
Soft iron is used for the construction of electromagnets because for iron
A). The area of the hysteresis loop is more.
B). Coercive force is high.
C). Retentivity is high.
D). Magnetic saturation limits are high and coercivity is low.
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: This question can be approached by the mindset that what electromagnets are, and what is their need. Because electromagnets are devices that are used whenever a variable magnetism is required. So the material to be used to construct electromagnets should be such that it gets magnetized easily as well as demagnetized easily when electric current is passed through it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electromagnets are devices that consist of a core of magnetic material, which is surrounded by a coil through which when an electric current is passed it magnetizes the core. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. These are used wherever controllable magnets are required. In other words, at instances where the magnetic flux needs to be varied, reversed, or switched on and off.
Retentivity refers to the ability of a substance to retain or resist magnetization. In other words it is the measure of the strength of the magnetic field that remains in a sample after removal of the inducing field.
Coercivity means the resistance of a magnetic material to change its state of magnetization. It is equivalent to the field intensity necessary to demagnetize a fully magnetized material.
Hysteresis loop is a closed curve showing the variation of the magnetic flux density of a magnetic material with the external magnetic field producing it, when this field is changed through a complete cycle. Additionally, the area of the hysteresis loop is proportional to the thermal energy developed per unit volume of the material as it goes through the hysteresis cycle.
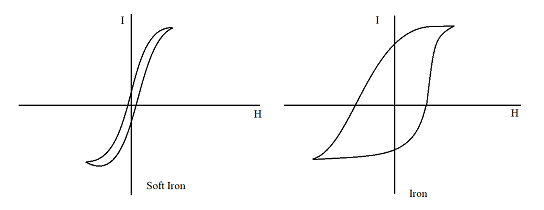
The above two diagrams show the hysteresis loop of iron and soft iron, respectively.
Now, clearly from the diagram the area of the hysteresis loop is larger for iron than for soft iron.
Thus the retentivity and the coercive force are larger for iron than for soft iron. Soft iron is therefore easily magnetized by a magnetizing field but only a small magnetization is retained when the field is removed. Also the loss of energy, as the material is taken through periodic variations in magnetizing fields, is small. Thus materials like soft iron are suitable for making electromagnets.
Hence, the correct option is D), i.e., Soft iron is used for the construction of electromagnets because for iron magnetic saturation limits are high and coercivity is low.
Note: It is very crucial for the students to understand the correlation between the physical quantities such as retentivity, coercivity and hysteresis loop. A lot of students confuse the two terms of retentivity and coercivity; hence fail to answer the question correctly. For better understanding students can divide the word “retentivity” as “retain”, the word retain means the ability to keep something. Thus “retentivity” can be memorized as the ability to retain magnetism.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electromagnets are devices that consist of a core of magnetic material, which is surrounded by a coil through which when an electric current is passed it magnetizes the core. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. These are used wherever controllable magnets are required. In other words, at instances where the magnetic flux needs to be varied, reversed, or switched on and off.
Retentivity refers to the ability of a substance to retain or resist magnetization. In other words it is the measure of the strength of the magnetic field that remains in a sample after removal of the inducing field.
Coercivity means the resistance of a magnetic material to change its state of magnetization. It is equivalent to the field intensity necessary to demagnetize a fully magnetized material.
Hysteresis loop is a closed curve showing the variation of the magnetic flux density of a magnetic material with the external magnetic field producing it, when this field is changed through a complete cycle. Additionally, the area of the hysteresis loop is proportional to the thermal energy developed per unit volume of the material as it goes through the hysteresis cycle.

The above two diagrams show the hysteresis loop of iron and soft iron, respectively.
Now, clearly from the diagram the area of the hysteresis loop is larger for iron than for soft iron.
Thus the retentivity and the coercive force are larger for iron than for soft iron. Soft iron is therefore easily magnetized by a magnetizing field but only a small magnetization is retained when the field is removed. Also the loss of energy, as the material is taken through periodic variations in magnetizing fields, is small. Thus materials like soft iron are suitable for making electromagnets.
Hence, the correct option is D), i.e., Soft iron is used for the construction of electromagnets because for iron magnetic saturation limits are high and coercivity is low.
Note: It is very crucial for the students to understand the correlation between the physical quantities such as retentivity, coercivity and hysteresis loop. A lot of students confuse the two terms of retentivity and coercivity; hence fail to answer the question correctly. For better understanding students can divide the word “retentivity” as “retain”, the word retain means the ability to keep something. Thus “retentivity” can be memorized as the ability to retain magnetism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




