
The enol form of acetone, after treatment with ${{D}_{2}}O$ gives:
(A)-
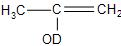
(B)-
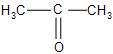
(C)-
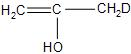
(D)-
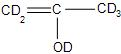
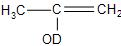



Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The acetone is present in two isomeric forms, which are favoured by the catalyses with an acid or base. The addition of acid causes the interconversion between the two forms to take place with ease.
Complete step by step answer:
The ketone has two isomeric forms which are called tautomers, having the same carbon structure but differ in their position of protons and electrons. It is the keto- form and the enol- form involving the intramolecular proton transfer.
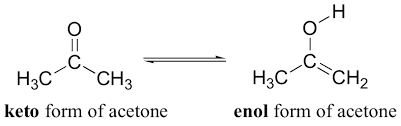
When the ketone is dissolved in the acid which acts as catalyst, the rate of incorporation of deuterium increases in both the forward and reverse direction. As it lowers the barrier between the interconversion.
Let the forward reaction rate (keto to enol) be ${{K}_{1}}$ and the reverse reaction rate (enol to keto) be ${{K}_{2}}$. Then,
- In the keto to enol conversion, carbonyl carbon becomes more electrophilic by the addition of deuterium to the carbonyl by acid. Then, the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group, that is, the $\alpha $-carbon becomes more acidic, making the loss of proton at $\alpha $-carbon easier. This facilitates the formation of enol, thus, increased ${{K}_{1}}$.
- In the enol to the keto form conversion, the $\alpha $-carbon is nucleophilic and attacks the acid which acts as an electrophile. Thus, stronger the acid acting as electrophile, more is the rate of reverse reaction, ${{K}_{2}}$. It is acidic at the oxygen in the O-D bond.
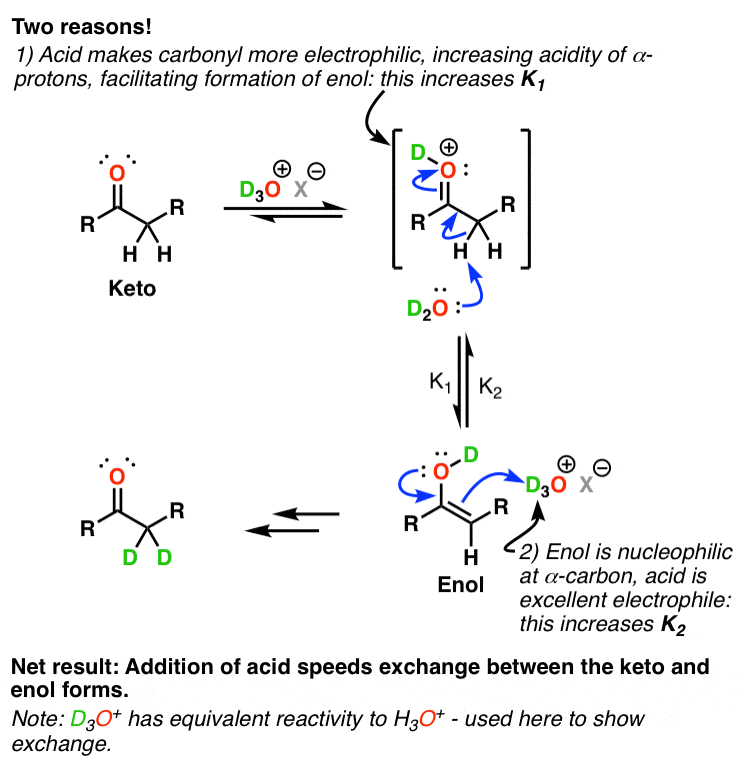
Therefore, addition to excess acid to acetone, all the $\alpha $- hydrogens are replaced by the deuterium atom.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The keto-enol tautomerization is catalysed by the presence of an acid or base. Under normal condition, the keto-form is more stable and favoured in the ratio $6600:1$.
Also, the keto-enol tautomerization under normal condition is favourable, in case of aldehyde and ketone, but not so, in ester, amides and carboxylic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
The ketone has two isomeric forms which are called tautomers, having the same carbon structure but differ in their position of protons and electrons. It is the keto- form and the enol- form involving the intramolecular proton transfer.
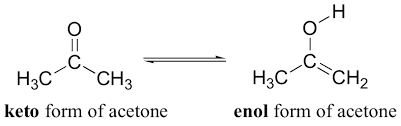
When the ketone is dissolved in the acid which acts as catalyst, the rate of incorporation of deuterium increases in both the forward and reverse direction. As it lowers the barrier between the interconversion.
Let the forward reaction rate (keto to enol) be ${{K}_{1}}$ and the reverse reaction rate (enol to keto) be ${{K}_{2}}$. Then,
- In the keto to enol conversion, carbonyl carbon becomes more electrophilic by the addition of deuterium to the carbonyl by acid. Then, the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group, that is, the $\alpha $-carbon becomes more acidic, making the loss of proton at $\alpha $-carbon easier. This facilitates the formation of enol, thus, increased ${{K}_{1}}$.
- In the enol to the keto form conversion, the $\alpha $-carbon is nucleophilic and attacks the acid which acts as an electrophile. Thus, stronger the acid acting as electrophile, more is the rate of reverse reaction, ${{K}_{2}}$. It is acidic at the oxygen in the O-D bond.

Therefore, addition to excess acid to acetone, all the $\alpha $- hydrogens are replaced by the deuterium atom.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The keto-enol tautomerization is catalysed by the presence of an acid or base. Under normal condition, the keto-form is more stable and favoured in the ratio $6600:1$.
Also, the keto-enol tautomerization under normal condition is favourable, in case of aldehyde and ketone, but not so, in ester, amides and carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




