
The area of application of PCR include
(i) Production of monoclonal antibodies.
(ii) Insertion of recombinant DNA into an organism.
(iii) Diagnosis of a specific mutation.
(iv) Detection of plant pathogens.
(a)(i) and (ii)
(b)(ii) and (iii)
(c)(iii) and (iv)
(d)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was originally developed by the American biochemist Kary Mullis in 1983. For his pioneering work, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.
Complete answer:
The area of application of Polymerase Chain Reaction includes the diagnosis of a specific mutation and detection of plant pathogens. PCR technique is used in the lab to make millions of copies of a particular section of DNA. PCR is a common tool used in medical and biological research laboratories.
Additional Information:
PCR is used within the early stages of processing DNA for sequencing and for detecting the presence or absence of a gene to assist in identifying pathogens during infection, and PCR is also used during generating forensic DNA profiles from tiny samples of DNA.
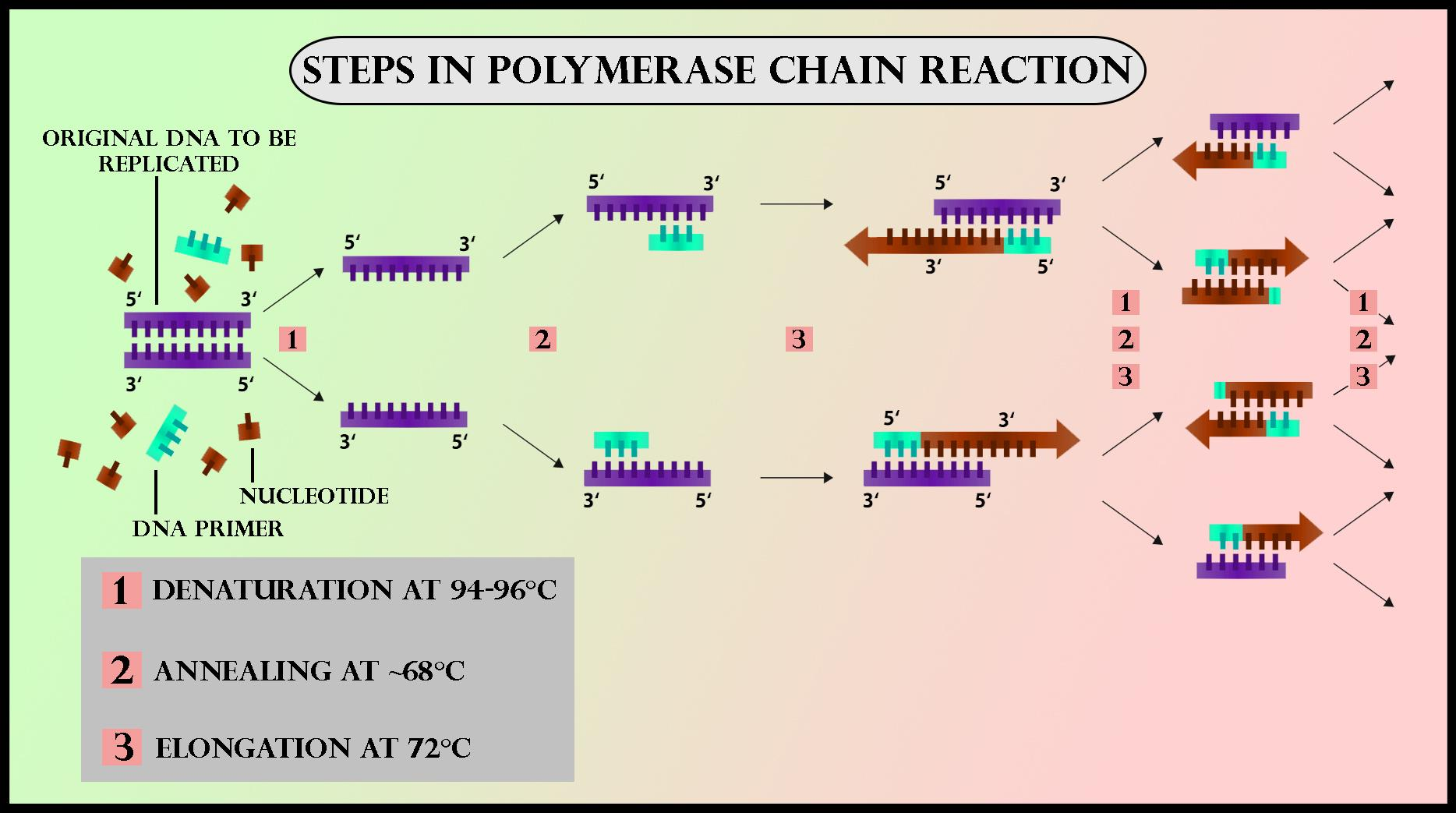
Polymerase Chain Reaction involves two main reagents – primers which are short single-strand DNA fragments also known as oligonucleotides that are a complementary sequence to the target DNA region and a DNA polymerase.
In the primary step of PCR, the 2 strands of the DNA helix are physically separated at a heat during a process called macromolecule denaturation.
In the second step, the temperature is lowered so that the primers can bind to the complementary sequences of DNA.
The two DNA strands then become templates for DNA polymerase to enzymatically assemble a replacement DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. As PCR progresses, the DNA generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a sequence reaction during which the first DNA template is exponentially amplified.
So, the correct option is option (c) '(iii) and (iv).
Note: PCR is used within the early stages of processing DNA for sequencing and for detecting the presence or absence of a gene to assist in identifying pathogens during infection.
Polymerase Chain Reaction involves two main reagents – primers and a DNA polymerase.
The two DNA strands then become templates for DNA polymerase to enzymatically assemble a replacement DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA.
Complete answer:
The area of application of Polymerase Chain Reaction includes the diagnosis of a specific mutation and detection of plant pathogens. PCR technique is used in the lab to make millions of copies of a particular section of DNA. PCR is a common tool used in medical and biological research laboratories.
Additional Information:
PCR is used within the early stages of processing DNA for sequencing and for detecting the presence or absence of a gene to assist in identifying pathogens during infection, and PCR is also used during generating forensic DNA profiles from tiny samples of DNA.
Polymerase Chain Reaction involves two main reagents – primers which are short single-strand DNA fragments also known as oligonucleotides that are a complementary sequence to the target DNA region and a DNA polymerase.
In the primary step of PCR, the 2 strands of the DNA helix are physically separated at a heat during a process called macromolecule denaturation.
In the second step, the temperature is lowered so that the primers can bind to the complementary sequences of DNA.
The two DNA strands then become templates for DNA polymerase to enzymatically assemble a replacement DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. As PCR progresses, the DNA generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a sequence reaction during which the first DNA template is exponentially amplified.
So, the correct option is option (c) '(iii) and (iv).

Note: PCR is used within the early stages of processing DNA for sequencing and for detecting the presence or absence of a gene to assist in identifying pathogens during infection.
Polymerase Chain Reaction involves two main reagents – primers and a DNA polymerase.
The two DNA strands then become templates for DNA polymerase to enzymatically assemble a replacement DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




