
How many structural isomers are possible for mono bromo benzene?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: The compounds which have the same molecular formula, but the bonds are arranged in a different manner, are termed as structural compounds. In the given molecule, benzene is the parent molecule. It is a six membered cyclic, conjugated ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is the parent group in the given molecule. It has six carbon atoms and has alternate double bonds. It has a planar structure. The chemical formula of benzene is ${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_{12}}$. In the given compound, the hydrogen atoms are substituted with other groups like bromine, chlorine. Since it is given that monobromo, there is only one bromine atom and dichloro means two chlorine atoms are substituted in the place of hydrogen atoms.
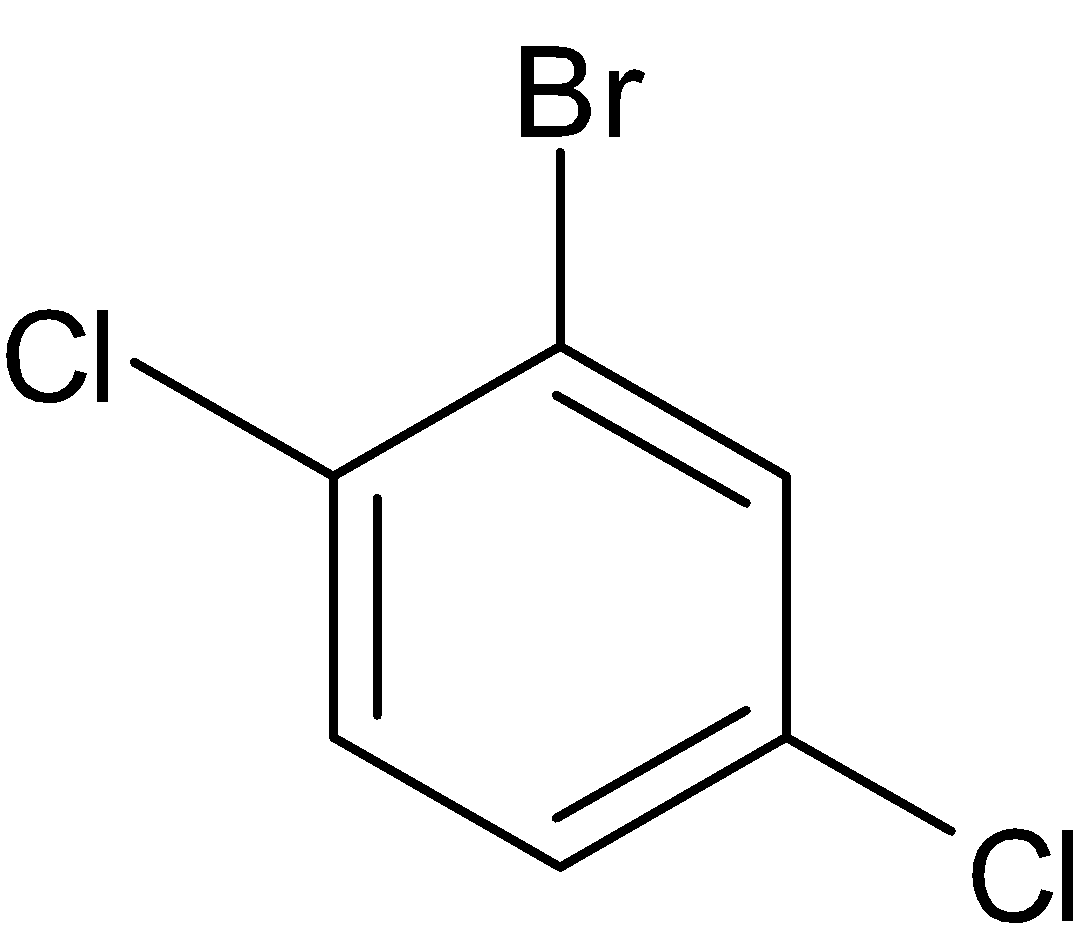
Thus the structure of the given molecule can be drawn as given below:
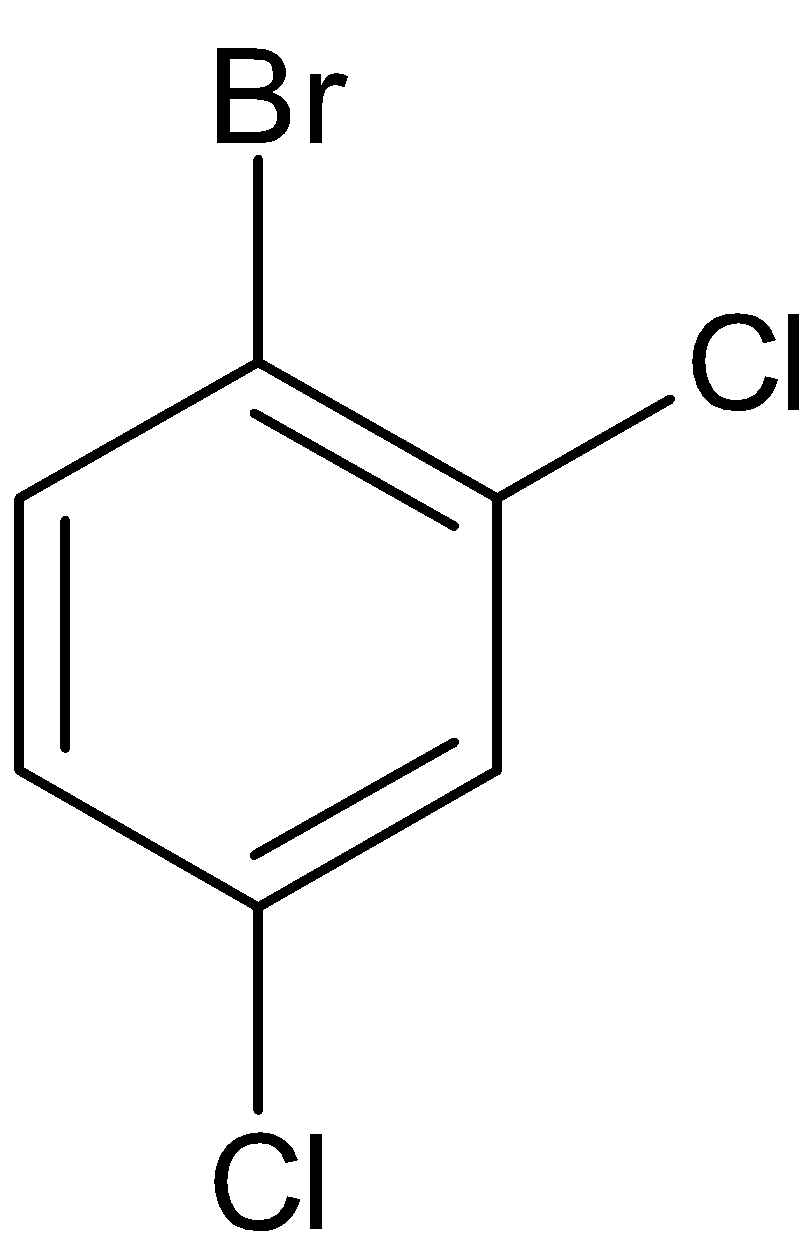
We have three substitutions in the benzene ring. When we keep bromine fixed, two chlorine atoms keep changing. So the structures become as follows:
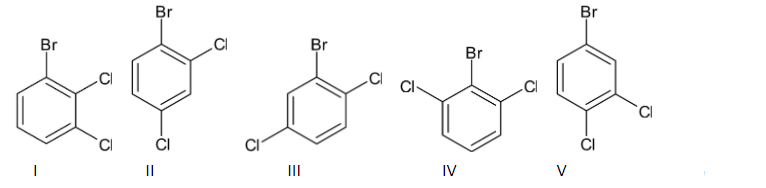
Thus we can say that the number of structural isomers are dependent on the number of substitutions. Here, there are three substitutions. Thus the number of structural isomers $ = 2 \times 3 = 6$. So there are six structural isomers present for the given molecule.
