
The anther and filament are parts of the
A.Pistil
B.Receptacle
C.Petal
D.Stamen
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The flower contains male and female reproductive parts. Both anther and filaments are the male parts of the flower. The male contribution broadly known as pollen is produced in the anther part and develops seeds in the ovary.
Complete answer
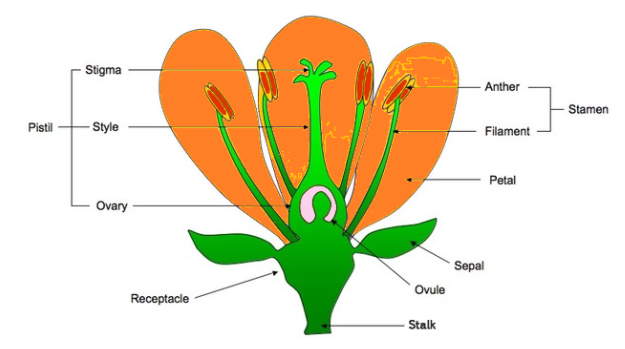
The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower that produces pollen. The stamen consists of two parts: anther and filament. The pistil is the female reproductive organ of a flower and is composed of stigma, style, and ovule. So, the correct answer is the stamen.
Additional infromation:The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flower flowers, e.g. Corn, papaya, and cucumber. The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers as mustard, rose, and petunia.
The anther contains pollen grains that produce male gametes. A pistil consists of stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule. In sexual reproduction a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
Note:The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination.When the pollen from the anther is accumulated on the stigma of the same or another flower on the same plant, then such pollination is called self-pollination. On the other hand, when the pollen from the anther of one flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species, then such pollination is known as cross-pollination.
Complete answer

The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower that produces pollen. The stamen consists of two parts: anther and filament. The pistil is the female reproductive organ of a flower and is composed of stigma, style, and ovule. So, the correct answer is the stamen.
Additional infromation:The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flower flowers, e.g. Corn, papaya, and cucumber. The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers as mustard, rose, and petunia.
The anther contains pollen grains that produce male gametes. A pistil consists of stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule. In sexual reproduction a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
Note:The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination.When the pollen from the anther is accumulated on the stigma of the same or another flower on the same plant, then such pollination is called self-pollination. On the other hand, when the pollen from the anther of one flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species, then such pollination is known as cross-pollination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




