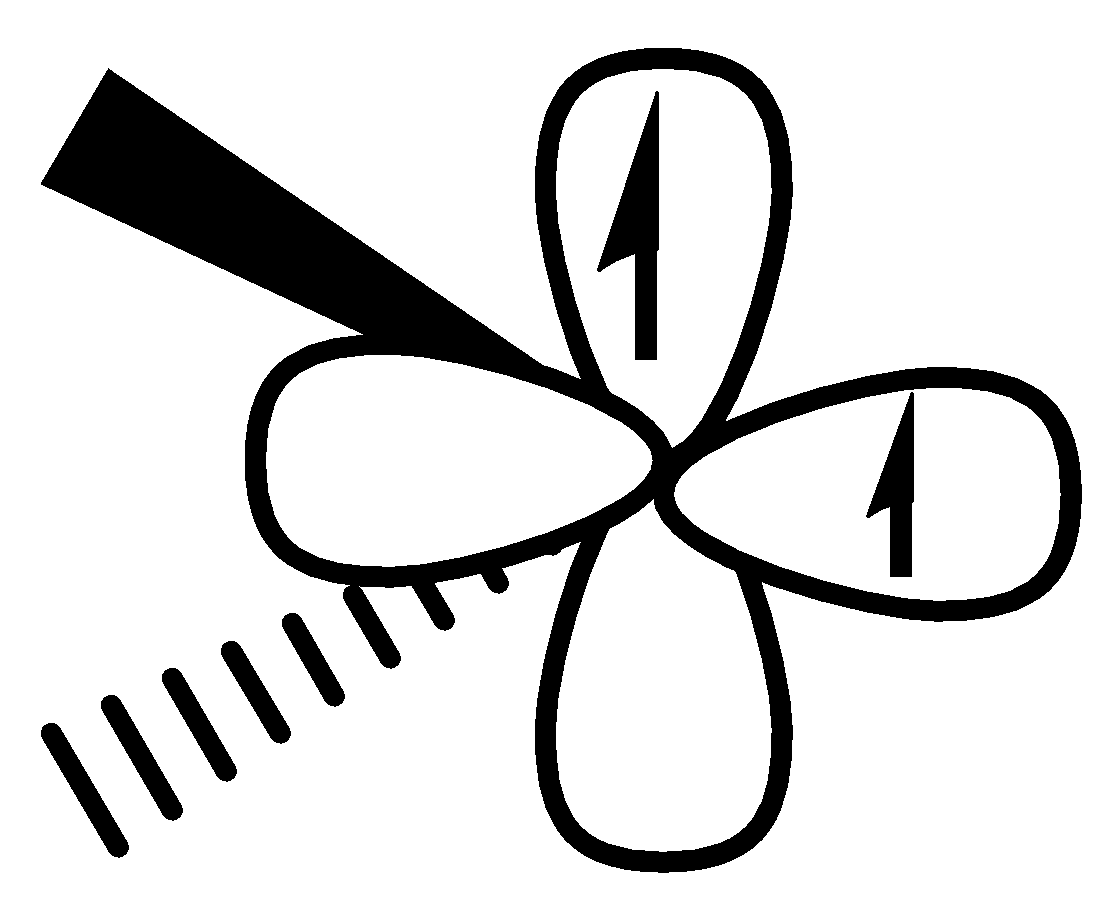
In case of triplet, two electrons are unpaired. These two electrons have the same spin.
$S = + \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2} = 1$
We can find the value of total spin,
${\text{Total spin = 2S + 1 = 2}} \times {\text{1 + 1 = 3}}$
Since the value of total spin comes out to be three, therefore the name triplet is given to such molecules.
Note: Substituents which are able to donate electron pairs might stabilize the singlet state. The triplet state is more stable than the singlet state as the triplet state follows Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity.
Complete step by step answer:
A carbene is a neutral divalent carbon species that contains two electrons that are not shared with other two atoms. The general formula is ${\text{R = C:}}$ where R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. Methylene compounds are called carbene. The representation of the carbene is as follows:

The carbon atom in this molecule has 6 electrons therefore it is an electron deficient species. Carbene therefore acts as an electrophile.
The carbene is generated as follows:-
a) By heating diazomethane:

When diazomethane is heated it generates carbene by releasing nitrogen gas.
There are two classes of carbene, they are singlet and triplet carbenes.
1) Singlet carbene: Singlet carbenes are spin paired. This molecule has ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybrid structure. The two electrons are in the same orbital. In case of singlet carbene electrons are paired. This carbene is therefore diamagnetic. It consists of three ${e^ - }$ pairs. Geometry of molecules is bent.

Structure is planar. Shape is bent. Geometry/shape of molecule is determined by the number of bond pairs in the molecule.
Singlet carbene is the name given according to the total spin. One electron carries a spin of -1/2 if it rotates anticlockwise and +1/2 if it rotates clockwise. If the electrons are paired then one will have spin of +1/2 while the other will have -1/2.
$S = + \dfrac{1}{2} - \dfrac{1}{2} = 0$
By using the value of spin of electrons we can find the value of total spin as follows:
${\text{Total spin = 2S + 1}}$
${\text{Total spin = 2}} \times {\text{0 + 1 = 1}}$. Since the value of total spin comes out to be one, thus the name singlet is given to this type of carbene.
2) Triplet carbene – It is represented as follows

Two electrons which are non-bonded are present in different orbitals. These two electrons are unpaired. Therefore, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Hybridisation of triplet carbene: For this molecule, there is a need of 4 orbitals. Among them, two bond pairs will require hybrid orbitals. The molecules will form a $\sigma $ bond. The two single electrons are in atomic orbitals. So there is a need for two atomic orbitals. Accordingly the hybridisation is sp. Shape will be linear.
Orbital diagram is as follows:

In case of triplet, two electrons are unpaired. These two electrons have the same spin.
$S = + \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2} = 1$
We can find the value of total spin,
${\text{Total spin = 2S + 1 = 2}} \times {\text{1 + 1 = 3}}$
Since the value of total spin comes out to be three, therefore the name triplet is given to such molecules.
Note: Substituents which are able to donate electron pairs might stabilize the singlet state. The triplet state is more stable than the singlet state as the triplet state follows Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




