
State whether true or false:
In the Carnot cycle, there are a total of 4 processes which take place?
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that when a system undergoes a series of processes and states and returns to its original state, a thermodynamics cycle has taken place. The Carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle which undergoes isothermal and adiabatic processes.
Complete step by step answer:
A Carnot cycle is a most efficient reversible heat engine cycle that operates between two temperatures, one is known as source and other is known as sink.
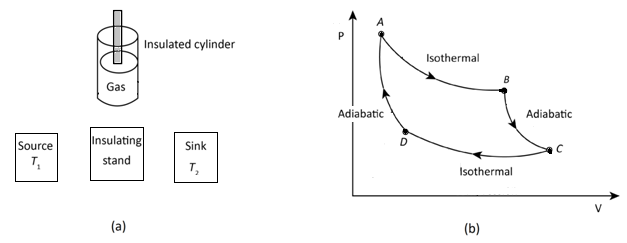
In the above figure, (a) represents the Carnot engine and (b) Carnot cycle.
The Carnot cycle consist of the following processes:
1. Isothermal expansion: In this process, the gas (working substance) attains the temperature of the source as it is placed on it and allows the gas to expand and do work on the surrounding. The temperature of the gas falls as the gas absorbs the required amount of heat from the source, to expand isothermally.
2. Adiabatic expansion: The gas is now placed on a thermally insulated stand and allowed to expand slowly till the temperature of the gas reaches to the temperature of the sink. There is no heat exchange taking place in order to expand the gas.
3. Isothermally compression: Now the gas is placed on the sink and slowly compressed so that the heat is generated and it easily flows to sink and thus the temperature of the gas remains the same.
4. Adiabatic compression: Now the gas is placed on the insulating stand again and the gas is further compressed slowly till it returns to its original state.
Thus, In Carnot cycle, there are total 4 processes which take place and this statement is true.
Note:
The assumptions of Carnot cycle: Isothermal compressions and expansion take place at extremely slow pace, the heat loss between the components is nil and the cycle does not have any friction.
The temperature of the gas falls as the gas absorbs the required amount of heat from the source, to expand isothermally.
Complete step by step answer:
A Carnot cycle is a most efficient reversible heat engine cycle that operates between two temperatures, one is known as source and other is known as sink.

In the above figure, (a) represents the Carnot engine and (b) Carnot cycle.
The Carnot cycle consist of the following processes:
1. Isothermal expansion: In this process, the gas (working substance) attains the temperature of the source as it is placed on it and allows the gas to expand and do work on the surrounding. The temperature of the gas falls as the gas absorbs the required amount of heat from the source, to expand isothermally.
2. Adiabatic expansion: The gas is now placed on a thermally insulated stand and allowed to expand slowly till the temperature of the gas reaches to the temperature of the sink. There is no heat exchange taking place in order to expand the gas.
3. Isothermally compression: Now the gas is placed on the sink and slowly compressed so that the heat is generated and it easily flows to sink and thus the temperature of the gas remains the same.
4. Adiabatic compression: Now the gas is placed on the insulating stand again and the gas is further compressed slowly till it returns to its original state.
Thus, In Carnot cycle, there are total 4 processes which take place and this statement is true.
Note:
The assumptions of Carnot cycle: Isothermal compressions and expansion take place at extremely slow pace, the heat loss between the components is nil and the cycle does not have any friction.
The temperature of the gas falls as the gas absorbs the required amount of heat from the source, to expand isothermally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