Additional information:
Following are the names of the six structural isomers given above:
I- 1-bromo-2,3-dichlorobenzene
II- 1-bromo-2,4-dichlorobenzene
III- 2-bromo-1,4-dichlorobenzene
IV- 2-bromo-1,3-dichlorobenzene
V- 4-bromo-1,2-dichlorobenzene
VI-1-bromo-3,5-dichloro benzene
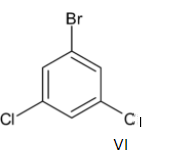
Note: There are two more structural isomers for the same molecule which is given below:
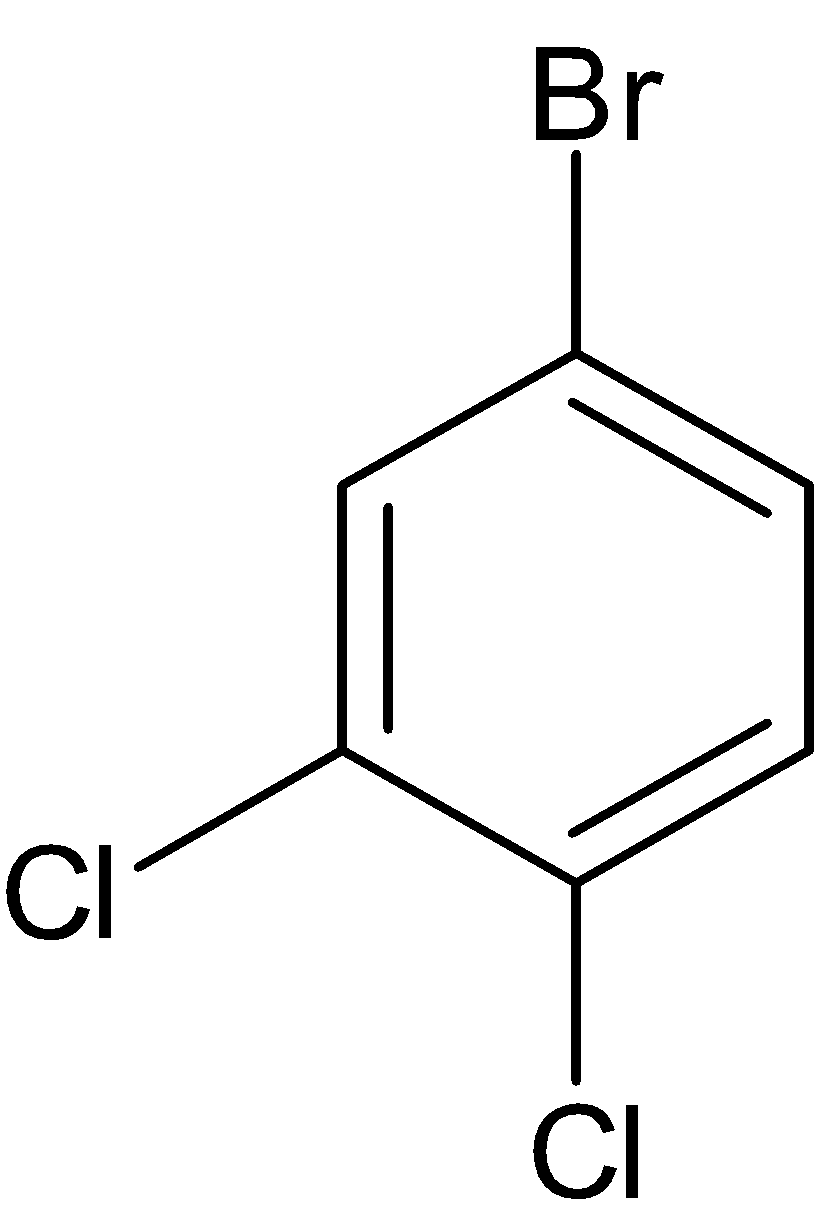
But these cannot be considered as structural isomers because both of them are similar to compounds III and V respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is the parent group in the given molecule. It has six carbon atoms and has alternate double bonds. It has a planar structure. The chemical formula of benzene is ${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_{12}}$. In the given compound, the hydrogen atoms are substituted with other groups like bromine, chlorine. Since it is given that monobromo, there is only one bromine atom and dichloro means two chlorine atoms are substituted in the place of hydrogen atoms.
Thus the structure of the given molecule can be drawn as given below:

We have three substitutions in the benzene ring. When we keep bromine fixed, two chlorine atoms keep changing. So the structures become as follows:


Thus we can say that the number of structural isomers are dependent on the number of substitutions. Here, there are three substitutions. Thus the number of structural isomers $ = 2 \times 3 = 6$. So there are six structural isomers present for the given molecule.
Additional information:
Following are the names of the six structural isomers given above:
I- 1-bromo-2,3-dichlorobenzene
II- 1-bromo-2,4-dichlorobenzene
III- 2-bromo-1,4-dichlorobenzene
IV- 2-bromo-1,3-dichlorobenzene
V- 4-bromo-1,2-dichlorobenzene
VI-1-bromo-3,5-dichloro benzene
Note: There are two more structural isomers for the same molecule which is given below:


But these cannot be considered as structural isomers because both of them are similar to compounds III and V respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




